
Swing (Java)
Encyclopedia
Java (programming language)
Java is a programming language originally developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems and released in 1995 as a core component of Sun Microsystems' Java platform. The language derives much of its syntax from C and C++ but has a simpler object model and fewer low-level facilities...
GUI
Gui
Gui or guee is a generic term to refer to grilled dishes in Korean cuisine. These most commonly have meat or fish as their primary ingredient, but may in some cases also comprise grilled vegetables or other vegetarian ingredients. The term derives from the verb, "gupda" in Korean, which literally...
widget toolkit
Widget toolkit
In computing, a widget toolkit, widget library, or GUI toolkit is a set of widgets for use in designing applications with graphical user interfaces...
. It is part of Oracle
Oracle Corporation
Oracle Corporation is an American multinational computer technology corporation that specializes in developing and marketing hardware systems and enterprise software products – particularly database management systems...
's Java Foundation Classes
Java Foundation Classes
The Java Foundation Classes are a graphical framework for building portable Java-based graphical user interfaces . JFC consists of the Abstract Window Toolkit , Swing and Java 2D. Together, they provide a consistent user interface for Java programs, regardless whether the underlying user interface...
(JFC) — an API
Application programming interface
An application programming interface is a source code based specification intended to be used as an interface by software components to communicate with each other...
for providing a graphical user interface
Graphical user interface
In computing, a graphical user interface is a type of user interface that allows users to interact with electronic devices with images rather than text commands. GUIs can be used in computers, hand-held devices such as MP3 players, portable media players or gaming devices, household appliances and...
(GUI) for Java programs.
Swing was developed to provide a more sophisticated set of GUI components than the earlier Abstract Window Toolkit
Abstract Window Toolkit
The Abstract Window Toolkit is Java's original platform-independent windowing, graphics, and user-interface widget toolkit. The AWT is now part of the Java Foundation Classes — the standard API for providing a graphical user interface for a Java program.AWT is also the GUI toolkit for a...
. Swing provides a native look and feel
Look and feel
In software design, look and feel is a term used in respect of a graphical user interface and comprises aspects of its design, including elements such as colors, shapes, layout, and typefaces , as well as the behavior of dynamic elements such as buttons, boxes, and menus...
that emulates the look and feel of several platforms, and also supports a pluggable look and feel
Pluggable look and feel
Pluggable look and feel is a mechanism used in the Java Swing widget toolkit allowing to change the look and feel of the graphical user interface at runtime....
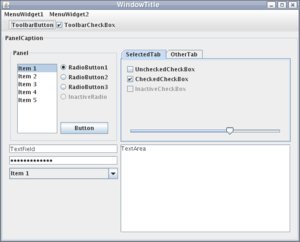
that allows applications to have a look and feel unrelated to the underlying platform. It has more powerful and flexible components than AWT. In addition to familiar components such as buttons, check box and labels, Swing provides several advanced components such as tabbed panel, scroll panes, trees, tables and lists.
Unlike AWT components, Swing components are not implemented by platform-specific code. Instead they are written entirely in Java and therefore are platform-independent. The term "lightweight" is used to describe such an element.
History
The Internet Foundation ClassesInternet Foundation Classes
The Internet Foundation Classes were a graphics library for Java originally developed by Netcode Corporation and first released by Netscape Corporation on December 16, 1996.-History:...
(IFC) were a graphics library
Graphics library
A graphics library is a program library designed to aid in rendering computer graphics to a monitor. This typically involves providing optimized versions of functions that handle common rendering tasks. This can be done purely in software and running on the CPU, common in embedded systems, or being...
for Java originally developed by Netscape Communications Corporation and first released on December 16, 1996. On April 2, 1997, Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems, Inc. was a company that sold :computers, computer components, :computer software, and :information technology services. Sun was founded on February 24, 1982...
and Netscape Communications Corporation announced their intention to incorporate IFC with other technologies to form the Java Foundation Classes
Java Foundation Classes
The Java Foundation Classes are a graphical framework for building portable Java-based graphical user interfaces . JFC consists of the Abstract Window Toolkit , Swing and Java 2D. Together, they provide a consistent user interface for Java programs, regardless whether the underlying user interface...
