_1996_tp66.gif)
(15875) 1996 TP66
Encyclopedia
, also written as 1996 TP66, is a resonant trans-Neptunian object
in 2:3 resonance
with Neptune
, like Pluto
(plutino
). It was discovered on October 11, 1996 by Chad Trujillo
, David C. Jewitt
, and Jane X. Luu at the Mauna Kea Observatory
, Hawaii
.
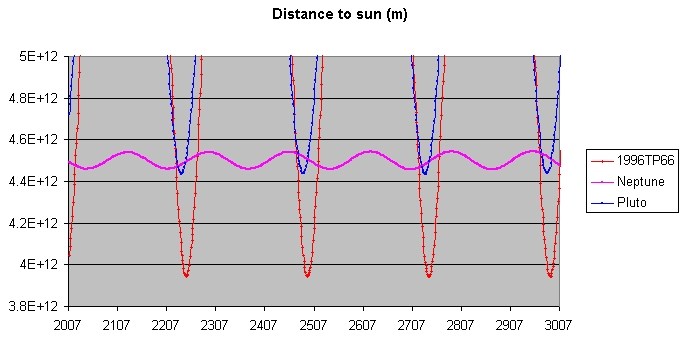
is currently 27 AU
from the Sun, and came to perihelion
(q=26.3 AU) in 2000. This means that this small plutino is currently well inside the orbit of the planet Neptune
. Like Pluto
, this plutino spends part of its orbit closer to the Sun than Neptune even though their orbits are dominated by Neptune
. Simulations by the Deep Ecliptic Survey
(DES) show that over the next 10 million years can acquire a perihelion distance (qmin) as small as 25.9 AU.
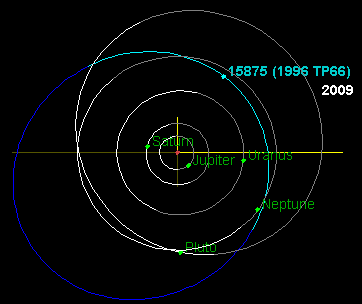
 Dwarf-planet candidate Huya
Dwarf-planet candidate Huya
and plutino are also currently inside the orbit of Neptune.
Calculations by the Minor Planet Center
in 1997 showed that the eccentric orbit
comes within 6.9 AU of Uranus
and stays more than 22.6 AU from Neptune over a 14,000-year period centered on the present.
Resonant trans-Neptunian object
In astronomy, a resonant trans-Neptunian object is a trans-Neptunian object in mean motion orbital resonance with Neptune. The orbital periods of the resonant objects are in a simple integer relations with the period of Neptune e.g. 1:2, 2:3 etc...
in 2:3 resonance
Orbital resonance
In celestial mechanics, an orbital resonance occurs when two orbiting bodies exert a regular, periodic gravitational influence on each other, usually due to their orbital periods being related by a ratio of two small integers. Orbital resonances greatly enhance the mutual gravitational influence of...
with Neptune
Neptune
Neptune is the eighth and farthest planet from the Sun in the Solar System. Named for the Roman god of the sea, it is the fourth-largest planet by diameter and the third largest by mass. Neptune is 17 times the mass of Earth and is slightly more massive than its near-twin Uranus, which is 15 times...
, like Pluto
Pluto
Pluto, formal designation 134340 Pluto, is the second-most-massive known dwarf planet in the Solar System and the tenth-most-massive body observed directly orbiting the Sun...
(plutino
Plutino
In astronomy, a plutino is a trans-Neptunian object in 2:3 mean motion resonance with Neptune. For every 2 orbits that a plutino makes, Neptune orbits 3 times. Plutinos are named after Pluto, which follows an orbit trapped in the same resonance, with the Italian diminutive suffix -ino...
). It was discovered on October 11, 1996 by Chad Trujillo
Chad Trujillo
Chadwick A. "Chad" Trujillo is an astronomer and the co-discoverer of the dwarf planet Eris.Trujillo works with computer software and has examined the orbits of the numerous trans-Neptunian objects , which is the outer area of the solar system that he specialized in. In late August 2005, it was...
, David C. Jewitt
David C. Jewitt
David C. Jewitt is a professor of astronomy formerly at the University of Hawaii Institute for Astronomy, now at UCLA. He was born in 1958 in England, and is a 1979 graduate of the University of London. Jewitt received an M.Sc. and a Ph.D. in astronomy at the California Institute of Technology in...
, and Jane X. Luu at the Mauna Kea Observatory
Mauna Kea Observatory
The Observatories at Mauna Kea, , are an independent collection of astronomical research facilities located on the summit of Mauna Kea on the Big Island of Hawai'i, USA. The facilities are located in a special land use zone known as the "Astronomy Precinct," which is located in the Mauna Kea...
, Hawaii
Hawaii
Hawaii is the newest of the 50 U.S. states , and is the only U.S. state made up entirely of islands. It is the northernmost island group in Polynesia, occupying most of an archipelago in the central Pacific Ocean, southwest of the continental United States, southeast of Japan, and northeast of...
