
Umbrella sampling
Encyclopedia
Computational physics
Computational physics is the study and implementation of numerical algorithms to solve problems in physics for which a quantitative theory already exists...
and chemistry
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
, used to improve sampling
Sampling (statistics)
In statistics and survey methodology, sampling is concerned with the selection of a subset of individuals from within a population to estimate characteristics of the whole population....
of a system (or different systems) where ergodicity
Ergodicity
In mathematics, the term ergodic is used to describe a dynamical system which, broadly speaking, has the same behavior averaged over time as averaged over space. In physics the term is used to imply that a system satisfies the ergodic hypothesis of thermodynamics.-Etymology:The word ergodic is...
is hindered by the form of the system's energy landscape
Energy landscape
In physics, an energy landscape is a mapping of all possible conformations of a molecular entity, or the spatial positions of interacting molecules in a system, and their corresponding energy levels, typically Gibbs free energy, on a two- or three-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system.In...
. It was first suggested by Torrie and Valleau in 1977http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6WHY-4DDR2HH-3V&_user=126524&_coverDate=02%2F28%2F1977&_rdoc=1&_fmt=&_orig=search&_sort=d&view=c&_acct=C000010360&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=126524&md5=950772b2b4de26ad320fd672ec611557. It is related to Importance sampling
Importance sampling
In statistics, importance sampling is a general technique for estimating properties of a particular distribution, while only having samples generated from a different distribution rather than the distribution of interest. It is related to Umbrella sampling in computational physics...
in statistics.
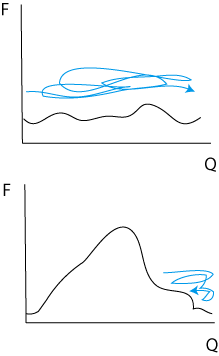
Systems in which an energy barrier separates two regions of configuration space may suffer from poor sampling in Metropolis Monte Carlo runs, as the low probability of overcoming the potential barrier can leave inaccessible configurations poorly sampled – or even entirely unsampled – by the simulation. An easily visualised example occurs with a solid at its melting point: considering the state of the system with an order parameter Q, both liquid (low Q) and solid (high Q) phases are low in energy, but are separated by a free energy
Thermodynamic free energy
The thermodynamic free energy is the amount of work that a thermodynamic system can perform. The concept is useful in the thermodynamics of chemical or thermal processes in engineering and science. The free energy is the internal energy of a system less the amount of energy that cannot be used to...
barrier at intermediate values of Q. This prevents the simulation from adequately sampling both phases.
Umbrella sampling is a means of "bridging the gap" in this situation. The standard Boltzmann weighting for Monte Carlo sampling is replaced by a potential chosen to cancel the influence of the energy barrier present. The Markov chain
Markov chain
A Markov chain, named after Andrey Markov, is a mathematical system that undergoes transitions from one state to another, between a finite or countable number of possible states. It is a random process characterized as memoryless: the next state depends only on the current state and not on the...
generated has a distribution given by:
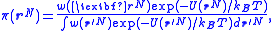
with w(rN) a function chosen to promote configurations that would otherwise be inaccessible to a Boltzmann-weighted Monte Carlo run. In the example above, w may be chosen such that w = w(Q), taking high values at intermediate Q and low values at low/high Q, facilitating barrier crossing.
Values for a thermodynamic property A deduced from a sampling run performed in this manner can be transformed into canonical-ensemble values by applying the formula:
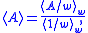
with the w subscript indicating values from the umbrella-sampled simulation. Series of umbrella sampling simulations can be analyzed using the weighted histogram analysis method or its generalization.
Subtleties exist in deciding the most computationally efficient way to apply the umbrella sampling method, as described in Frenkel & Smit's book Understanding Molecular Simulation.
Alternatives to umbrella sampling for computing potentials of mean force
Potential of mean force
The Potential of Mean Force of a system with N molecules is strictly the potential that gives the average force over all the configurations of all the n+1...N molecules acting on a particle at any fixed configuration keeping fixed a set of molecules 1...n...
or reaction rates
Reaction rate
The reaction rate or speed of reaction for a reactant or product in a particular reaction is intuitively defined as how fast or slow a reaction takes place...
are free energy perturbation
Free energy perturbation
Free energy perturbation theory is a method based on statistical mechanics that is used in computational chemistry for computing free energy differences from molecular dynamics or Metropolis Monte Carlo simulations. The FEP method was introduced by R. W. Zwanzig in 1954...
and transition interface sampling. A further alternative which functions in full non-equilibrium is S-PRES.

