
Bromley equation
Encyclopedia
The Bromley equation was developed in 1973 with the objective of calculating activity coefficient
s for aqueous electrolyte
solutions whose concentrations are above the range of validity of the Debye–Hückel equation This equation, together with Specific ion interaction theory
(SIT) and Pitzer equations
is important for the understanding of the behaviour of ions dissolved in natural waters such as rivers, lakes and sea-water.
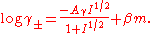
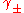 is the mean molal activity coefficient. The first term on the right-hand side is the Debye–Hückel term, with a constant, A, and the ionic strength
is the mean molal activity coefficient. The first term on the right-hand side is the Debye–Hückel term, with a constant, A, and the ionic strength
I. β is an interaction coefficient and m the molal concentration
of the electrolyte. As the concentration decreases so the second term becomes less important until, at very low concentrations,the Debye-Hückel equation gives a satisfactory account of the activity coefficient.
Bromley observed that experimental values of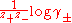 were often approximately proportional to ionic strength. Accordingly he developed the equation, for a salt of general formula
were often approximately proportional to ionic strength. Accordingly he developed the equation, for a salt of general formula 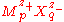
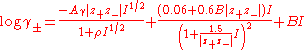
At 25°C Aγ is equal to 0.511 and ρ is equal to one. Bromley tabulated values if the interaction coefficient B. He noted that the equation gave satisfactory agreement with experimental data up to ionic strength of 6 molal, though with decreasing precision when extrapolating to very high ionic strength. As with other equations, it is not satisfactory when there is ion-association
as, for example, with divalent
metal sulphates. Bromley also found that B could be expressed in terms of single-ion quantities as
where the + subscript refers to a cation and the minus subscript refers to an anion. Bromley's equation can easily be transformed for the calculation of osmotic coefficient
s, and Bromley also proposed extensions to multicomponent solutions and for the effect of temperature change.
A modified version of the Bromley equation has been used extensively by Madariaga and co-workers. In a comparison of Bromley, SIT and Pitzer models, little difference was found in the quality of fit. The Bromley equation is essentially an empirical equation. The B parameters are relatively easy to determine. However, SIT theory, as extended by Scatchard. and Ciavatta is much more widely used.
By contrast the Pitzer equation is based on rigorous thermodynamics
. The determination Pitzer parameters is more laborious. Whilst the Bromley and SIT approaches are based on pair-wise interactions between oppositely charged ions, the Pitzer approach also allows for interactions between three ions. These equations are important for the understanding of the behaviour of ions in natural waters such as rivers, lakes and sea-water.
For some complex electrolytes, Ge et al. obtained the new set of Bromley parameters using up-to-date measured or critically reviewed osmotic coefficient or activity coefficient data.
Activity coefficient
An activity coefficient is a factor used in thermodynamics to account for deviations from ideal behaviour in a mixture of chemical substances. In an ideal mixture, the interactions between each pair of chemical species are the same and, as a result, properties of the mixtures can be expressed...
s for aqueous electrolyte
Electrolyte
In chemistry, an electrolyte is any substance containing free ions that make the substance electrically conductive. The most typical electrolyte is an ionic solution, but molten electrolytes and solid electrolytes are also possible....
solutions whose concentrations are above the range of validity of the Debye–Hückel equation This equation, together with Specific ion interaction theory
Specific ion interaction theory
Specific ion Interaction Theory is a theory used to estimate single-ion activity coefficients in electrolyte solutions at relatively high concentrations. It does so by taking into consideration interaction coefficients between the various ions present in solution...
(SIT) and Pitzer equations
Pitzer equations
Pitzer equations are important for the understanding of the behaviour of ions dissolved in natural waters such as rivers, lakes and sea-water. The parameters of the Pitzer equations are linear combinations of parameters, of a virial expansion of the excess Gibbs free energy, which characterise...
is important for the understanding of the behaviour of ions dissolved in natural waters such as rivers, lakes and sea-water.
Description
Guggenheim had proposed an extension of the Debye-Hückel equation which is the basis of SIT theory. The equation can be written, in its simplest form for a 1:1 electrolyte, MX, as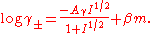
 is the mean molal activity coefficient. The first term on the right-hand side is the Debye–Hückel term, with a constant, A, and the ionic strength
is the mean molal activity coefficient. The first term on the right-hand side is the Debye–Hückel term, with a constant, A, and the ionic strengthIonic strength
The ionic strength of a solution is a measure of the concentration of ions in that solution. Ionic compounds, when dissolved in water, dissociate into ions. The total electrolyte concentration in solution will affect important properties such as the dissociation or the solubility of different salts...
I. β is an interaction coefficient and m the molal concentration
Concentration
In chemistry, concentration is defined as the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Four types can be distinguished: mass concentration, molar concentration, number concentration, and volume concentration...
of the electrolyte. As the concentration decreases so the second term becomes less important until, at very low concentrations,the Debye-Hückel equation gives a satisfactory account of the activity coefficient.
Bromley observed that experimental values of
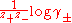 were often approximately proportional to ionic strength. Accordingly he developed the equation, for a salt of general formula
were often approximately proportional to ionic strength. Accordingly he developed the equation, for a salt of general formula 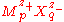
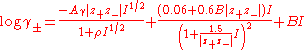
At 25°C Aγ is equal to 0.511 and ρ is equal to one. Bromley tabulated values if the interaction coefficient B. He noted that the equation gave satisfactory agreement with experimental data up to ionic strength of 6 molal, though with decreasing precision when extrapolating to very high ionic strength. As with other equations, it is not satisfactory when there is ion-association
Ion-association
Ion-association is a chemical reaction whereby ions of opposite electrical charge come together in solution to form a distinct chemical entity. Ion-associates are classified according to the number of ions that associate with each other, and the nature of the interaction. The most important factor...
as, for example, with divalent
Divalent
In chemistry, a divalent ion or molecule has a valence of two and thus can form two bonds with other ions or molecules. An older term for divalent is bivalent....
metal sulphates. Bromley also found that B could be expressed in terms of single-ion quantities as

where the + subscript refers to a cation and the minus subscript refers to an anion. Bromley's equation can easily be transformed for the calculation of osmotic coefficient
Osmotic coefficient
An osmotic coefficient φ is a quantity which characterises the deviation of a solvent from ideal behaviour, referenced to Raoult's law. The osmotic coefficient on a molality basis is defined by:and on an amount fraction basis by:...
s, and Bromley also proposed extensions to multicomponent solutions and for the effect of temperature change.
A modified version of the Bromley equation has been used extensively by Madariaga and co-workers. In a comparison of Bromley, SIT and Pitzer models, little difference was found in the quality of fit. The Bromley equation is essentially an empirical equation. The B parameters are relatively easy to determine. However, SIT theory, as extended by Scatchard. and Ciavatta is much more widely used.
By contrast the Pitzer equation is based on rigorous thermodynamics
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a physical science that studies the effects on material bodies, and on radiation in regions of space, of transfer of heat and of work done on or by the bodies or radiation...
. The determination Pitzer parameters is more laborious. Whilst the Bromley and SIT approaches are based on pair-wise interactions between oppositely charged ions, the Pitzer approach also allows for interactions between three ions. These equations are important for the understanding of the behaviour of ions in natural waters such as rivers, lakes and sea-water.
For some complex electrolytes, Ge et al. obtained the new set of Bromley parameters using up-to-date measured or critically reviewed osmotic coefficient or activity coefficient data.