. The "Java Foundation Classes" were later renamed "Swing".
Swing introduced a mechanism that allowed the look and feel
Look and feel
In software design, look and feel is a term used in respect of a graphical user interface and comprises aspects of its design, including elements such as colors, shapes, layout, and typefaces , as well as the behavior of dynamic elements such as buttons, boxes, and menus...
of every component in an application to be altered without making substantial changes to the application code. The introduction of support for a pluggable look and feel
Pluggable look and feel
Pluggable look and feel is a mechanism used in the Java Swing widget toolkit allowing to change the look and feel of the graphical user interface at runtime....
allows Swing components to emulate the appearance of native components while still retaining the benefits of platform independence.
Originally distributed as a separately downloadable library, Swing has been included as part of the Java Standard Edition
Java Platform, Standard Edition
Java Platform, Standard Edition or Java SE is a widely used platform for programming in the Java language. It is the Java Platform used to deploy portable applications for general use...
since release 1.2. The Swing classes and components are contained in the package
Java package
A Java package is a mechanism for organizing Java classes into namespaces similar to the modules of Modula. Java packages can be stored in compressed files called JAR files, allowing classes to download faster as a group rather than one at a time...
hierarchy.
The Swing Architecture
Swing is a platform-independent, Model-View-ControllerModel-view-controller
Model–view–controller is a software architecture, currently considered an architectural pattern used in software engineering. The pattern isolates "domain logic" from the user interface , permitting independent development, testing and maintenance of each .Model View Controller...
GUI
Gui
Gui or guee is a generic term to refer to grilled dishes in Korean cuisine. These most commonly have meat or fish as their primary ingredient, but may in some cases also comprise grilled vegetables or other vegetarian ingredients. The term derives from the verb, "gupda" in Korean, which literally...
framework for Java. It follows a single-threaded programming model, and possesses the following traits:
Foundations
Swing is platform independent both in terms of expression (Java) and implementation (Look-and-Feel).Extensible
Swing is a highly partitioned architecture, which allows for the "plugging" of various custom implementations of specified framework interfaces: Users can provide their own custom implementation(s) of these components to override the default implementations. In general, Swing users can extend the framework by extending existing (framework) classes and/or providing alternative implementations of core components.Swing is a component-based framework. The distinction and components is a fairly subtle point: concisely, a component is a well-behaved object with a known/specified characteristic pattern of behaviour. Swing objects asynchronously fire events, have "bound" properties, and respond to a well-known set of commands (specific to the component.) Specifically, Swing components are Java Beans components, compliant with the Java Beans Component Architecture specifications.
Swing derived from Applet, Swing is modified version of Applet.
Customizable
Given the programmatic rendering model of the Swing framework, fine control over the details of rendering of a component is possible in Swing. As a general pattern, the visual representation of a Swing component is a composition of a standard set of elements, such as a "border", "inset", decorations, etc. Typically, users will programmatically customize a standard Swing component (such as a JTable) by assigning specific Borders, Colors, Backgrounds, opacities, etc., as the properties of that component. The core component will then use these properties (settings) to determine the appropriate renderers to use in painting its various aspects. However, it is also completely possible to create unique GUI controls with highly customized visual representation.Configurable
Swing's heavy reliance on runtime mechanisms and indirect composition patterns allows it to respond at runtime to fundamental changes in its settings. For example, a Swing-based application can change its look and feel at runtime. Further, users can provide their own look and feel implementation, which allows for uniform changes in the look and feel of existing Swing applications without any programmatic change to the application code.Lightweight UI:
Swing's configurability is a result of a choice not to use the native host OS's GUI controls for displaying itself. Swing "paints" its controls programmatically through the use of Java 2D APIs, rather than calling into a native user interface toolkit. Thus, a Swing component does not have a corresponding native OS GUI component, and is free to render itself in any way that is possible with the underlying graphics APIs.
