Transport in Tunisia
Encyclopedia
Tunisia
has a number of international airports to service its sizable tourist trade. Tunis
is the center of the transport system as the largest city having the largest port and a light transit system.
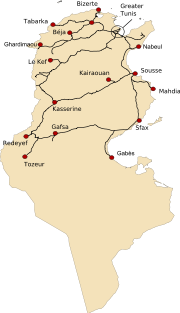 Tunisia inherited much of its rail transport system from the French and the Tunisian Government has developed infrastructure further. The railways are operated by the Société Nationale de Chemins de Fer Tunisiens (SNCFT), the Tunisian national railway. A modernisation program is currently underway. It has a total of 2,152 km consisting of 468 km of standard gauge
Tunisia inherited much of its rail transport system from the French and the Tunisian Government has developed infrastructure further. The railways are operated by the Société Nationale de Chemins de Fer Tunisiens (SNCFT), the Tunisian national railway. A modernisation program is currently underway. It has a total of 2,152 km consisting of 468 km of standard gauge
rail ways and 1,674 kilometres of metre gauge
. Tunis has a light rail system. In the south of Tunisia, there is a narrow gauge railway called the Sfax-Gafsa Railway which delivers phosphates and iron ore to the harbour at Sfax
. Tunisia has rail links with the neighbouring country of Algeria
Algeria
via the Ghardimaou
-Souk Ahras
line, and another connection to Tébessa
, however, the latter link is currently not used.
There are no railways yet in neighbouring Libya
Libya
though some are under construction in 2008; some gauge conversion
would be required for efficient connections.
- railways under construction - break-of-gauge
- / until gauge conversion
(some gauge would need to be converted to ). Algeria
- yes - Same gauge -
in 2002 to be used to improve roads in the country including €120 million towards building a motorway between Tunis and Sfax. (MEED Middle East Economic Digest, Oct 11, 2002 v46 i41 p19(1))
passes through Tunisia, linking it to North African nations including Algeria, Morocco, Libya
and Egypt
, and to West African nations via Mauritania
. In addition a feeder road links Tunisia to the Trans-Sahara Highway
from Algeria to West Africa.
through the Trans-Mediterranean gas pipeline
. (IPR Strategic Business Information Database, Dec 18, 2003) Libya's National Oil Corporation
formed a joint venture with Societe Tunisienne de l'Electricite et du Gaz to construct a national gas pipeline between the two countries. (Petroleum Economist, Dec 2003 v70 i12 p43(1))
including Bizerte
, Gabès
, La Goulette
, Sfax, Sousse
and Zarzis
. Tunisia's merchant marine consisted of 14 ships as at 2002.
but other significant airports serve Sfax, Houmt Souk
, Monastir
, Tozeur
and Tabarka
. Tunisair
is the national airline.
Tunisia
Tunisia , officially the Tunisian RepublicThe long name of Tunisia in other languages used in the country is: , is the northernmost country in Africa. It is a Maghreb country and is bordered by Algeria to the west, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Its area...
has a number of international airports to service its sizable tourist trade. Tunis
Tunis
Tunis is the capital of both the Tunisian Republic and the Tunis Governorate. It is Tunisia's largest city, with a population of 728,453 as of 2004; the greater metropolitan area holds some 2,412,500 inhabitants....
is the center of the transport system as the largest city having the largest port and a light transit system.
Railways

Standard gauge
The standard gauge is a widely-used track gauge . Approximately 60% of the world's existing railway lines are built to this gauge...
rail ways and 1,674 kilometres of metre gauge
Metre gauge
Metre gauge refers to narrow gauge railways and tramways with a track gauge of . In some African, American and Asian countries it is the main gauge. In Europe it has been used for local railways in France, Germany, and Belgium, most of which were closed down in mid 20th century. Only in Switzerland...
. Tunis has a light rail system. In the south of Tunisia, there is a narrow gauge railway called the Sfax-Gafsa Railway which delivers phosphates and iron ore to the harbour at Sfax
Sfax
Sfax is a city in Tunisia, located southeast of Tunis. The city, founded in AD 849 on the ruins of Taparura and Thaenae, is the capital of the Sfax Governorate , and a Mediterranean port. Sfax has population of 340,000...
. Tunisia has rail links with the neighbouring country of
 Algeria
AlgeriaTransport in Algeria
- Railways :There are a total of 3,973 km of railways: 2,888 km is standard gauge, with 283 km of that being electrified and 215 km of that being double tracked...
via the Ghardimaou
Ghardimaou
Ghardimaou is a town in the north-west of Tunisia about 192 km from Tunis. It belongs to the Jendouba Governorate. The town has about 70,000 inhabitants Ghardimaou is a town in the north-west of Tunisia about 192 km from Tunis. It belongs to the Jendouba Governorate. The town has...
