
Toxic mold
Encyclopedia
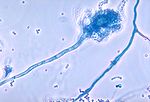
Mold
Molds are fungi that grow in the form of multicellular filaments called hyphae. Molds are not considered to be microbes but microscopic fungi that grow as single cells called yeasts...
s.
Mold
Mold
Molds are fungi that grow in the form of multicellular filaments called hyphae. Molds are not considered to be microbes but microscopic fungi that grow as single cells called yeasts...
s (also spelled "moulds") are ubiquitous in the biosphere, and mold spores are a common component of household and workplace dust. However, when mold spores are present in abnormally high quantities, they can present a health hazard to humans, potentially causing allergic reactions, producing mycotoxins, or causing fungal infection (mycosis
Mycosis
A mycosis is a fungal infection of animals, including humans. Mycoses are common, and a variety of environmental and physiological conditions can contribute to the development of fungal diseases...
).
Mold-associated conditions
Health problems associated with high levels of airborne mold spores include allergic reactions, asthmaAsthma
Asthma is the common chronic inflammatory disease of the airways characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and bronchospasm. Symptoms include wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath...
episodes, irritations of the eye, nose and throat, sinus congestion, and other respiratory problems. For example, residents of homes with mold are at an elevated risk for both respiratory infections and bronchitis. When mold spores are inhaled by an immunocompromise
Immunodeficiency
Immunodeficiency is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious disease is compromised or entirely absent. Immunodeficiency may also decrease cancer immunosurveillance. Most cases of immunodeficiency are acquired but some people are born with defects in their immune system,...
d individual, some mold spores may begin to grow on living tissue, attaching to cells along the respiratory tract
Respiratory tract
In humans the respiratory tract is the part of the anatomy involved with the process of respiration.The respiratory tract is divided into 3 segments:*Upper respiratory tract: nose and nasal passages, paranasal sinuses, and throat or pharynx...
and causing further problems. Generally, when this occurs, the illness is an epiphenomenon
Epiphenomenon
An epiphenomenon is a secondary phenomenon that occurs alongside or in parallel to a primary phenomenon.-Medicine:...
and not the primary pathology. Also, mold may produce mycotoxins, either before or after exposure to humans, potentially causing toxicity.
Fungal infection
A serious health threat from mold exposure for immunocompromised individuals is systemic fungal infection (systemic mycosisMycosis
A mycosis is a fungal infection of animals, including humans. Mycoses are common, and a variety of environmental and physiological conditions can contribute to the development of fungal diseases...
). Immunocompromised individuals exposed to high levels of mold, or individuals with chronic exposure may become infected. Sinuses and digestive tract infections are most common; lung
Human lung
The human lungs are the organs of respiration in humans. Humans have two lungs, with the left being divided into two lobes and the right into three lobes. Together, the lungs contain approximately of airways and 300 to 500 million alveoli, having a total surface area of about in...
and skin
Human skin
The human skin is the outer covering of the body. In humans, it is the largest organ of the integumentary system. The skin has multiple layers of ectodermal tissue and guards the underlying muscles, bones, ligaments and internal organs. Human skin is similar to that of most other mammals,...
infections are also possible. Mycotoxins may or may not be produced by the invading mold.
Dermatophyte
Dermatophyte
Dermatophytes are a common label for a group of three types of fungus that commonly causes skin disease in animals and humans. These anamorphic genera are: Microsporum, Epidermophyton and Trichophyton. There are about 40 species in these three genera...
s are the parasitic fungi that cause skin infections such as athlete's foot
Athlete's foot
Athlete's foot is a fungal infection of the skin that causes scaling, flaking, and itch of affected areas. It is caused by fungi in the genus Trichophyton and is typically transmitted in moist areas where people walk barefoot, such as showers or bathhouses...
and tinea cruris. Most dermataphyte fungi take the form of a mold, as opposed to a yeast, with appearance (when cultured) that is similar to other molds.
