
Applications of evolution
Encyclopedia
Evolutionary biology, in particular the understanding of how organisms evolve through natural selection, is an area of science with many practical applications.
. For example, evolutionary thinking is key to life history theory
. Annotation of genes and their function relies heavily on comparative, that is evolutionary, approaches. The field of evolutionary developmental biology
investigates how developmental processes work by using the comparative method to determine how they evolved.
, which is the intentional selection of certain traits in a population of organisms. Humans have used artificial selection for thousands of years in the domestication
of plants and animals. More recently, such selection has become a vital part of genetic engineering
, with selectable marker
s such as antibiotic resistance genes being used to manipulate DNA in molecular biology
. It is also possible to use repeated rounds of mutation and selection to evolve proteins with particular properties, such as modified enzyme
s or new antibodies
, in a process called directed evolution
.
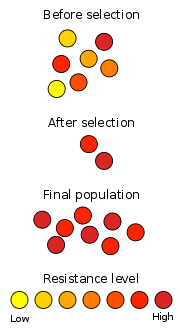 Antibiotic resistance
Antibiotic resistance
can be a result of point mutations in the pathogen
genome
at a rate of about 1 in 108 per chromosomal replication. The antibiotic action against the pathogen can be seen as an environmental pressure; those bacteria which have a mutation allowing them to survive will live on to reproduce. They will then pass this trait to their offspring, which will result in a fully resistant colony.
Understanding the changes that have occurred during organism's evolution can reveal the genes needed to construct parts of the body, genes which may be involved in human genetic disorder
s. For example, the Mexican tetra
is an albino cavefish that lost its eyesight during evolution. Breeding together different populations of this blind fish produced some offspring with functional eyes, since different mutations had occurred in the isolated populations that had evolved in different caves. This helped identify genes required for vision and pigmentation, such as crystallin
s and the melanocortin 1 receptor
. Similarly, comparing the genome of the Antarctic icefish
, which lacks red blood cell
s, to close relatives such as the Antarctic rockcod revealed genes needed to make these blood cells.
. Here, simulations of evolution using evolutionary algorithm
s and artificial life
started with the work of Nils Aall Barricelli in the 1960s, and was extended by Alex Fraser
, who published a series of papers on simulation of artificial selection
. Artificial evolution
became a widely recognised optimisation method as a result of the work of Ingo Rechenberg
in the 1960s and early 1970s, who used evolution strategies
to solve complex engineering problems. Genetic algorithm
s in particular became popular through the writing of John Holland
. As academic interest grew, dramatic increases in the power of computers allowed practical applications, including the automatic evolution of computer programs. Evolutionary algorithms are now used to solve multi-dimensional problems more efficiently than software produced by human designers, and also to optimise the design of systems.
Wider biology
The evolutionary approach is key to much current research in biology that does not set out to study evolution per se, especially in organismal biology and ecologyEcology
Ecology is the scientific study of the relations that living organisms have with respect to each other and their natural environment. Variables of interest to ecologists include the composition, distribution, amount , number, and changing states of organisms within and among ecosystems...
. For example, evolutionary thinking is key to life history theory
Life history theory
Life history theory posits that the schedule and duration of key events in an organism's lifetime are shaped by natural selection to produce the largest possible number of surviving offspring...
. Annotation of genes and their function relies heavily on comparative, that is evolutionary, approaches. The field of evolutionary developmental biology
Evolutionary developmental biology
Evolutionary developmental biology is a field of biology that compares the developmental processes of different organisms to determine the ancestral relationship between them, and to discover how developmental processes evolved...
investigates how developmental processes work by using the comparative method to determine how they evolved.
Artificial selection
A major technological application of evolution is artificial selectionArtificial selection
Artificial selection describes intentional breeding for certain traits, or combination of traits. The term was utilized by Charles Darwin in contrast to natural selection, in which the differential reproduction of organisms with certain traits is attributed to improved survival or reproductive...
, which is the intentional selection of certain traits in a population of organisms. Humans have used artificial selection for thousands of years in the domestication
Domestication
Domestication or taming is the process whereby a population of animals or plants, through a process of selection, becomes accustomed to human provision and control. In the Convention on Biological Diversity a domesticated species is defined as a 'species in which the evolutionary process has been...
of plants and animals. More recently, such selection has become a vital part of genetic engineering
Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification, is the direct human manipulation of an organism's genome using modern DNA technology. It involves the introduction of foreign DNA or synthetic genes into the organism of interest...
, with selectable marker
Selectable marker
A selectable marker is a gene introduced into a cell, especially a bacterium or to cells in culture, that confers a trait suitable for artificial selection. They are a type of reporter gene used in laboratory microbiology, molecular biology, and genetic engineering to indicate the success of a...
s such as antibiotic resistance genes being used to manipulate DNA in molecular biology
Molecular biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that deals with the molecular basis of biological activity. This field overlaps with other areas of biology and chemistry, particularly genetics and biochemistry...
. It is also possible to use repeated rounds of mutation and selection to evolve proteins with particular properties, such as modified enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
s or new antibodies
Antibody
An antibody, also known as an immunoglobulin, is a large Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique part of the foreign target, termed an antigen...
, in a process called directed evolution
Directed evolution
thumb|250px|right|An example of a possible round to evolve a protein based fluorescent sensor for a specific analyte using two consecutive FACS sortings...
.