-Souk Ahras
Souk Ahras
Souk Ahras is a province in Algeria, named after its capital, Souk Ahras. It stands on the border between Algeria and Tunisia.- Geography :Souk Ahras is situated in the extreme north east of Algeria, it is 4360 km²....
line, and another connection to Tébessa
Tébessa
Tébessa is the capital city of Tébessa Province, Algeria, 20 kilometers west from the border with Tunisia. Nearby is also a phosphate mine. The city is famous for the traditional Algerian carpets in the region, and is home to over 161,440 people.-History:...
, however, the latter link is currently not used.
There are no railways yet in neighbouring
 Libya
LibyaTransport in Libya
-Railways:Libya has had no railway in operation since 1965, all previous narrow gauge lines having been dismantled. Plans for a new network have been under development for some time , and in 2008 and 2009 various contracts were placed and construction work started on a standard gauge railway...
though some are under construction in 2008; some gauge conversion
Gauge conversion
In rail transport, gauge conversion is the process of converting a railway from one rail gauge to another, through the alteration of the railway tracks...
would be required for efficient connections.
Railway links to adjacent countries
LibyaTransport in Libya
-Railways:Libya has had no railway in operation since 1965, all previous narrow gauge lines having been dismantled. Plans for a new network have been under development for some time , and in 2008 and 2009 various contracts were placed and construction work started on a standard gauge railway...
- railways under construction - break-of-gauge
Break-of-gauge
With railways, a break-of-gauge occurs where a line of one gauge meets a line of a different gauge. Trains and rolling stock cannot run through without some form of conversion between gauges, and freight and passengers must otherwise be transloaded...
- / until gauge conversion
Gauge conversion
In rail transport, gauge conversion is the process of converting a railway from one rail gauge to another, through the alteration of the railway tracks...
(some gauge would need to be converted to ). Algeria
Transport in Algeria
- Railways :There are a total of 3,973 km of railways: 2,888 km is standard gauge, with 283 km of that being electrified and 215 km of that being double tracked...
- yes - Same gauge -
- TGMTGMTunis-Goulette-Marsa or TGM is a 19 km Tunisian railway line linking the capital Tunis with La Marsa via La Goulette.The TGM was the first railway in Tunisia and inaugurated in 1872. Since 1905 it has been known as the TGM...
- Lézard rougeLézard rougeThe lézard rouge is a historic Tunisian train, once the property of the Bey of Tunis but now used for tourists. It runs from Metlaoui to Redeyef and passes through the Selja Gorge, taking some 40 minutes for the journey. The track was originally used by mining trains carrying phosphates.- External...
, a tourist train - Métro léger de TunisMétro léger de TunisThe Métro léger de Tunis is an expanding public transportation network for the Tunis area that was started in 1985...
- Réseau Ferroviaire RapideRéseau Ferroviaire RapideThe Réseau Ferroviaire Rapide is a planned urban rail system in Tunis, in Tunisia.-Network:In Phase I of the project, a 17·9 km, Y-shaped network will be built, with 14 stations. Both lines will terminate at a station at place de Barcelone; Line D will run to Gobaâ and Line E will run to...
Highways
As of 2004, there were 18,997 km of highway including 12,310 of paved road and 6,387 of unpaved road. The major cities are all linked by road through the interior. In 2002, Tunisia borrowed €300 million from the European Investment BankEuropean Investment Bank
The European Investment Bank is the European Union's long-term lending institution established in 1958 under the Treaty of Rome. A policy-driven bank, the EIB supports the EU’s priority objectives, especially European integration and the development of economically weak regions...
in 2002 to be used to improve roads in the country including €120 million towards building a motorway between Tunis and Sfax. (MEED Middle East Economic Digest, Oct 11, 2002 v46 i41 p19(1))
Motorways
- A1 motorwayA1 motorway (Tunisia)The A1 motorway is a road connecting Tunis and Sfax....
- A2 motorway
- A3 motorwayA3 motorway (Tunisia)TheA3 links Tunis capital of Tunisia, the village of Oued Zarga . Eventually, the highway linking the capital to the border Algeria nne through Bou Salem, or 217 miles across the Tunisian territory....
- A4 motorwayA4 motorway (Tunisia)The A4 is a motorway connecting Tunis and Bizerte....
International highways
Route 1 in the Trans-African Highway networkTrans-African Highway network
The Trans-African Highway network comprises transcontinental road projects in Africa being developed by the United Nations Economic Commission for Africa , the African Development Bank , and the African Union in conjunction with regional international communities...
passes through Tunisia, linking it to North African nations including Algeria, Morocco, Libya
Libya
Libya is an African country in the Maghreb region of North Africa bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Sudan to the southeast, Chad and Niger to the south, and Algeria and Tunisia to the west....
and Egypt
Egypt
Egypt , officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, Arabic: , is a country mainly in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula forming a land bridge in Southwest Asia. Egypt is thus a transcontinental country, and a major power in Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Middle East and the Muslim world...
, and to West African nations via Mauritania
Mauritania
Mauritania is a country in the Maghreb and West Africa. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean in the west, by Western Sahara in the north, by Algeria in the northeast, by Mali in the east and southeast, and by Senegal in the southwest...
