
Stream power
Encyclopedia
Stream power is the rate of energy dissipation against the bed and banks of a river
or stream per unit downstream length. It is given by the equation:
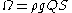
where Ω is the stream power, ρ is the density of water (1000 kg/m3), g is acceleration due to gravity
(9.8 m/s2), Q is discharge
(m3/s), and S is the channel slope
.
It can be derived by the fact that if the water is not accelerating and the river cross-section stays constant (generally good assumptions for an averaged reach of a stream over a modest distance), all of the potential energy
lost as the water flows downstream must be used up in friction or work against the bed: none can be added to kinetic energy
. Therefore, the potential energy drop is equal to the work done to the bed and banks, which is the stream power.
We know that change in potential energy over change in time is given by the equation:
where water mass and gravitational acceleration are constant. We can use the channel slope and the stream velocity as a stand-in for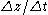 : the water will lose elevation at a rate given by the downward component of velocity
: the water will lose elevation at a rate given by the downward component of velocity 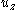 . For an channel slope (as measured from the horizontal) of
. For an channel slope (as measured from the horizontal) of  :
: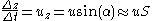
where is the downstream flow velocity. It is noted that for small angles,
is the downstream flow velocity. It is noted that for small angles,  . Rewriting the first equation, we now have:
. Rewriting the first equation, we now have:
Remembering that power is energy per time and using the equivalence between work against the bed and loss in potential energy, we can write: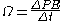
Finally, we know that mass is equal to density times volume. From this, we can rewrite the mass on the right hand side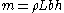
where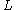 is the channel length,
is the channel length, 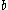 is the channel width (breadth), and
is the channel width (breadth), and 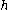 is the channel depth (height). We use the definition of discharge
is the channel depth (height). We use the definition of discharge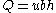
where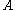 is the cross-sectional area, which can often be reasonably approximated as a rectangle with the characteristic width and depth. This absorbs velocity, width, and depth. We define stream power per unit channel length, so that term goes to 1, and the derivation is complete.
is the cross-sectional area, which can often be reasonably approximated as a rectangle with the characteristic width and depth. This absorbs velocity, width, and depth. We define stream power per unit channel length, so that term goes to 1, and the derivation is complete.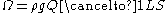
Unit stream power is stream power per unit channel width, and is given by the equation:
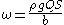
where ω is the unit stream power, and b is the width of the channel.
Stream power is used extensively in models of landscape evolution
and river incision. Unit stream power is often used for this, because simple models use and evolve a 1-dimensional downstream profile of the river channel. It is also used with relation to river channel migration
, and in some cases is applied to sediment transport
.
River
A river is a natural watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, a lake, a sea, or another river. In a few cases, a river simply flows into the ground or dries up completely before reaching another body of water. Small rivers may also be called by several other names, including...
or stream per unit downstream length. It is given by the equation:
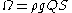
where Ω is the stream power, ρ is the density of water (1000 kg/m3), g is acceleration due to gravity
Gravitational acceleration
In physics, gravitational acceleration is the acceleration on an object caused by gravity. Neglecting friction such as air resistance, all small bodies accelerate in a gravitational field at the same rate relative to the center of mass....
(9.8 m/s2), Q is discharge
Discharge (hydrology)
In hydrology, discharge is the volume rate of water flow, including any suspended solids , dissolved chemical species and/or biologic material , which is transported through a given cross-sectional area...
(m3/s), and S is the channel slope
Slope
In mathematics, the slope or gradient of a line describes its steepness, incline, or grade. A higher slope value indicates a steeper incline....
.
It can be derived by the fact that if the water is not accelerating and the river cross-section stays constant (generally good assumptions for an averaged reach of a stream over a modest distance), all of the potential energy
Potential energy
In physics, potential energy is the energy stored in a body or in a system due to its position in a force field or due to its configuration. The SI unit of measure for energy and work is the Joule...
lost as the water flows downstream must be used up in friction or work against the bed: none can be added to kinetic energy
Kinetic energy
The kinetic energy of an object is the energy which it possesses due to its motion.It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its acceleration, the body maintains this kinetic energy unless its speed changes...
. Therefore, the potential energy drop is equal to the work done to the bed and banks, which is the stream power.
We know that change in potential energy over change in time is given by the equation:

where water mass and gravitational acceleration are constant. We can use the channel slope and the stream velocity as a stand-in for
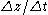 : the water will lose elevation at a rate given by the downward component of velocity
: the water will lose elevation at a rate given by the downward component of velocity 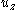 . For an channel slope (as measured from the horizontal) of
. For an channel slope (as measured from the horizontal) of  :
: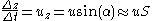
where
 is the downstream flow velocity. It is noted that for small angles,
is the downstream flow velocity. It is noted that for small angles,  . Rewriting the first equation, we now have:
. Rewriting the first equation, we now have:
Remembering that power is energy per time and using the equivalence between work against the bed and loss in potential energy, we can write:
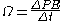
Finally, we know that mass is equal to density times volume. From this, we can rewrite the mass on the right hand side
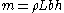
where
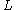 is the channel length,
is the channel length, 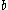 is the channel width (breadth), and
is the channel width (breadth), and 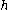 is the channel depth (height). We use the definition of discharge
is the channel depth (height). We use the definition of discharge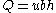
where
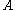 is the cross-sectional area, which can often be reasonably approximated as a rectangle with the characteristic width and depth. This absorbs velocity, width, and depth. We define stream power per unit channel length, so that term goes to 1, and the derivation is complete.
is the cross-sectional area, which can often be reasonably approximated as a rectangle with the characteristic width and depth. This absorbs velocity, width, and depth. We define stream power per unit channel length, so that term goes to 1, and the derivation is complete.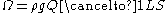
Unit stream power is stream power per unit channel width, and is given by the equation:
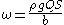
where ω is the unit stream power, and b is the width of the channel.
Stream power is used extensively in models of landscape evolution
Landscape evolution model
A landscape evolution model is a physically based numerical model that simulates changing terrain over the course of time. This can be due to glacial erosion and deposition; erosion, sediment transport, and deposition in fluvial systems such as rivers; regolith production; the movement of material...
and river incision. Unit stream power is often used for this, because simple models use and evolve a 1-dimensional downstream profile of the river channel. It is also used with relation to river channel migration
River channel migration
River channel migration is the lateral motion of an alluvial river channel across its floodplain due to processes of erosion of and deposition on its banks and bars. In meandering streams, channel migration typically takes place by erosion of the cut bank and deposition on the point bar...
, and in some cases is applied to sediment transport
Sediment transport
Sediment transport is the movement of solid particles , typically due to a combination of the force of gravity acting on the sediment, and/or the movement of the fluid in which the sediment is entrained...
.