However, at its core every Swing component relies on an AWT
Abstract Window Toolkit
The Abstract Window Toolkit is Java's original platform-independent windowing, graphics, and user-interface widget toolkit. The AWT is now part of the Java Foundation Classes — the standard API for providing a graphical user interface for a Java program.AWT is also the GUI toolkit for a...
container, since (Swing's) extends (AWT's) Container. This allows Swing to plug into the host OS's GUI management framework, including the crucial device/screen mappings and user interactions, such as key presses or mouse movements. Swing simply "transposes" its own (OS agnostic) semantics over the underlying (OS specific) components. So, for example, every Swing component paints its rendition on the graphic device in response to a call to component.paint, which is defined in (AWT) Container. But unlike AWT components, which delegated the painting to their OS-native "heavyweight" widget, Swing components are responsible for their own rendering.
This transposition and decoupling is not merely visual, and extends to Swing's management and application of its own OS-independent semantics for events fired within its component containment hierarchies. Generally speaking, the Swing Architecture delegates the task of mapping the various flavors of OS GUI semantics onto a simple, but generalized, pattern to the AWT container. Building on that generalized platform, it establishes its own rich and complex GUI semantics in the form of the model.
Loosely-Coupled and MVC
The Swing library makes heavy use of the Model/View/ControllerModel-view-controller
Model–view–controller is a software architecture, currently considered an architectural pattern used in software engineering. The pattern isolates "domain logic" from the user interface , permitting independent development, testing and maintenance of each .Model View Controller...
software design pattern
Design pattern (computer science)
In software engineering, a design pattern is a general reusable solution to a commonly occurring problem within a given context in software design. A design pattern is not a finished design that can be transformed directly into code. It is a description or template for how to solve a problem that...
, which conceptually decouples the data being viewed from the user interface controls through which it is viewed. Because of this, most Swing components have associated models (which are specified in terms of Java interfaces
Interface (computer science)
In the field of computer science, an interface is a tool and concept that refers to a point of interaction between components, and is applicable at the level of both hardware and software...
), and the programmer can use various default implementations or provide their own. The framework provides default implementations of model interfaces for all of its concrete components. The typical use of the Swing framework does not require the creation of custom models, as the framework provides a set of default implementations that are transparently, by default, associated with the corresponding child class in the Swing library. In general, only complex components, such as tables, trees and sometimes lists, may require the custom model implementations around the application-specific data structures. To get a good sense of the potential that the Swing architecture makes possible, consider the hypothetical situation where custom models for tables and lists are wrappers over DAO
Data Access Object
In computer software, a data access object is an object that provides an abstract interface to some type of database or persistence mechanism, providing some specific operations without exposing details of the database. It provides a mapping from application calls to the persistence layer...
and/or EJB services..
Typically, Swing component model objects are responsible for providing a concise interface defining events fired, and accessible properties for the (conceptual) data model for use by the associated JComponent. Given that the overall MVC pattern is a loosely-coupled collaborative object relationship pattern, the model provides the programmatic means for attaching event listeners to the data model object. Typically, these events are model centric (ex: a "row inserted" event in a table model) and are mapped by the JComponent specialization into a meaningful event for the GUI component.
For example, the has a model called that describes an interface for how a table would access tabular data. A default implementation of this operates on a two-dimensional array.
The view component of a Swing JComponent is the object used to graphically "represent" the conceptual GUI control. A distinction of Swing, as a GUI framework, is in its reliance on programmatically-rendered GUI controls (as opposed to the use of the native host OS's GUI controls). Prior to Java 6 Update 10, this distinction was a source of complications when mixing AWT controls, which use native controls, with Swing controls in a GUI (see Mixing AWT and Swing components).