.
Inside the orbit of Neptune
This plutinoPlutino
In astronomy, a plutino is a trans-Neptunian object in 2:3 mean motion resonance with Neptune. For every 2 orbits that a plutino makes, Neptune orbits 3 times. Plutinos are named after Pluto, which follows an orbit trapped in the same resonance, with the Italian diminutive suffix -ino...
is currently 27 AU
Astronomical unit
An astronomical unit is a unit of length equal to about or approximately the mean Earth–Sun distance....
from the Sun, and came to perihelion
Apsis
An apsis , plural apsides , is the point of greatest or least distance of a body from one of the foci of its elliptical orbit. In modern celestial mechanics this focus is also the center of attraction, which is usually the center of mass of the system...
(q=26.3 AU) in 2000. This means that this small plutino is currently well inside the orbit of the planet Neptune
Neptune
Neptune is the eighth and farthest planet from the Sun in the Solar System. Named for the Roman god of the sea, it is the fourth-largest planet by diameter and the third largest by mass. Neptune is 17 times the mass of Earth and is slightly more massive than its near-twin Uranus, which is 15 times...
. Like Pluto
Pluto
Pluto, formal designation 134340 Pluto, is the second-most-massive known dwarf planet in the Solar System and the tenth-most-massive body observed directly orbiting the Sun...
, this plutino spends part of its orbit closer to the Sun than Neptune even though their orbits are dominated by Neptune
Resonant trans-Neptunian object
In astronomy, a resonant trans-Neptunian object is a trans-Neptunian object in mean motion orbital resonance with Neptune. The orbital periods of the resonant objects are in a simple integer relations with the period of Neptune e.g. 1:2, 2:3 etc...
. Simulations by the Deep Ecliptic Survey
Deep Ecliptic Survey
The Deep Ecliptic Survey is a project to find Kuiper belt objects , using the facilities of the National Optical Astronomy Observatory .The principal investigator is Bob Millis....
(DES) show that over the next 10 million years can acquire a perihelion distance (qmin) as small as 25.9 AU.
 This small plutino Plutino In astronomy, a plutino is a trans-Neptunian object in 2:3 mean motion resonance with Neptune. For every 2 orbits that a plutino makes, Neptune orbits 3 times. Plutinos are named after Pluto, which follows an orbit trapped in the same resonance, with the Italian diminutive suffix -ino... is currently well inside the orbit of Neptune even though its orbit is dominated by Neptune Resonant trans-Neptunian object In astronomy, a resonant trans-Neptunian object is a trans-Neptunian object in mean motion orbital resonance with Neptune. The orbital periods of the resonant objects are in a simple integer relations with the period of Neptune e.g. 1:2, 2:3 etc... . |
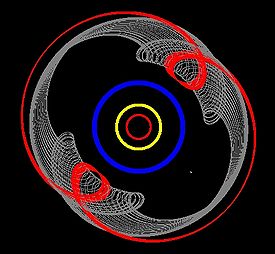 The motion of (15875) 1996 TP66 (red) and Pluto Pluto Pluto, formal designation 134340 Pluto, is the second-most-massive known dwarf planet in the Solar System and the tenth-most-massive body observed directly orbiting the Sun... (grey) in a rotating frame with a period equal to Neptune Neptune Neptune is the eighth and farthest planet from the Sun in the Solar System. Named for the Roman god of the sea, it is the fourth-largest planet by diameter and the third largest by mass. Neptune is 17 times the mass of Earth and is slightly more massive than its near-twin Uranus, which is 15 times... 's orbital period Orbital period The orbital period is the time taken for a given object to make one complete orbit about another object.When mentioned without further qualification in astronomy this refers to the sidereal period of an astronomical object, which is calculated with respect to the stars.There are several kinds of... . (Neptune is held stationary.) |

38628 Huya
38628 Huya is a trans-Neptunian object . It was discovered in March 2000 by Ignacio Ferrin and announced on 24 October 2000. It is classified as a plutino being in a 2:3 mean motion resonance with Neptune. With a Spitzer size estimate of , this plutino is also a likely dwarf-planet. It is expected...
and plutino are also currently inside the orbit of Neptune.
Calculations by the Minor Planet Center
Minor Planet Center
The Minor Planet Center operates at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory , which is part of the Center for Astrophysics along with the Harvard College Observatory ....
in 1997 showed that the eccentric orbit
Orbital eccentricity
The orbital eccentricity of an astronomical body is the amount by which its orbit deviates from a perfect circle, where 0 is perfectly circular, and 1.0 is a parabola, and no longer a closed orbit...
comes within 6.9 AU of Uranus
Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. It has the third-largest planetary radius and fourth-largest planetary mass in the Solar System. It is named after the ancient Greek deity of the sky Uranus , the father of Cronus and grandfather of Zeus...
and stays more than 22.6 AU from Neptune over a 14,000-year period centered on the present.