Opportunistic infection
Opportunistic infection
An opportunistic infection is an infection caused by pathogens, particularly opportunistic pathogens—those that take advantage of certain situations—such as bacterial, viral, fungal or protozoan infections that usually do not cause disease in a healthy host, one with a healthy immune system...
by molds such as Penicillium marneffei
Penicillium marneffei
Penicillium species are usually regarded as unimportant in terms of causing human disease. Penicillium marneffei, discovered in 1956, is different...
and Aspergillus fumigatus
Aspergillus fumigatus
Aspergillus fumigatus is a fungus of the genus Aspergillus, and is one of the most common Aspergillus species to cause disease in individuals with an immunodeficiency....
is a common cause of illness and death among immunocompromise
Immunodeficiency
Immunodeficiency is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious disease is compromised or entirely absent. Immunodeficiency may also decrease cancer immunosurveillance. Most cases of immunodeficiency are acquired but some people are born with defects in their immune system,...
d people, including people with HIV
HIV
Human immunodeficiency virus is a lentivirus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome , a condition in humans in which progressive failure of the immune system allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive...
, AIDS
AIDS
Acquired immune deficiency syndrome or acquired immunodeficiency syndrome is a disease of the human immune system caused by the human immunodeficiency virus...
, and asthma
Asthma
Asthma is the common chronic inflammatory disease of the airways characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and bronchospasm. Symptoms include wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath...
to name a few.
Mold-induced hypersensitivity
The most common form of hypersensitivityHypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity refers to undesirable reactions produced by the normal immune system, including allergies and autoimmunity. These reactions may be damaging, uncomfortable, or occasionally fatal. Hypersensitivity reactions require a pre-sensitized state of the host. The four-group classification...
is caused by the direct exposure to inhaled mold spores that can be dead or alive or hypha
Hypha
A hypha is a long, branching filamentous structure of a fungus, and also of unrelated Actinobacteria. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium; yeasts are unicellular fungi that do not grow as hyphae.-Structure:A hypha consists of one or...
l fragments which can lead to allergic asthma or allergic rhinitis
Allergic rhinitis
Allergic rhinitis, also known as pollenosis or hay fever, is an allergic inflammation of the nasal airways.It occurs when an allergen, such as pollen, dust or animal dander is inhaled by an individual with a sensitized immune system...
. The most common effects are rhinorrhea
Rhinorrhea
Rhinorrhea or rhinorrhoea is a condition where the nasal cavity is filled with a significant amount of mucous fluid. The condition, commonly known as "runny nose", occurs relatively frequently and is not usually considered dangerous. Rhinorrhea is a common symptom of allergies or certain diseases,...
(runny nose), watery eyes, coughing and asthma attacks
Asthma
Asthma is the common chronic inflammatory disease of the airways characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and bronchospasm. Symptoms include wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath...
. Another form of hypersensitivity is hypersensitivity pneumonitis
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis is an inflammation of the alveoli within the lung caused by hypersensitivity to inhaled organic dusts. Sufferers are commonly exposed to the dust by their occupation or hobbies.-Pathophysiology:Hypersensitivity pneumonitis involves inhalation of an antigen...
. Exposure can occur at home, at work or in other settings. It is predicted that about 5% of people have some airway symptoms due to allergic reactions to molds in their lifetimes.
Hypersensitivity may also be a reaction toward an established fungal infection in allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
In medicine, allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis is a condition characterised by an exaggerated response of the immune system to the fungus Aspergillus . It occurs most often in patients with asthma or cystic fibrosis...
.
