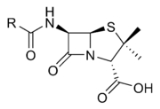
Penicillin
Overview
Penicillin is a group of antibiotic
s derived from Penicillium
fungi. They include penicillin G
, procaine penicillin
, benzathine penicillin
, and penicillin V
.
Penicillin antibiotics are historically significant because they are the first drugs that were effective against many previously serious diseases, such as syphilis
, and infections caused by staphylococci
and streptococci
. Penicillins are still widely used today, though many types of bacteria
are now resistant
. All penicillins are β-lactam antibiotic
s and are used in the treatment of bacteria
l infection
s caused by susceptible, usually Gram-positive
, organisms.
The term "penicillin" is often used generically to refer to benzylpenicillin
(penicillin G), procaine benzylpenicillin
(procaine penicillin), benzathine benzylpenicillin
(benzathine penicillin), and phenoxymethylpenicillin
(penicillin V).
Procaine penicillin and benzathine penicillin have the same antibacterial activity as benzylpenicillin but act for a longer period.
Antibiotic
An antibacterial is a compound or substance that kills or slows down the growth of bacteria.The term is often used synonymously with the term antibiotic; today, however, with increased knowledge of the causative agents of various infectious diseases, antibiotic has come to denote a broader range of...
s derived from Penicillium
Penicillium
Penicillium is a genus of ascomycetous fungi of major importance in the natural environment as well as food and drug production. Members of the genus produce penicillin, a molecule that is used as an antibiotic, which kills or stops the growth of certain kinds of bacteria inside the body...
fungi. They include penicillin G
Benzylpenicillin
Benzylpenicillin, commonly known as penicillin G, is the gold standard type of penicillin. 'G' in the name 'Penicillin G' refers to 'Gold Standard'. Penicillin G is typically given by a parenteral route of administration because it is unstable in the hydrochloric acid of the stomach...
, procaine penicillin
Procaine benzylpenicillin
Procaine benzylpenicillin , also known as procaine penicillin, is a form of penicillin which is a combination of benzylpenicillin and the local anaesthetic agent procaine...
, benzathine penicillin
Benzathine benzylpenicillin
Benzathine benzylpenicillin is a form of penicillin also known as benzathine penicillin. It is slowly absorbed into the circulation, after intramuscular injection, and hydrolysed to benzylpenicillin in vivo...
, and penicillin V
Phenoxymethylpenicillin
Phenoxymethylpenicillin, commonly known as penicillin V, is a penicillin antibiotic that is orally active. It is less active than benzylpenicillin against Gram-negative bacteria. Phenoxymethylpenicillin is more acid-stable than benzylpenicillin, which allows it to be given orally...
.
Penicillin antibiotics are historically significant because they are the first drugs that were effective against many previously serious diseases, such as syphilis
Syphilis
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the spirochete bacterium Treponema pallidum subspecies pallidum. The primary route of transmission is through sexual contact; however, it may also be transmitted from mother to fetus during pregnancy or at birth, resulting in congenital syphilis...
, and infections caused by staphylococci
Staphylococcus
Staphylococcus is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria. Under the microscope they appear round , and form in grape-like clusters....
and streptococci
Streptococcus
Streptococcus is a genus of spherical Gram-positive bacteria belonging to the phylum Firmicutes and the lactic acid bacteria group. Cellular division occurs along a single axis in these bacteria, and thus they grow in chains or pairs, hence the name — from Greek στρεπτος streptos, meaning...
. Penicillins are still widely used today, though many types of bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
are now resistant
Antibiotic resistance
Antibiotic resistance is a type of drug resistance where a microorganism is able to survive exposure to an antibiotic. While a spontaneous or induced genetic mutation in bacteria may confer resistance to antimicrobial drugs, genes that confer resistance can be transferred between bacteria in a...
. All penicillins are β-lactam antibiotic
Beta-lactam antibiotic
β-Lactam antibiotics are a broad class of antibiotics, consisting of all antibiotic agents that contains a β-lactam nucleus in its molecular structure. This includes penicillin derivatives , cephalosporins , monobactams, and carbapenems...
s and are used in the treatment of bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
l infection
Infection
An infection is the colonization of a host organism by parasite species. Infecting parasites seek to use the host's resources to reproduce, often resulting in disease...
s caused by susceptible, usually Gram-positive
Gram-positive
Gram-positive bacteria are those that are stained dark blue or violet by Gram staining. This is in contrast to Gram-negative bacteria, which cannot retain the crystal violet stain, instead taking up the counterstain and appearing red or pink...
, organisms.
The term "penicillin" is often used generically to refer to benzylpenicillin
Benzylpenicillin
Benzylpenicillin, commonly known as penicillin G, is the gold standard type of penicillin. 'G' in the name 'Penicillin G' refers to 'Gold Standard'. Penicillin G is typically given by a parenteral route of administration because it is unstable in the hydrochloric acid of the stomach...
(penicillin G), procaine benzylpenicillin
Procaine benzylpenicillin
Procaine benzylpenicillin , also known as procaine penicillin, is a form of penicillin which is a combination of benzylpenicillin and the local anaesthetic agent procaine...
(procaine penicillin), benzathine benzylpenicillin
Benzathine benzylpenicillin
Benzathine benzylpenicillin is a form of penicillin also known as benzathine penicillin. It is slowly absorbed into the circulation, after intramuscular injection, and hydrolysed to benzylpenicillin in vivo...
(benzathine penicillin), and phenoxymethylpenicillin
Phenoxymethylpenicillin
Phenoxymethylpenicillin, commonly known as penicillin V, is a penicillin antibiotic that is orally active. It is less active than benzylpenicillin against Gram-negative bacteria. Phenoxymethylpenicillin is more acid-stable than benzylpenicillin, which allows it to be given orally...
(penicillin V).
Procaine penicillin and benzathine penicillin have the same antibacterial activity as benzylpenicillin but act for a longer period.
Unanswered Questions

