
Terpinene
Encyclopedia
| Terpinenes | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical structure Chemical structure A chemical structure includes molecular geometry, electronic structure and crystal structure of molecules. Molecular geometry refers to the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule and the chemical bonds that hold the atoms together. Molecular geometry can range from the very simple, such as... s |
 |
 |
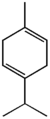 |
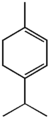
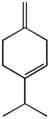
| α-Terpinene | β-Terpinene | γ-Terpinene | |
| Chemical name IUPAC nomenclature A chemical nomenclature is a set of rules to generate systematic names for chemical compounds. The nomenclature used most frequently worldwide is the one created and developed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry .... s |
α: 4-methyl-1-(1-methylethyl)-1,3-cyclohexadiene β: 4-methylene-1-(1-methylethyl)cyclohexene γ: 4-methyl-1-(1-methylethyl)-1,4-cyclohexadiene |
||
| Chemical formula Chemical formula A chemical formula or molecular formula is a way of expressing information about the atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound.... |
C10H16 | ||
| Molecular mass Molecular mass The molecular mass of a substance is the mass of one molecule of that substance, in unified atomic mass unit u... |
136.24 g/mol | ||
| CAS numbers CAS registry number CAS Registry Numbersare unique numerical identifiers assigned by the "Chemical Abstracts Service" toevery chemical described in the... |
α: [99-86-5] β: [99-84-3] γ: [99-85-4] |
||
| Densities Density The mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight... |
α: 0.8375 g/cm3 β: 0.838 g/cm3 γ: 0.853 g/cm3 |
||
| Melting point Melting point The melting point of a solid is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase exist in equilibrium. The melting point of a substance depends on pressure and is usually specified at standard atmospheric pressure... |
α: 60-61°C | ||
| Boiling point Boiling point The boiling point of an element or a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the environmental pressure surrounding the liquid.... s |
α: 173.5-174.8 °C β: 173-174 °C γ: 183 °C |
||
| SMILES Simplified molecular input line entry specification The simplified molecular-input line-entry specification or SMILES is a specification in form of a line notation for describing the structure of chemical molecules using short ASCII strings... |
α: CC1=CC=C(C(C)C)CC1 β: C=C1CC=C(C(C)C)CC1 γ: CC1=CCC(C(C)C)=CC1 |
||
| Disclaimer and references | |||
The terpinenes are three isomer
Isomer
In chemistry, isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. Isomers do not necessarily share similar properties, unless they also have the same functional groups. There are many different classes of isomers, like stereoisomers, enantiomers, geometrical...
ic hydrocarbons that are classified as terpene
Terpene
Terpenes are a large and diverse class of organic compounds, produced by a variety of plants, particularly conifers, though also by some insects such as termites or swallowtail butterflies, which emit terpenes from their osmeterium. They are often strong smelling and thus may have had a protective...
s. They each have the same molecular formula and carbon framework, but they differ in the position of carbon-carbon double bonds. α-Terpinene has been isolated from cardamom
Cardamom
Cardamom refers to several plants of the genera Elettaria and Amomum in the ginger family Zingiberaceae. Both genera are native to India and Bhutan; they are recognised by their small seed pod, triangular in cross-section and spindle-shaped, with a thin papery outer shell and small black seeds...
and marjoram
Marjoram
Marjoram is a somewhat cold-sensitive perennial herb or undershrub with sweet pine and citrus flavours...
oils, and from other natural sources. β-Terpinene has no known natural source, but has been prepared synthetically from sabinene
Sabinene
Sabinene is a natural bicyclic monoterpene with the molecular formula C10H16. It is isolated from the essential oils of a variety of plants including holm oak and Norway spruce...
. γ-Terpinene is natural and has been isolated from a variety of plant sources.
Biosynthesis of α-Terpinene
α-Terpinene is considered a monoterpene, a class of terpenoids that are C-10 precursors. The biosynthesis of α-terpinene and other terpenoids occurs via the Mevalonate Pathway because it’s starting reactant, dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (abbreviated DMAPP), is derived from mevalonic acid. Though α-terpinene is commonly considered a perfume and flavoring chemical and therefore used in the cosmetics and food industries, its use both in the pharmaceutical and electronics semi-conductor manufacturing industries have also proven to be valuable.GPP (geranyl diphosphate) is produced from the reaction of a resonance-stable allylic cation, formed from the loss of the diphosphate group from DMAPP, and IPP (isopentyl diphosphate), and a subsequent the loss of a proton. GPP then loses the diphosphate group to form the resonance-stable geranyl cation. The reintroduction of the diphosphate group to the cation produces GPP isomer, known as LPP (Linalyl PP). LPP then forms a resonance-stable cation by losing its diphosphate group. Cyclization is then completed thanks to this more favorable stereochemisty of the LPP cation, now yielding the menthyl/α-terpinyl cation. Finally, a 1,2-hydride shift via a Wagner-Meerwein rearrangement produces the terpinen-4-yl cation. It is the loss of a hydrogen from this cation that generates α-Terpinene.
List of the plants that contain one of the chemicals
- Cuminum cyminum
- Melaleuca alternifoliaMelaleuca alternifoliaMelaleuca alternifolia, commonly known as Narrow-leaved Paperbark, Narrow-leaved Tea-tree, Narrow-leaved Ti-tree, or Snow-in-summer, is a species of tree or tall shrub in the plant genus Melaleuca. Native to Australia, it occurs on the north coast and adjacent ranges of New South Wales...