Mycotoxin toxicity
Molds excrete toxic compounds called mycotoxinMycotoxin
A mycotoxin is a toxic secondary metabolite produced by organisms of the fungus kingdom, commonly known as molds. The term ‘mycotoxin’ is usually reserved for the toxic chemical products produced by fungi that readily colonize crops...
s, secondary metabolites produced by fungi under certain environmental conditions. These environmental conditions affect the production of mycotoxins at the transcription level. Temperature, water activity and pH, strongly influence mycotoxin biosynthesis by increasing the level of transcription within the fungal spore. It has also been found that low levels of fungicides can boost mycotoxin synthesis. Certain mycotoxins can be harmful or lethal to humans and animals when exposure is high enough.
Extreme exposure to very high levels of mycotoxins can lead to neurological problems and in some cases death; fortunately, such exposures rarely to never occur in normal exposure scenarios, even in residences with serious mold problems. Prolonged exposure, e.g. daily workplace exposure, can be particularly harmful.
However, not all mycotoxins are harmful, and some are even beneficial to humans, e.g. penicillin
Penicillin
Penicillin is a group of antibiotics derived from Penicillium fungi. They include penicillin G, procaine penicillin, benzathine penicillin, and penicillin V....
.
The health hazards produced by mold have been associated with sick building syndrome
Sick building syndrome
Sick building syndrome is a combination of ailments associated with an individual's place of work or residence. A 1984 World Health Organization report into the syndrome suggested up to 30% of new and remodeled buildings worldwide may be linked to symptoms of SBS...
, but no validated studies have been able to demonstrate that normal indoor exposures to these common organisms pose a significant threat.
It is thought that all molds may produce mycotoxins and thus all molds may be potentially toxic if large enough quantities are ingested, or the human becomes exposed to extreme quantities of mold. Mycotoxins are not produced all the time, but only under specific growing conditions. Mycotoxins are harmful or lethal to humans and animals only when exposure is high enough.
Mycotoxins can be found on the mold spore and mold fragments, and therefore they can also be found on the substrate upon which the mold grows. Routes of entry for these insults can include ingestion, dermal exposure and inhalation.
Some mycotoxins cause immune system responses that vary considerably, depending on the individual. The duration of exposure, the frequency of exposure and the concentration of the insult (exposure) are elements in triggering immune system response.
Aflatoxin
Aflatoxin
Aflatoxins are naturally occurring mycotoxins that are produced by many species of Aspergillus, a fungus, the most notable ones being Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus. Aflatoxins are toxic and among the most carcinogenic substances known...
is an example of a mycotoxin. It is a cancer-causing poison produced by certain fungi in or on foods and feeds, especially in field corn and peanuts.
Originally, toxic effects
Toxicity
Toxicity is the degree to which a substance can damage a living or non-living organisms. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a substructure of the organism, such as a cell or an organ , such as the liver...
from mold were thought to be the result of exposure to the mycotoxin
Mycotoxin
A mycotoxin is a toxic secondary metabolite produced by organisms of the fungus kingdom, commonly known as molds. The term ‘mycotoxin’ is usually reserved for the toxic chemical products produced by fungi that readily colonize crops...
s of some mold species, such as Stachybotrys chartarum
Stachybotrys chartarum
Stachybotrys chartarum, also called Stachybotrys atra, Stachybotrys alternans or Stilbospora chartarum, is a black mold that produces its conidia in slime heads. It is sometimes found in soil and grain, but mostly isolated from cellulose-rich building materials in damp or water-damaged buildings. S...
. However, studies are suggesting that the so-called toxic effects are actually the result of chronic activation of the immune system, leading to chronic inflammation. Studies indicate that up to 25% of the population have the genetic capability of experiencing chronic inflammation to mold exposure, but only 2% actually experience such symptoms. A 1993–94 case study
Case study
A case study is an intensive analysis of an individual unit stressing developmental factors in relation to context. The case study is common in social sciences and life sciences. Case studies may be descriptive or explanatory. The latter type is used to explore causation in order to find...
based on cases of pulmonary hemorrhage
Pulmonary hemorrhage
Pulmonary hemorrhage is an acute bleeding from the lung, especially in the upper respiratory tract and the endotracheal tube. When evident clinically, the condition is usually massive, associated with bleeding in other sites as well as more than one third of the lungs...
in infants in Cleveland
Cleveland, Ohio
Cleveland is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and is the county seat of Cuyahoga County, the most populous county in the state. The city is located in northeastern Ohio on the southern shore of Lake Erie, approximately west of the Pennsylvania border...
