
Trouton's rule
Encyclopedia
Trouton’s rule states that the entropy of vaporization is almost the same value, about 87–88 J K−1 mol−1, for various kinds of liquid
s. The entropy of vaporization is defined as the ratio between the enthalpy
of vaporization and the boiling temperature. It is named after Frederick Thomas Trouton
.
Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
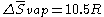
where R is the gas constant
Trouton’s rule is valid for many liquids; for instance, the entropy of vaporization of toluene
is 87.30 J K−1 mol−1, that of benzene
is 89.45 J K−1 mol−1, and that of chloroform
is 87.92 J K−1 mol−1. Because of its convenience, the rule is used to estimate the enthalpy of vaporization of liquids whose boiling point
s are known.
The rule, however, has some exceptions. For example, the entropies of vaporization of water, ethanol
, and formic acid
are far from the predicted values. The characteristic of those liquids to which Trouton’s rule cannot be applied is their special interaction between molecules such as hydrogen bonding. The entropy of vaporization of water and ethanol shows positive deviance from the rule; this is because the hydrogen bonding in the liquid phase lessens the entropy of the phase. In contrast, the entropy of vaporization of formic acid has negative deviance. This fact indicates the existence of an orderly structure in the gas phase; it is known that formic acid forms a dimer structure even in the gas phase. Negative deviance can also occur as a result of a small gas phase entropy owing to a low population of excited rotational states in the gas phase, particularly in small molecules such as methane - a small moment of inertia I giving rise to a large rotational constant B, with correspondingly widely separated rotational energy levels and, via Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution, a small population of excited rotational states and hence a low rotational entropy.
Trouton's rule validity can be increased by considering
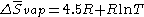
Here, if T = 400 K, we find the original formulation for Trouton's rule
Another equation which Tboiling < 2100 K is ΔHboiling = 87 Tboiling − 0.4 J/K.
Liquid
Liquid is one of the three classical states of matter . Like a gas, a liquid is able to flow and take the shape of a container. Some liquids resist compression, while others can be compressed. Unlike a gas, a liquid does not disperse to fill every space of a container, and maintains a fairly...
s. The entropy of vaporization is defined as the ratio between the enthalpy
Enthalpy
Enthalpy is a measure of the total energy of a thermodynamic system. It includes the internal energy, which is the energy required to create a system, and the amount of energy required to make room for it by displacing its environment and establishing its volume and pressure.Enthalpy is a...
of vaporization and the boiling temperature. It is named after Frederick Thomas Trouton
Frederick Thomas Trouton
Frederick Thomas Trouton FRS was an Irish physicist known for Trouton's Rule and experiments to detect the Earth's motion through the luminiferous aether.- Life and work :...
.
Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
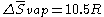
where R is the gas constant
Gas constant
The gas constant is a physical constant which is featured in many fundamental equations in the physical sciences, such as the ideal gas law and the Nernst equation. It is equivalent to the Boltzmann constant, but expressed in units of energy The gas constant (also known as the molar, universal,...
Trouton’s rule is valid for many liquids; for instance, the entropy of vaporization of toluene
Toluene
Toluene, formerly known as toluol, is a clear, water-insoluble liquid with the typical smell of paint thinners. It is a mono-substituted benzene derivative, i.e., one in which a single hydrogen atom from the benzene molecule has been replaced by a univalent group, in this case CH3.It is an aromatic...
is 87.30 J K−1 mol−1, that of benzene
Benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound. It is composed of 6 carbon atoms in a ring, with 1 hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom, with the molecular formula C6H6....
is 89.45 J K−1 mol−1, and that of chloroform
Chloroform
Chloroform is an organic compound with formula CHCl3. It is one of the four chloromethanes. The colorless, sweet-smelling, dense liquid is a trihalomethane, and is considered somewhat hazardous...
is 87.92 J K−1 mol−1. Because of its convenience, the rule is used to estimate the enthalpy of vaporization of liquids whose boiling point
Boiling point
The boiling point of an element or a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the environmental pressure surrounding the liquid....
s are known.
The rule, however, has some exceptions. For example, the entropies of vaporization of water, ethanol
Ethanol
Ethanol, also called ethyl alcohol, pure alcohol, grain alcohol, or drinking alcohol, is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid. It is a psychoactive drug and one of the oldest recreational drugs. Best known as the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages, it is also used in thermometers, as a...
, and formic acid
Formic acid
Formic acid is the simplest carboxylic acid. Its chemical formula is HCOOH or HCO2H. It is an important intermediate in chemical synthesis and occurs naturally, most notably in the venom of bee and ant stings. In fact, its name comes from the Latin word for ant, formica, referring to its early...
are far from the predicted values. The characteristic of those liquids to which Trouton’s rule cannot be applied is their special interaction between molecules such as hydrogen bonding. The entropy of vaporization of water and ethanol shows positive deviance from the rule; this is because the hydrogen bonding in the liquid phase lessens the entropy of the phase. In contrast, the entropy of vaporization of formic acid has negative deviance. This fact indicates the existence of an orderly structure in the gas phase; it is known that formic acid forms a dimer structure even in the gas phase. Negative deviance can also occur as a result of a small gas phase entropy owing to a low population of excited rotational states in the gas phase, particularly in small molecules such as methane - a small moment of inertia I giving rise to a large rotational constant B, with correspondingly widely separated rotational energy levels and, via Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution, a small population of excited rotational states and hence a low rotational entropy.
Trouton's rule validity can be increased by considering
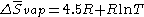
Here, if T = 400 K, we find the original formulation for Trouton's rule
Another equation which Tboiling < 2100 K is ΔHboiling = 87 Tboiling − 0.4 J/K.
Further reading
- Publication of Trouton's rule- Atkins, PeterPeter AtkinsPeter William Atkins is a British chemist and former Professor of Chemistry at the University of Oxford and a Fellow of Lincoln College. He is a prolific writer of popular chemistry textbooks, including Physical Chemistry, Inorganic Chemistry, and Molecular Quantum Mechanics...
(1978). Physical Chemistry Oxford University PressOxford University PressOxford University Press is the largest university press in the world. It is a department of the University of Oxford and is governed by a group of 15 academics appointed by the Vice-Chancellor known as the Delegates of the Press. They are headed by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as...
ISBN 0-7167-3539-X

