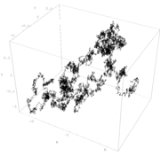
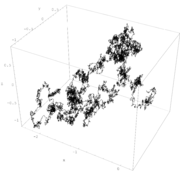
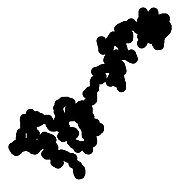
Wiener sausage
Encyclopedia
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
field of probability
Probability
Probability is ordinarily used to describe an attitude of mind towards some proposition of whose truth we arenot certain. The proposition of interest is usually of the form "Will a specific event occur?" The attitude of mind is of the form "How certain are we that the event will occur?" The...
, the Wiener sausage is a neighborhood of the trace of a Brownian motion
Brownian motion
Brownian motion or pedesis is the presumably random drifting of particles suspended in a fluid or the mathematical model used to describe such random movements, which is often called a particle theory.The mathematical model of Brownian motion has several real-world applications...
up to a time t, given by taking all points within a fixed distance of Brownian motion. It can be visualized as a sausage of fixed radius whose centerline is Brownian motion. The Wiener sausage was named after Norbert Wiener
Norbert Wiener
Norbert Wiener was an American mathematician.A famous child prodigy, Wiener later became an early researcher in stochastic and noise processes, contributing work relevant to electronic engineering, electronic communication, and control systems.Wiener is regarded as the originator of cybernetics, a...
by because of its relation to the Wiener process
Wiener process
In mathematics, the Wiener process is a continuous-time stochastic process named in honor of Norbert Wiener. It is often called standard Brownian motion, after Robert Brown...
; the name is also a pun on Vienna sausage
Vienna sausage
A Vienna sausage is a kind of hot dog...
, as "Wiener" means "Viennese" in German
German language
German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union....
.
The Wiener sausage is one of the simplest non-Markovian
Markov process
In probability theory and statistics, a Markov process, named after the Russian mathematician Andrey Markov, is a time-varying random phenomenon for which a specific property holds...
functionals of Brownian motion. Its applications include stochastic
Stochastic
Stochastic refers to systems whose behaviour is intrinsically non-deterministic. A stochastic process is one whose behavior is non-deterministic, in that a system's subsequent state is determined both by the process's predictable actions and by a random element. However, according to M. Kac and E...
phenomena including heat conduction. It was first described by , and it was used by to explain results of a Bose–Einstein condensate
Bose–Einstein condensate
A Bose–Einstein condensate is a state of matter of a dilute gas of weakly interacting bosons confined in an external potential and cooled to temperatures very near absolute zero . Under such conditions, a large fraction of the bosons occupy the lowest quantum state of the external potential, at...
, with proofs published by .
Definitions
The Wiener sausage Wδ(t) of radius δ and length t is the set-valued random variableRandom variable
In probability and statistics, a random variable or stochastic variable is, roughly speaking, a variable whose value results from a measurement on some type of random process. Formally, it is a function from a probability space, typically to the real numbers, which is measurable functionmeasurable...
on Brownian paths b (in some Euclidean space) defined by
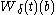 is the set of points within a distance δ of some point b(x) of the path b with 0≤x≤t.
is the set of points within a distance δ of some point b(x) of the path b with 0≤x≤t.The volume of the Wiener sausage
There has been a lot of work on the behavior of the volume (Lebesgue measureLebesgue measure
In measure theory, the Lebesgue measure, named after French mathematician Henri Lebesgue, is the standard way of assigning a measure to subsets of n-dimensional Euclidean space. For n = 1, 2, or 3, it coincides with the standard measure of length, area, or volume. In general, it is also called...
) |Wδ(t)| of the Wiener sausage as it becomes thin (δ→0); by rescaling, this is essentially equivalent to studying the volume as the sausage becomes long (t→∞).
showed that in 3 dimensions the expected value of the volume of the sausage is
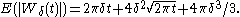
In dimension d at least 3 the volume of the Wiener sausage is asymptotic to
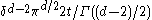
as t tends to infinity. In dimensions 1 and 2 this formula gets replaced by
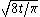 and
and 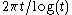 respectively. , a student of Spitzer, proved similar results for generalizations of Wiener sausages with cross sections given by more general compacts sets than balls.
respectively. , a student of Spitzer, proved similar results for generalizations of Wiener sausages with cross sections given by more general compacts sets than balls.