, Ohio
Ohio
Ohio is a Midwestern state in the United States. The 34th largest state by area in the U.S.,it is the 7th‑most populous with over 11.5 million residents, containing several major American cities and seven metropolitan areas with populations of 500,000 or more.The state's capital is Columbus...
originally concluded there was causal relationship
Causality
Causality is the relationship between an event and a second event , where the second event is understood as a consequence of the first....
between the exposure and the disease. The investigators revisited the cases and established that there was no link to the exposure to S. chartrum and the infants in their homes.
Exposure sources and prevention
The main sources of mold exposure are from the indoor air in buildings with substantial mold growth, and from ingestion of food with mold growths.Air
Prevention of mold exposure and ensuing health issues include prevention of mold growth in the first place by avoiding a mold-supporting environment such as humid air. Extensive flooding and water damage can support huge numbers of mold growth. Following hurricanes, homes with greater flood damage, especially those with more than 3 feet of indoor flooding, demonstrated higher levels of mold growth compared with homes with little or no flooding. The aftermath of a hurricane is the worst case scenario, but the concept of water damage supporting widespread mold growth.It is useful to perform an assessment of the location and extent of the mold hazard in a structure. Various practices of remediation can be followed to mitigate mold issues in buildings, the most important of which is to reduce moisture levels. Removal of affected materials after the source of moisture has been reduced and/or eliminated may be necessary. Thus, the concept of mold growth, assessment, and remediation
Mold growth, assessment, and remediation
Mold assessment and mold remediation are techniques used in occupational health: mold assessment is the process of identifying the location and extent of the mold hazard in a structure, and mold remediation is the process of removal and/or cleanup of mold from an indoor environment.-Health...
is essential in prevention of mold health issues.
A common issue with mold hazards in the household is the placement of furniture, and the lack of ventilation which this provides certain parts of the wall. The simplest method of avoiding mold in the home is to move the furniture in question.
Adverse respiratory health effects are associated with occupancy in buildings with moisture and mold damage. Asthma can be aggravated or even induced with exposure to certain fungal species and some fungi cause skin infections such as athletes foot or ring worm.
Molds may excrete liquids or low-volatility gases, but the concentrations are so low that frequently they cannot be detected even with sensitive analytical sampling techniques. Sometimes these by-products are detectable by odor, in which case they are referred to as "ergonomic odors" meaning the odors are detectable, but do not indicate toxicologically significant exposures.
Food
Molds that are most often found on meat and poultry are AlternariaAlternaria
Alternaria is a genus of ascomycete fungi. Alternaria species are known as major plant pathogens. They are also common allergens in humans, growing indoors and causing hay fever or hypersensitivity reactions that sometimes lead to asthma...
, Aspergillus
Aspergillus
Aspergillus is a genus consisting of several hundred mold species found in various climates worldwide. Aspergillus was first catalogued in 1729 by the Italian priest and biologist Pier Antonio Micheli...
, Botrytis
Botrytis
Botrytis may refer to:*Botrytis, the anamorphs of fungi of the genus Botryotinia**Botrytis cinerea, a mold important in wine making*Botrytis, the cauliflower cultivar group of Brassica oleracea...
, Cladosporium
Cladosporium
Cladosporium is a genus of fungi including some of the most common indoor and outdoor molds. Species produce olive-green to brown or black colonies, and have dark-pigmented conidia that are formed in simple or branching chains....
, Fusarium
Fusarium
Fusarium is a large genus of filamentous fungi widely distributed in soil and in association with plants. Most species are harmless saprobes, and are relatively abundant members of the soil microbial community. Some species produce mycotoxins in cereal crops that can affect human and animal health...
