
Siroheme
Encyclopedia
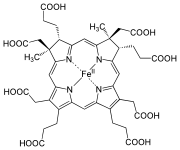
Heme
A heme or haem is a prosthetic group that consists of an iron atom contained in the center of a large heterocyclic organic ring called a porphyrin. Not all porphyrins contain iron, but a substantial fraction of porphyrin-containing metalloproteins have heme as their prosthetic group; these are...
-like prosthetic group
Cofactor (biochemistry)
A cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound that is bound to a protein and is required for the protein's biological activity. These proteins are commonly enzymes, and cofactors can be considered "helper molecules" that assist in biochemical transformations....
used by some enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
s to accomplish the six-electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
reduction
Redox
Redox reactions describe all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed....
of sulfur
Sulfur
Sulfur or sulphur is the chemical element with atomic number 16. In the periodic table it is represented by the symbol S. It is an abundant, multivalent non-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow...
and nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
. Siroheme is synthesized from uroporphyrinogen III
Uroporphyrinogen III
Uroporphyrinogen III is an metabolic intermediate in the biosynthesis of protoporphyrin. It is created by the enzyme uroporphyrinogen III synthase, and is converted into coproporphyrinogen III by the enzyme uroporphyrinogen III decarboxylase.-See also:...
, a heme and vitamin B12
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12, vitamin B12 or vitamin B-12, also called cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin with a key role in the normal functioning of the brain and nervous system, and for the formation of blood. It is one of the eight B vitamins...
precursor.
It plays a major role in the sulfur assimilation
Sulfur assimilation
Sulfur is an essential element for growth and physiological functioning of plants. However, its content strongly varies between plant species and it ranges from 0.1 to 6 % of the plants' dry weight. Sulfates taken up by the roots are the major sulfur source for growth, though it has to be reduced...
pathway: converting sulfite
Sulfite
Sulfites are compounds that contain the sulfite ion SO. The sulfite ion is the conjugate base of bisulfite. Although the acid itself is elusive, its salts are widely used.-Structure:...
to a biologically useful sulfide
Sulfide
A sulfide is an anion of sulfur in its lowest oxidation state of 2-. Sulfide is also a slightly archaic term for thioethers, a common type of organosulfur compound that are well known for their bad odors.- Properties :...
, which can be incorporated into the organic compound homocysteine
Homocysteine
Homocysteine is a non-protein amino acid with the formula HSCH2CH2CHCO2H. It is a homologue of the amino acid cysteine, differing by an additional methylene group. It is biosynthesized from methionine by the removal of its terminal Cε methyl group...
.
See also
- Ferredoxin-nitrite reductaseFerredoxin-nitrite reductaseIn enzymology, a ferredoxin—nitrite reductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactionThe 3 substrates of this enzyme are NH3, H2O, and oxidized ferredoxin, whereas its 3 products are nitrite, reduced ferredoxin, and H+....
- Hydrogensulfite reductaseHydrogensulfite reductaseIn enzymology, a hydrogensulfite reductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactionThe 4 substrates of this enzyme are trithionate, acceptor, H2O, and OH-, whereas its two products are bisulfite and reduced acceptor....
- Nitrite reductase (NAD(P)H)Nitrite reductase (NAD(P)H)In enzymology, a nitrite reductase [NADH] is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactionThe 4 substrates of this enzyme are ammonium hydroxide, NAD+, NADP+, and H2O, whereas its 4 products are nitrite, NADH, NADPH, and H+....

