Armed forces
Encyclopedia
The armed forces of a country
are its government
-sponsored defense, fighting forces, and organizations. They exist to further the foreign and domestic policies of their governing body, and to defend that body and the nation it represents from external aggressors. In some countries paramilitary
forces are included in a nation's armed forces. Armed force is the use of armed forces to achieve political objectives.
The study of the use of armed forces is called military science
. Broadly speaking, this involves considering offense and defense at three "levels": strategy
, operational art, and tactics
. All three levels study the application of the use of force in order to achieve a desired objective.
 The obvious benefit to a country in maintaining armed forces is in providing protection from foreign threats and from internal conflict. In recent decades armed forces personnel have also been used as emergency civil support roles in post-disaster situations. On the other hand, they may also harm a society by engaging in counter-productive (or merely unsuccessful) warfare.
The obvious benefit to a country in maintaining armed forces is in providing protection from foreign threats and from internal conflict. In recent decades armed forces personnel have also been used as emergency civil support roles in post-disaster situations. On the other hand, they may also harm a society by engaging in counter-productive (or merely unsuccessful) warfare.
Expenditure on science and technology to develop weapons and systems sometimes produces side benefits, although some claim that greater benefits could come from targeting the money directly.
Armed forces of the world
Country
A country is a region legally identified as a distinct entity in political geography. A country may be an independent sovereign state or one that is occupied by another state, as a non-sovereign or formerly sovereign political division, or a geographic region associated with a previously...
are its government
Government
Government refers to the legislators, administrators, and arbitrators in the administrative bureaucracy who control a state at a given time, and to the system of government by which they are organized...
-sponsored defense, fighting forces, and organizations. They exist to further the foreign and domestic policies of their governing body, and to defend that body and the nation it represents from external aggressors. In some countries paramilitary
Paramilitary
A paramilitary is a force whose function and organization are similar to those of a professional military, but which is not considered part of a state's formal armed forces....
forces are included in a nation's armed forces. Armed force is the use of armed forces to achieve political objectives.
The study of the use of armed forces is called military science
Military science
Military science is the process of translating national defence policy to produce military capability by employing military scientists, including theorists, researchers, experimental scientists, applied scientists, designers, engineers, test technicians, and military personnel responsible for...
. Broadly speaking, this involves considering offense and defense at three "levels": strategy
Strategy
Strategy, a word of military origin, refers to a plan of action designed to achieve a particular goal. In military usage strategy is distinct from tactics, which are concerned with the conduct of an engagement, while strategy is concerned with how different engagements are linked...
, operational art, and tactics
Military tactics
Military tactics, the science and art of organizing an army or an air force, are the techniques for using weapons or military units in combination for engaging and defeating an enemy in battle. Changes in philosophy and technology over time have been reflected in changes to military tactics. In...
. All three levels study the application of the use of force in order to achieve a desired objective.
Organization
In most countries the armed forces are divided into basic Armed servicesArmed Services
Armed Services is a collective term that refers to the major organisational entities of national armed forces, so named because they service a combat need in a specific combat environment. In most states Armed Services include the Army also known as Land Force or Ground Force, Navy also know a...
Benefits and costs


Expenditure on science and technology to develop weapons and systems sometimes produces side benefits, although some claim that greater benefits could come from targeting the money directly.
See also
- MercenaryMercenaryA mercenary, is a person who takes part in an armed conflict based on the promise of material compensation rather than having a direct interest in, or a legal obligation to, the conflict itself. A non-conscript professional member of a regular army is not considered to be a mercenary although he...
- MilitariaMilitariaMilitaria are artifacts or replicas of military, police, etc., collected for their historical significance. Such antiques include firearms, swords, knives, and other weapons such as; uniforms, helmets, other military headgear, and armour; military orders and decorations; challenge coins and...
- MilitaryMilitaryA military is an organization authorized by its greater society to use lethal force, usually including use of weapons, in defending its country by combating actual or perceived threats. The military may have additional functions of use to its greater society, such as advancing a political agenda e.g...
- Military organizationMilitary organizationMilitary organization is the structuring of the armed forces of a state so as to offer military capability required by the national defence policy. In some countries paramilitary forces are included in a nation's armed forces...
- Military fiatMilitary fiatMilitary fiat is a process whereby a decision is made and enforced by military means without the participation of other political elements. The Latin term fiat, translated as "let it be," suggests the autocratic attitude ascribed to such a process...
- Military historyMilitary historyMilitary history is a humanities discipline within the scope of general historical recording of armed conflict in the history of humanity, and its impact on the societies, their cultures, economies and changing intra and international relationships....
- Military incompetenceMilitary incompetenceMilitary incompetence refers to incompetencies and failures of military organisations, whether through incompetent individuals or through a flawed institutional culture....
- Military intelligenceMilitary intelligenceMilitary intelligence is a military discipline that exploits a number of information collection and analysis approaches to provide guidance and direction to commanders in support of their decisions....
- Military dictatorshipMilitary dictatorshipA military dictatorship is a form of government where in the political power resides with the military. It is similar but not identical to a stratocracy, a state ruled directly by the military....
- Military juntaMilitary juntaA junta or military junta is a government led by a committee of military leaders. The term derives from the Spanish language junta meaning committee, specifically a board of directors...
- Military rule (disambiguation)
- Military scienceMilitary scienceMilitary science is the process of translating national defence policy to produce military capability by employing military scientists, including theorists, researchers, experimental scientists, applied scientists, designers, engineers, test technicians, and military personnel responsible for...
- Military Aid to the Civil PowerMilitary Aid to the Civil PowerMilitary aid to the civil power is assistance by the armed forces to the civil authorities of the state with the provision of specialist equipment or trained personnel...
- Military Aid to the Civil CommunityMilitary Aid to the Civil CommunityMilitary Aid to the Civil Community is a phrase referring to the armed forces providing a service to the civilian community. It is used in many countries, particularly the United Kingdom.-United Kingdom:...
- List of battles
- ParamilitaryParamilitaryA paramilitary is a force whose function and organization are similar to those of a professional military, but which is not considered part of a state's formal armed forces....
- Staff (military)
- Civil-military relationsCivil-military relationsCivil–military relations describes the relationship between civil society as a whole and the military organization or organizations established to protect it. More narrowly, it describes the relationship between the civil authority of a given society and its military authority...
Armed forces of the world
- List of militaries by country
- List of militaries that recruit foreigners
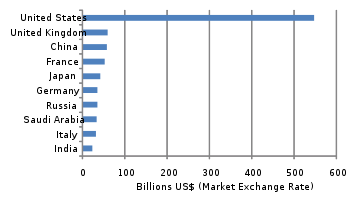
- List of countries by military expenditures
- List of countries by number of active troops
- List of countries by size of armed forces
- List of countries without an army
- List of air forces
- List of armies
- List of navies