, Geotrichum
Geotrichum
Geotrichum is a genus of fungi found worldwide in soil, water, air, and sewage, as well as in plants, cereals, and dairy products; it is also commonly found in normal human flora and is isolated from sputum and feces....
, Monilia, Manoscus, Mortierella
Mortierella
Mortierella is a genus of fungi in the Mortierellaceae family of the Zygomycota. The widespread genus contains about 85 species.-Reproduction:...
, Mucor
Mucor
Mucor is a microbial genus of about 3000 species of moulds commonly found in soil, digestive systems, plant surfaces, and rotten vegetable matter.-Description:...
, Neurospora
Neurospora
Neurospora is a genus of Ascomycete fungi. The genus name, meaning "nerve spore" refers to the characteristic striations on the spores that resemble axons....
, Oidium
Oidium
This article is about a type of fungal spore. For the ascomycete genus, see Oidium . For the fungus that causes powdery mildew on grapes, see Uncinula necator....
, Oosproa, Penicillium
Penicillium
Penicillium is a genus of ascomycetous fungi of major importance in the natural environment as well as food and drug production. Members of the genus produce penicillin, a molecule that is used as an antibiotic, which kills or stops the growth of certain kinds of bacteria inside the body...
, Rhizopus
Rhizopus
Rhizopus is a genus of common saprobic fungi on plants and specialized parasites on animals. They are found on a wide variety of organic substrates, including "mature fruits and vegetables", faeces, jellies, syrups, leather, bread, peanuts and tobacco. Some Rhizopus species are opportunistic agents...
and Thamnidium.
Roughly 25% of the worlds food is contaminated by mycotoxins according to the World Health Organization. Grains incur considerable losses both in field and storage due to pathogens and insects. Some of the pathogens and resultant mycotoxins reduce the nutritional quality of the product. Mycotoxins are toxigenic fungal compounds that can cause cancer and suppress growth.
Mycotoxins contaminate grains and other food products across the globe and can significantly impact human health. They can be found growing on grains before harvest and in storage. When ingested, inhaled, or absorbed through skin, mycotoxins may reduce appetite and general performance, and cause sickness or death in some cases.
Mold growing in or on field corn and peanuts are the ones most likely to produce aflatoxin
Aflatoxin
Aflatoxins are naturally occurring mycotoxins that are produced by many species of Aspergillus, a fungus, the most notable ones being Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus. Aflatoxins are toxic and among the most carcinogenic substances known...
.
Prevention of mold exposure from food is generally to not buy or to discard food that has mold growths on it. Also, mold growth in the first place can be prevented by the same concept of mold growth, assessment, and remediation
Mold growth, assessment, and remediation
Mold assessment and mold remediation are techniques used in occupational health: mold assessment is the process of identifying the location and extent of the mold hazard in a structure, and mold remediation is the process of removal and/or cleanup of mold from an indoor environment.-Health...
that prevents air exposure. In addition, it is especially useful to clean the inside of the refrigerator, and having clean dishcloths, towels, sponges and mops.
Ruminants are considered to be resistant to the toxic effects of mycotoxins, presumably due to their superior mycotoxin-degrading microbes. This suggests that since mycotoxins are difficult to digest by human microbes due to better degradation by rumen microbes as compared to mono-gastric animals like humans. The carryover of toxins in animal food may have severe consequences on human health.
History
In the 1930s, mold was identified as the cause behind the mysterious deaths of farm animals in Russia and other countries. Stachybotrys chartarumStachybotrys chartarum
Stachybotrys chartarum, also called Stachybotrys atra, Stachybotrys alternans or Stilbospora chartarum, is a black mold that produces its conidia in slime heads. It is sometimes found in soil and grain, but mostly isolated from cellulose-rich building materials in damp or water-damaged buildings. S...
was found growing on wet grain used for animal feed. The illnesses and deaths also occurred in humans when starving peasants ate large quantities of rotten food grains and cereals that were heavily overgrown with the Stachybotrys mold.
