
Two phase
Encyclopedia
Polyphase system
A polyphase system is a means of distributing alternating current electrical power. Polyphase systems have three or more energized electrical conductors carrying alternating currents with a definite time offset between the voltage waves in each conductor. Polyphase systems are particularly useful...
alternating current
Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
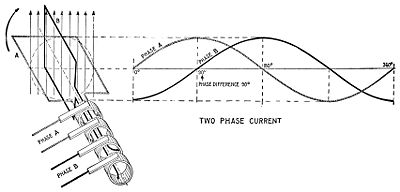
electric power distribution system. Two circuits were used, with voltage phase
Phase (waves)
Phase in waves is the fraction of a wave cycle which has elapsed relative to an arbitrary point.-Formula:The phase of an oscillation or wave refers to a sinusoidal function such as the following:...
s differing by 90 degree
Degree (angle)
A degree , usually denoted by ° , is a measurement of plane angle, representing 1⁄360 of a full rotation; one degree is equivalent to π/180 radians...
s. Usually circuits used four wires, two for each phase. Less frequently, three wires were used, with a common wire with a larger-diameter conductor. Some early two-phase generators had two complete rotor and field assemblies, with windings physically offset by 90 electrical degrees to provide two-phase power. The generators at Niagara Falls
Niagara Falls
The Niagara Falls, located on the Niagara River draining Lake Erie into Lake Ontario, is the collective name for the Horseshoe Falls and the adjacent American Falls along with the comparatively small Bridal Veil Falls, which combined form the highest flow rate of any waterfalls in the world and has...
installed in 1895 were the largest generators in the world at the time and were two-phase machines.
The advantage of two-phase electrical power was that it allowed for simple, self-starting electric motors. In the early days of electrical engineering
Electrical engineering
Electrical engineering is a field of engineering that generally deals with the study and application of electricity, electronics and electromagnetism. The field first became an identifiable occupation in the late nineteenth century after commercialization of the electric telegraph and electrical...
, it was easier to analyze and design two-phase systems where the phases were completely separated. It was not until the invention of the method of symmetrical components
Symmetrical components
In electrical engineering, the method of symmetrical components is used to simplify analysis of unbalanced three phase power systems under both normal and abnormal conditions.-Description:...
in 1918 that polyphase power systems had a convenient mathematical tool for describing unbalanced load cases. The revolving magnetic field produced with a two-phase system allowed electric motors to provide torque
Torque
Torque, moment or moment of force , is the tendency of a force to rotate an object about an axis, fulcrum, or pivot. Just as a force is a push or a pull, a torque can be thought of as a twist....
from zero motor speed, which was not possible with a single-phase induction motor
Induction motor
An induction or asynchronous motor is a type of AC motor where power is supplied to the rotor by means of electromagnetic induction. These motors are widely used in industrial drives, particularly polyphase induction motors, because they are robust and have no brushes...
(without extra starting means). Induction motors designed for two-phase operation use the same winding configuration as capacitor start single-phase motors.
Three-phase electric power
Three-phase electric power
Three-phase electric power is a common method of alternating-current electric power generation, transmission, and distribution. It is a type of polyphase system and is the most common method used by grids worldwide to transfer power. It is also used to power large motors and other heavy loads...
requires less conductor mass for the same voltage and overall amount of power, compared with a two-phase four-wire circuit of the same carrying capacity. It has replaced two-phase power for commercial distribution of electrical energy, but two-phase circuits are still found in certain control systems. Power transfer in a three-phase system with balanced loads is constant, whereas it pulsates at twice the line frequency in single-phase systems. These power pulsations tend to cause increased mechanical noise in transformer and motor laminations due to magnestriction and torsional vibration in generator and motor drive shafts.
Two-phase circuits typically use two separate pairs of current-carrying conductors. Alternatively, three wires may be used, but the common conductor carries the vector sum of the phase currents, which requires a larger conductor. Three-phase can share conductors so that the three phases can be carried on three conductors of the same size. In electrical power distribution, a requirement of only three conductors, rather than four, represented a considerable distribution-wire cost savings due to the expense of conductors and installation.
Two-phase power can be derived from a three-phase source using two transformer
Transformer
A transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another through inductively coupled conductors—the transformer's coils. A varying current in the first or primary winding creates a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core and thus a varying magnetic field...
s in a Scott connection: One transformer primary is connected across two phases of the supply. The second transformer is connected to a center-tap of the first transformer, and is wound for 86.6% of the phase-to-phase voltage on the three-phase system. The secondaries of the transformers will have two phases 90 degrees apart in time, and a balanced two-phase load will be evenly balanced over the three supply phases.
Three-wire, 120/240 volt single phase power used in the United States and Canada is sometimes incorrectly called "two-phase". The proper term is split phase
Split phase
A split-phase electricity distribution system is a 3-wire single-phase distribution system, commonly used in North America for single-family residential and light commercial applications. It is the AC equivalent of the original Edison 3-wire direct current system...
or 3-wire single-phase. The two live outputs of a 3-wire single phase transformer secondary winding are properly called "legs".

