
Y-factor
Encyclopedia
The Y-factor method is a widely used technique for measuring the gain
and noise temperature of an amplifier
. It is based on the Johnson-Nyquist noise of a resistor
at two different, known temperatures.
Consider a microwave
amplifier with a 50 ohm
impedance
with a 50 ohm resistor
connected to the amplifier input. If the resistor is at a physical temperature
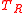 , then the Johnson-Nyquist noise power coupled to the amplifier input is
, then the Johnson-Nyquist noise power coupled to the amplifier input is 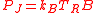 , where
, where 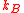 is Boltzmann’s constant and
is Boltzmann’s constant and  is the bandwidth. The noise power at the output of the amplifier (i.e. the noise power coupled to an impedance-matched load that is connected to the amplifier output) is
is the bandwidth. The noise power at the output of the amplifier (i.e. the noise power coupled to an impedance-matched load that is connected to the amplifier output) is 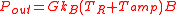 , where G is the amplifier power gain and
, where G is the amplifier power gain and 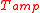 is the amplifier noise temperature. For the Y-factor technique,
is the amplifier noise temperature. For the Y-factor technique, 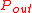 is measured for two different, known values of
is measured for two different, known values of 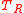 .
. 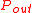 is then converted to an effective temperature
is then converted to an effective temperature  (in units of kelvin
(in units of kelvin
) by dividing by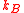 and the measurement bandwidth
and the measurement bandwidth  . The two values of
. The two values of  are then plotted as a function of
are then plotted as a function of 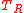 (also in units of kelvin), and a line is fit to these two points (see figure). The slope of this line is equal to the amplifier power gain. The x-intercept of the line is equal the negative of the amplifier noise temperature -
(also in units of kelvin), and a line is fit to these two points (see figure). The slope of this line is equal to the amplifier power gain. The x-intercept of the line is equal the negative of the amplifier noise temperature -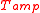 in kelvin.
in kelvin.
Gain
In electronics, gain is a measure of the ability of a circuit to increase the power or amplitude of a signal from the input to the output. It is usually defined as the mean ratio of the signal output of a system to the signal input of the same system. It may also be defined on a logarithmic scale,...
and noise temperature of an amplifier
Electronic amplifier
An electronic amplifier is a device for increasing the power of a signal.It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude...
. It is based on the Johnson-Nyquist noise of a resistor
Resistor
A linear resistor is a linear, passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element.The current through a resistor is in direct proportion to the voltage across the resistor's terminals. Thus, the ratio of the voltage applied across a resistor's...
at two different, known temperatures.
Consider a microwave
Microwave
Microwaves, a subset of radio waves, have wavelengths ranging from as long as one meter to as short as one millimeter, or equivalently, with frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz. This broad definition includes both UHF and EHF , and various sources use different boundaries...
amplifier with a 50 ohm
Ohm
The ohm is the SI unit of electrical resistance, named after German physicist Georg Simon Ohm.- Definition :The ohm is defined as a resistance between two points of a conductor when a constant potential difference of 1 volt, applied to these points, produces in the conductor a current of 1 ampere,...
impedance
Electrical impedance
Electrical impedance, or simply impedance, is the measure of the opposition that an electrical circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current circuit...
with a 50 ohm resistor
Resistor
A linear resistor is a linear, passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element.The current through a resistor is in direct proportion to the voltage across the resistor's terminals. Thus, the ratio of the voltage applied across a resistor's...
connected to the amplifier input. If the resistor is at a physical temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
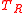 , then the Johnson-Nyquist noise power coupled to the amplifier input is
, then the Johnson-Nyquist noise power coupled to the amplifier input is 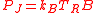 , where
, where 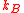 is Boltzmann’s constant and
is Boltzmann’s constant and  is the bandwidth. The noise power at the output of the amplifier (i.e. the noise power coupled to an impedance-matched load that is connected to the amplifier output) is
is the bandwidth. The noise power at the output of the amplifier (i.e. the noise power coupled to an impedance-matched load that is connected to the amplifier output) is 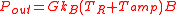 , where G is the amplifier power gain and
, where G is the amplifier power gain and  is the amplifier noise temperature. For the Y-factor technique,
is the amplifier noise temperature. For the Y-factor technique, 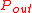 is measured for two different, known values of
is measured for two different, known values of 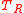 .
. 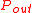 is then converted to an effective temperature
is then converted to an effective temperature  (in units of kelvin
(in units of kelvinKelvin
The kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all...
) by dividing by
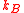 and the measurement bandwidth
and the measurement bandwidth  . The two values of
. The two values of  are then plotted as a function of
are then plotted as a function of 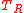 (also in units of kelvin), and a line is fit to these two points (see figure). The slope of this line is equal to the amplifier power gain. The x-intercept of the line is equal the negative of the amplifier noise temperature -
(also in units of kelvin), and a line is fit to these two points (see figure). The slope of this line is equal to the amplifier power gain. The x-intercept of the line is equal the negative of the amplifier noise temperature - in kelvin.
in kelvin.