. In addition a feeder road links Tunisia to the Trans-Sahara Highway
Trans-Sahara Highway
The Trans-Sahara Highway is a transnational highway project to pave, improve and ease border formalities on an existing trade route across the Sahara Desert...
from Algeria to West Africa.
Pipelines
Tunisia has an extensive pipeline network including 3,059 km of gas pipelines, 1,203 kilometres of oil pipeline and 345 km of refined products. Petrochemicals are Tunisia's third most important export despite the small size of its oil and gas fields as compared to Libya and Algeria. It also gets a royalty rate of 5 per cent on the Algerian gas that runs through Tunis to SicilySicily
Sicily is a region of Italy, and is the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Along with the surrounding minor islands, it constitutes an autonomous region of Italy, the Regione Autonoma Siciliana Sicily has a rich and unique culture, especially with regard to the arts, music, literature,...
through the Trans-Mediterranean gas pipeline
Trans-Mediterranean Pipeline
The Trans-Mediterranean Pipeline is a natural gas pipeline from Algeria via Tunisia to Sicily and thence to mainland Italy. An extension of the TransMed pipeline delivers Algerian gas to Slovenia.-History:...
. (IPR Strategic Business Information Database, Dec 18, 2003) Libya's National Oil Corporation
National Oil Corporation
The National Oil Corporation is the national oil company of Libya. It dominates Libya's oil industry, along with a number of smaller subsidiaries, which combined account for around 70% the country's oil output...
formed a joint venture with Societe Tunisienne de l'Electricite et du Gaz to construct a national gas pipeline between the two countries. (Petroleum Economist, Dec 2003 v70 i12 p43(1))
Ports and harbours
Tunis is the most significant port in Tunisia with other significant ports on the Mediterranean SeaMediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean surrounded by the Mediterranean region and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Anatolia and Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant...
including Bizerte
Bizerte
Bizerte or Benzert , is the capital city of Bizerte Governorate in Tunisia and the northernmost city in Africa. It has a population of 230,879 .-History:...
, Gabès
Gabès
Gabès , also spelt Cabès, Cabes, Kabes, Gabbs and Gaps, the ancient Tacape, is the capital city of the Gabès Governorate, a province of Tunisia. It lies on the coast of the Gulf of Gabès. With a population of 116,323 it is the 6th largest Tunisian city.-History:Strabo refers to Tacape as an...
, La Goulette
La Goulette
La Goulette is the port of Tunis, the capital of Tunisia. The Kasbah fortress was built in 1535 by Charles I of Spain but was captured by the Ottoman Turks in 1574...
, Sfax, Sousse
Sousse
Sousse is a city in Tunisia. Located 140 km south of the capital Tunis, the city has 173,047 inhabitants . Sousse is in the central-east of the country, on the Gulf of Hammamet, which is a part of the Mediterranean Sea. The name may be of Berber origin: similar names are found in Libya and in...
and Zarzis
Zarzis
Zarzis is a commune and coastal town in southeastern Tunisia, on the coast of Mediterranean Sea. The climate is mainly dry and sunny, making it a popular tourist destination mixing the old and the traditional...
. Tunisia's merchant marine consisted of 14 ships as at 2002.
Aviation
As of 2002, Tunisia had 30 airports including several international airports. The most important one is the Tunis-Carthage International AirportTunis-Carthage International Airport
Tunis–Carthage Airport is the international airport serving Tunis in Tunisia.The airport is named for the historic city of Carthage, located just north of the airport. It is the base of operations for four airlines: Tunisair, Nouvelair Tunisia, Tunisair Express and Tunisavia...
but other significant airports serve Sfax, Houmt Souk
Houmt Souk
Houmt Souk , meaning literally: "The Market neighborhood", is a commune and the main town of the island of Djerba, Tunisia. A popular tourist destination, it is best-known for its traditional souk and the Aghlabid fortress....
, Monastir
Monastir, Tunisia
-Areas within Monastir:Monastir's north-eastern territories lead into a place called Route de la Falaise, through which you will reach its most notable suburb, Skanes, which is 6 miles from Monastir's town centre...
, Tozeur
Tozeur
Tozeur is an oasis and a city in south west Tunisia. The city is located North West of Chott el-Djerid, in between this Chott and the smaller Chott el-Gharsa. It is the capital of the Tozeur Governorate....
and Tabarka
Tabarka
Tabarka is a coastal town located in north-western Tunisia, at about , close to the border with Algeria. It has been famous for its coral fishing, the Coral Festival of underwater photography and the annual jazz festival. Tabarka's history is a colorful mosaic of Phoenician, Roman, Arabic and...
. Tunisair
Tunisair
Société Tunisienne de l'Air, or Tunisair is the flag carrier airline of Tunisia. Formed in 1948, it operates scheduled international services to European, African and Middle Eastern destinations. Its main base is Tunis-Carthage International Airport...
is the national airline.