In the 1970s, building construction
Construction
In the fields of architecture and civil engineering, construction is a process that consists of the building or assembling of infrastructure. Far from being a single activity, large scale construction is a feat of human multitasking...
techniques changed in response to the changing economic realities including the energy crisis
Energy crisis
An energy crisis is any great bottleneck in the supply of energy resources to an economy. In popular literature though, it often refers to one of the energy sources used at a certain time and place, particularly those that supply national electricity grids or serve as fuel for vehicles...
. As a result, homes and buildings became more airtight. Also, cheaper materials such as drywall
Drywall
Drywall, also known as plasterboard, wallboard or gypsum board is a panel made of gypsum plaster pressed between two thick sheets of paper...
came into common use. The newer building materials reduced the drying potential of the structures making moisture problems more prevalent. This combination of increased moisture and suitable substrates contributed to increased mold growth inside buildings.
Today, the US Food and Drug Administration and the agriculture industry closely monitor mold and mycotoxin levels in grains and foodstuffs in order to keep the contamination of animal feed and human food supplies below specific levels. In 2005 Diamond Pet Foods
Diamond Pet Foods
Diamond Pet Foods, Inc. is the name under which Schell and Kampeter, Inc. does business as a U.S.-based commercial pet food manufacturer with plants located in Meta, Missouri, Lathrop, California and Gaston, South Carolina...
, a US pet food manufacturer, experienced a significant rise in the number of corn shipments containing elevated levels of aflatoxin
Aflatoxin
Aflatoxins are naturally occurring mycotoxins that are produced by many species of Aspergillus, a fungus, the most notable ones being Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus. Aflatoxins are toxic and among the most carcinogenic substances known...
. This mold toxin eventually made it into the pet food supply, and dozens of dogs and cats died before the company was forced to recall affected products.
See also
- Building biologyBuilding biologyBuilding biology is a field of building science that investigates the indoor living environment for a variety of irritants. Practitioners consider the built environment as something with which the occupants interact, and believe its functioning can produce a restful or stressful environment...
- Environmental healthEnvironmental healthEnvironmental health is the branch of public health that is concerned with all aspects of the natural and built environment that may affect human health...
- Occupational asthmaOccupational asthmaOccupational asthma is an occupational condition defined as: "a disease characterized by variable airflow limitation and/or airway hyper-responsiveness due to causes and conditions attributable to a particular occupational environment and not stimuli encountered outside the workplace".Asthma is...
- Environmental engineeringEnvironmental engineeringEnvironmental engineering is the application of science and engineering principles to improve the natural environment , to provide healthy water, air, and land for human habitation and for other organisms, and to remediate polluted sites...
- Ventilation issues in houses
- Occupational safety and healthOccupational safety and healthOccupational safety and health is a cross-disciplinary area concerned with protecting the safety, health and welfare of people engaged in work or employment. The goal of all occupational safety and health programs is to foster a safe work environment...
External links
- NIH: Environmental Health Perspectives Volume 108, Number 1, January 2000 : Mycotoxins: of Molds and Maladies
- MSI Mold and Spore Information: Toxic Mold Symptoms
- CDC: http://www.cdc.gov/mold/default.htm
- US EPA: Mold Information - U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
- US EPA: EPA Publication #402-K-02-003 "A Brief Guide to Mold, Moisture, and Your Home"
- NIBS: Whole Building Design Guide: Air Decontamination
- NPIC: Mold Pest Control Information - National Pesticide Information Center
- Mycotoxins in grains and the food supply:
- http://www.indianacrop.org/Mycotoxin.htm
- http://cropwatch.unl.edu/aflatoxin.html
- http://agbiopubs.sdstate.edu/articles/FS907.pdf