Finally, in terms of visual composition and management, Swing favors relative layouts
Layout manager
Layout managers are software components used in widget toolkits which have the ability to lay out widgets by their relative positions without using distance units. It is often more natural to define component layouts in this manner than to define their position in pixels or common distance units,...
(which specify the positional relationships between components) as opposed to absolute layouts (which specify the exact location and size of components). This bias towards "fluid"' visual ordering is due to its origins in the applet
Java applet
A Java applet is an applet delivered to users in the form of Java bytecode. Java applets can run in a Web browser using a Java Virtual Machine , or in Sun's AppletViewer, a stand-alone tool for testing applets...
operating environment that framed the design and development of the original Java GUI toolkit. (Conceptually, this view of the layout management is quite similar to that which informs the rendering of HTML content in browsers, and addresses the same set of concerns that motivated the former.)
Relationship to AWT
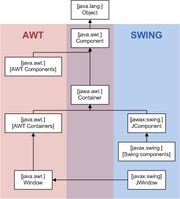
Abstract Window Toolkit
The Abstract Window Toolkit is Java's original platform-independent windowing, graphics, and user-interface widget toolkit. The AWT is now part of the Java Foundation Classes — the standard API for providing a graphical user interface for a Java program.AWT is also the GUI toolkit for a...
(AWT) has provided platform-independent APIs for user interface components. In AWT, each component is rendered and controlled by a native peer component specific to the underlying windowing system.
By contrast, Swing components are often described as lightweight because they do not require allocation of native resources in the operating system's windowing toolkit. The AWT components are referred to as heavyweight components.
Much of the Swing API is generally a complementary extension of the AWT rather than a direct replacement. In fact, every Swing lightweight interface ultimately exists within an AWT heavyweight component because all of the top-level components in Swing extend an AWT top-level container. Prior to Java 6 Update 10, the use of both lightweight and heavyweight components within the same window was generally discouraged due to Z-order
Z-order
Z-order is an ordering of overlapping two-dimensional objects, such as windows in a graphical user interface , shapes in a vector graphics editor, or objects in a 3D application. One of the features of a typical GUI is that windows may overlap, so that one window hides part or all of another...
incompatibilities. However, later versions of Java have fixed these issues, and both Swing and AWT components can now be used in one GUI without Z-order issues.
The core rendering functionality used by Swing to draw its lightweight components is provided by Java 2D
Java 2D
In computing, Java 2D is an API for drawing two-dimensional graphics using the Java programming language. Every Java 2D drawing operation can ultimately be treated as filling a shape using a paint and compositing the result onto the screen....
, another part of JFC.
Relationship to SWT
The Standard Widget ToolkitStandard Widget Toolkit
The Standard Widget Toolkit is a graphical widget toolkit for use with the Java platform. It was originally developed by IBM and is now maintained by the Eclipse Foundation in tandem with the Eclipse IDE...
(SWT) is a competing toolkit originally developed by IBM
IBM
International Business Machines Corporation or IBM is an American multinational technology and consulting corporation headquartered in Armonk, New York, United States. IBM manufactures and sells computer hardware and software, and it offers infrastructure, hosting and consulting services in areas...
and now maintained by the Eclipse
Eclipse (software)
Eclipse is a multi-language software development environment comprising an integrated development environment and an extensible plug-in system...
community
Free software community
The free-software community is an informal term that refers to the users and developers of free software as well as supporters of the free-software movement. The movement is sometimes referred to as the open-source software community or a subset thereof...
. SWT's implementation has more in common with the heavyweight components of AWT. This confers benefits such as more accurate fidelity with the underlying native windowing toolkit, at the cost of an increased exposure to the native platform in the programming model.