Medicine

Antibiotic resistance
Antibiotic resistance is a type of drug resistance where a microorganism is able to survive exposure to an antibiotic. While a spontaneous or induced genetic mutation in bacteria may confer resistance to antimicrobial drugs, genes that confer resistance can be transferred between bacteria in a...
can be a result of point mutations in the pathogen
Pathogen
A pathogen gignomai "I give birth to") or infectious agent — colloquially, a germ — is a microbe or microorganism such as a virus, bacterium, prion, or fungus that causes disease in its animal or plant host...
genome
Genome
In modern molecular biology and genetics, the genome is the entirety of an organism's hereditary information. It is encoded either in DNA or, for many types of virus, in RNA. The genome includes both the genes and the non-coding sequences of the DNA/RNA....
at a rate of about 1 in 108 per chromosomal replication. The antibiotic action against the pathogen can be seen as an environmental pressure; those bacteria which have a mutation allowing them to survive will live on to reproduce. They will then pass this trait to their offspring, which will result in a fully resistant colony.
Understanding the changes that have occurred during organism's evolution can reveal the genes needed to construct parts of the body, genes which may be involved in human genetic disorder
Genetic disorder
A genetic disorder is an illness caused by abnormalities in genes or chromosomes, especially a condition that is present from before birth. Most genetic disorders are quite rare and affect one person in every several thousands or millions....
s. For example, the Mexican tetra
Mexican tetra
The Mexican tetra or Blind Cave Fish is a freshwater fishof the characin family oforder Characiformes....
is an albino cavefish that lost its eyesight during evolution. Breeding together different populations of this blind fish produced some offspring with functional eyes, since different mutations had occurred in the isolated populations that had evolved in different caves. This helped identify genes required for vision and pigmentation, such as crystallin
Crystallin
In anatomy, a crystallin is a water-soluble structural protein found in the lens and the cornea of the eye accounting for the transparency of the structure. It has also been identified in other places such as the heart, and in aggressive breast cancer tumors....
s and the melanocortin 1 receptor
Melanocortin 1 receptor
The melanocortin 1 receptor , also known as melanocyte-stimulating hormone receptor , melanin-activating peptide receptor, or melanotropin receptor, is a G protein-coupled receptor which binds to a class of pituitary peptide hormones known as the melanocortins, of which include adrenocorticotropic...
. Similarly, comparing the genome of the Antarctic icefish
Notothenioidei
The Antarctic icefish belong to the perciform suborder Notothenioidei and are the largely endemic, dominant fish taxa in the cold continental shelf waters surrounding Antarctica. At present, the suborder includes 8 families with 43 genera and 122 species...
, which lacks red blood cell
Red blood cell
Red blood cells are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate organism's principal means of delivering oxygen to the body tissues via the blood flow through the circulatory system...
s, to close relatives such as the Antarctic rockcod revealed genes needed to make these blood cells.
Computer science
As evolution can produce highly optimised processes and networks, it has many applications in computer scienceComputer science
Computer science or computing science is the study of the theoretical foundations of information and computation and of practical techniques for their implementation and application in computer systems...
. Here, simulations of evolution using evolutionary algorithm
Evolutionary algorithm
In artificial intelligence, an evolutionary algorithm is a subset of evolutionary computation, a generic population-based metaheuristic optimization algorithm. An EA uses some mechanisms inspired by biological evolution: reproduction, mutation, recombination, and selection...
s and artificial life
Artificial life
Artificial life is a field of study and an associated art form which examine systems related to life, its processes, and its evolution through simulations using computer models, robotics, and biochemistry. The discipline was named by Christopher Langton, an American computer scientist, in 1986...
started with the work of Nils Aall Barricelli in the 1960s, and was extended by Alex Fraser
Alex Fraser (scientist)
Alex Fraser was a major innovator in the development of the computer modeling of population genetics and his work has stimulated many advances in genetic research over the past decades....
, who published a series of papers on simulation of artificial selection
Artificial selection
Artificial selection describes intentional breeding for certain traits, or combination of traits. The term was utilized by Charles Darwin in contrast to natural selection, in which the differential reproduction of organisms with certain traits is attributed to improved survival or reproductive...
. Artificial evolution
Evolutionary algorithm
In artificial intelligence, an evolutionary algorithm is a subset of evolutionary computation, a generic population-based metaheuristic optimization algorithm. An EA uses some mechanisms inspired by biological evolution: reproduction, mutation, recombination, and selection...
became a widely recognised optimisation method as a result of the work of Ingo Rechenberg
Ingo Rechenberg
Ingo Rechenberg is a German computer scientist and professor. Rechenberg is a pioneer of the fields of evolutionary computation and artificial evolution. In the 1960s and 1970s he invented a highly influential set of optimization methods known as evolution strategies...
in the 1960s and early 1970s, who used evolution strategies
Evolution strategy
In computer science, evolution strategy is an optimization technique based on ideas of adaptation and evolution. It belongs to the general class of evolutionary computation or artificial evolution methodologies.-History:...
to solve complex engineering problems. Genetic algorithm
Genetic algorithm
A genetic algorithm is a search heuristic that mimics the process of natural evolution. This heuristic is routinely used to generate useful solutions to optimization and search problems...
s in particular became popular through the writing of John Holland
John Henry Holland
John Henry Holland is an American scientist and Professor of Psychology and Professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. He is a pioneer in complex systems and nonlinear science. He is known as the father of genetic algorithms. He was awarded...
. As academic interest grew, dramatic increases in the power of computers allowed practical applications, including the automatic evolution of computer programs. Evolutionary algorithms are now used to solve multi-dimensional problems more efficiently than software produced by human designers, and also to optimise the design of systems.

