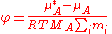Osmotic coefficient
Encyclopedia
An osmotic coefficient φ is a quantity which characterises the deviation of a solvent
from ideal behaviour, referenced to Raoult's law. The osmotic coefficient on a molality basis is defined by:
and on an amount fraction basis by:
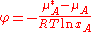
where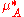 is the chemical potential
is the chemical potential
of the pure solvent and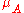 is the chemical potential of the solvent in a solution, MA is its molar mass
is the chemical potential of the solvent in a solution, MA is its molar mass
, xA its amount fraction, R the gas constant
and T the temperature
in kelvin
s. The latter osmotic
coefficient is sometimes called the rational osmotic coefficient. The values for the two definitions are different, but since
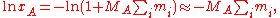
the two definitions are similar, and in fact both go to 1 as the concentration goes to zero.
In a single solute solution, the (molality based) osmotic coefficient and the solute activity coefficient are related to the excess Gibbs free energy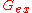 by the relations:
by the relations:
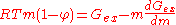
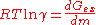
and there is thus a differential relationship between them (temperature and pressure held constant):
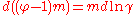
In ionic solutions, Debye-Hückel theory implies that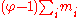 is asymptotic to
is asymptotic to 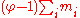 , where I is ionic strength
, where I is ionic strength
and A is the Debye-Hückel constant (equal to about 1.17 for water at 25 °C). This means that, at least at low concentrations, the vapor pressure of the solvent will be greater than that predicted by Raoult's law. For instance, for solutions of magnesium chloride
, the vapor pressure is slightly greater than that predicted by Raoult's law up to a concentration of 0.7 mol/kg, after which the vapor pressure is lower than Raoult's law predicts.
For aqueous solutions, the osmotic coefficients can be calculated theoretically by Pitzer equations
or TCPC model.
Solvent
A solvent is a liquid, solid, or gas that dissolves another solid, liquid, or gaseous solute, resulting in a solution that is soluble in a certain volume of solvent at a specified temperature...
from ideal behaviour, referenced to Raoult's law. The osmotic coefficient on a molality basis is defined by:
and on an amount fraction basis by:
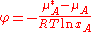
where
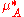 is the chemical potential
is the chemical potentialChemical potential
Chemical potential, symbolized by μ, is a measure first described by the American engineer, chemist and mathematical physicist Josiah Willard Gibbs. It is the potential that a substance has to produce in order to alter a system...
of the pure solvent and
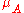 is the chemical potential of the solvent in a solution, MA is its molar mass
is the chemical potential of the solvent in a solution, MA is its molar massMolar mass
Molar mass, symbol M, is a physical property of a given substance , namely its mass per amount of substance. The base SI unit for mass is the kilogram and that for amount of substance is the mole. Thus, the derived unit for molar mass is kg/mol...
, xA its amount fraction, R the gas constant
Gas constant
The gas constant is a physical constant which is featured in many fundamental equations in the physical sciences, such as the ideal gas law and the Nernst equation. It is equivalent to the Boltzmann constant, but expressed in units of energy The gas constant (also known as the molar, universal,...
and T the temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
in kelvin
Kelvin
The kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all...
s. The latter osmotic
coefficient is sometimes called the rational osmotic coefficient. The values for the two definitions are different, but since
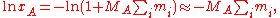
the two definitions are similar, and in fact both go to 1 as the concentration goes to zero.
In a single solute solution, the (molality based) osmotic coefficient and the solute activity coefficient are related to the excess Gibbs free energy
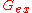 by the relations:
by the relations: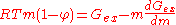
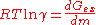
and there is thus a differential relationship between them (temperature and pressure held constant):
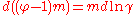
In ionic solutions, Debye-Hückel theory implies that
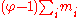 is asymptotic to
is asymptotic to 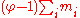 , where I is ionic strength
, where I is ionic strengthIonic strength
The ionic strength of a solution is a measure of the concentration of ions in that solution. Ionic compounds, when dissolved in water, dissociate into ions. The total electrolyte concentration in solution will affect important properties such as the dissociation or the solubility of different salts...
and A is the Debye-Hückel constant (equal to about 1.17 for water at 25 °C). This means that, at least at low concentrations, the vapor pressure of the solvent will be greater than that predicted by Raoult's law. For instance, for solutions of magnesium chloride
Magnesium chloride
Magnesium chloride is the name for the chemical compounds with the formulas MgCl2 and its various hydrates MgCl2x. These salts are typical ionic halides, being highly soluble in water. The hydrated magnesium chloride can be extracted from brine or sea water...
, the vapor pressure is slightly greater than that predicted by Raoult's law up to a concentration of 0.7 mol/kg, after which the vapor pressure is lower than Raoult's law predicts.
For aqueous solutions, the osmotic coefficients can be calculated theoretically by Pitzer equations
Pitzer equations
Pitzer equations are important for the understanding of the behaviour of ions dissolved in natural waters such as rivers, lakes and sea-water. The parameters of the Pitzer equations are linear combinations of parameters, of a virial expansion of the excess Gibbs free energy, which characterise...
or TCPC model.