The advent of SWT has given rise to a great deal of division among Java desktop developers, with many strongly favoring either SWT
Standard Widget Toolkit
The Standard Widget Toolkit is a graphical widget toolkit for use with the Java platform. It was originally developed by IBM and is now maintained by the Eclipse Foundation in tandem with the Eclipse IDE...
or Swing.
There has been significant debate and speculation about the performance of SWT versus Swing; some hinted that SWT's heavy dependence on JNI
Java Native Interface
The Java Native Interface is a programming framework that enables Java code running in a Java Virtual Machine to call and to be called by native applications and libraries written in other languages such as C, C++ and assembly.-Purpose and features:JNI enables one to write native methods to...
would make it slower when the GUI component and Java need to communicate data, but faster at rendering when the data model has been loaded into the GUI, but this has not been confirmed either way. A fairly thorough set of benchmarks in 2005 concluded that neither Swing nor SWT clearly outperformed the other in the general case.
SWT serves the Windows platform very well but is considered by some to be less effective as a technology for cross-platform development. By using the high-level features of each native windowing toolkit, SWT returns to the issues seen in the mid 1990s (with toolkits like zApp, Zinc, XVT and IBM/Smalltalk) where toolkits attempted to mask differences in focus behaviour, event triggering and graphical layout. Failure to match behavior on each platform can cause subtle but difficult-to-resolve bugs that impact user interaction and the appearance of the GUI.
A basic example
The following is a rather simple Swing-based program. It displays a window (a ) containing a label and a button.Notice how all instantiation and handling of all Swing components are done on the Event Dispatch Thread by use of the method ) and an anonymous Runnable class (see Swing and thread safety).
// Import the swing and AWT classes needed
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.SwingUtilities;
/**
* Basic Swing example.
*/
public class SwingExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Make sure all Swing/AWT instantiations and accesses are done on the
// Event Dispatch Thread (EDT)
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(new Runnable {
public void run {
// Create a JFrame, which is a Window with "decorations", i.e.
// title, border and close-button
JFrame f = new JFrame("Swing Example Window");
// Set a simple Layout Manager that arranges the contained
// Components
f.setLayout(new FlowLayout);
// Add some Components
f.add(new JLabel("Hello, world!"));
f.add(new JButton("Press me!"));
// "Pack" the window, making it "just big enough".
f.pack;
// Set the default close operation for the window, or else the
// program won't exit when clicking close button
// (The default is HIDE_ON_CLOSE, which just makes the window
// invisible, and thus doesn't exit the app)
f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE);
// Set the visibility as true, thereby displaying it
f.setVisible(true);
}
});
}
}
See also
- Abstract Window ToolkitAbstract Window ToolkitThe Abstract Window Toolkit is Java's original platform-independent windowing, graphics, and user-interface widget toolkit. The AWT is now part of the Java Foundation Classes — the standard API for providing a graphical user interface for a Java program.AWT is also the GUI toolkit for a...
- Layout managerLayout managerLayout managers are software components used in widget toolkits which have the ability to lay out widgets by their relative positions without using distance units. It is often more natural to define component layouts in this manner than to define their position in pixels or common distance units,...
- SwingLabsSwingLabsswingLabs is a Sun open source project proposing extensions to the Java Swing GUI toolkit. Available components include:* Sorting, filtering, highlighting for tables, trees, and lists* Find/search* Auto-completion* Login/authentication framework...
- Extensions to Swing that might be included in Swing in the future - Standard Widget ToolkitStandard Widget ToolkitThe Standard Widget Toolkit is a graphical widget toolkit for use with the Java platform. It was originally developed by IBM and is now maintained by the Eclipse Foundation in tandem with the Eclipse IDE...
- A third party widget toolkit maintained by the Eclipse FoundationEclipse FoundationThe Eclipse Foundation is a not-for-profit, member supported corporation that hosts the open-source Eclipse Projects and helps cultivate both an open source community and an ecosystem of complementary products and services...
.

