
Cofactor (biochemistry)
Encyclopedia
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
chemical compound
Chemical compound
A chemical compound is a pure chemical substance consisting of two or more different chemical elements that can be separated into simpler substances by chemical reactions. Chemical compounds have a unique and defined chemical structure; they consist of a fixed ratio of atoms that are held together...
that is bound
Binding (molecular)
Molecular binding is an attractive interaction between two molecules which results in a stable association in which the molecules are in close proximity to each other...
to a protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
and is required for the protein's biological activity. These proteins are commonly enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
s, and cofactors can be considered "helper molecules" that assist in biochemical transformations.
Cofactors are either organic or inorganic. They can also be classified depending on how tightly they bind to an enzyme, with loosely-bound cofactors termed coenzymes and tightly-bound cofactors termed prosthetic groups. Some sources also limit the use of the term "cofactor" to inorganic substances. An inactive enzyme, without the cofactor is called an apoenzyme, while the complete enzyme with cofactor is the holoenzyme.
Some enzymes or enzyme complexes require several cofactors. For example, the multienzyme complex pyruvate dehydrogenase
Pyruvate dehydrogenase
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is a complex of three enzymes that transform pyruvate into acetyl-CoA by a process called pyruvate decarboxylation. Acetyl-CoA may then be used in the citric acid cycle to carry out cellular respiration, and this complex links the glycolysis metabolic pathway to the...
at the junction of glycolysis
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+...
and the citric acid cycle
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle — also known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle , the Krebs cycle, or the Szent-Györgyi-Krebs cycle — is a series of chemical reactions which is used by all aerobic living organisms to generate energy through the oxidization of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and...
requires five organic cofactors and one metal ion: loosely bound thiamine pyrophosphate
Thiamine pyrophosphate
Thiamine pyrophosphate , or thiamine diphosphate , is a thiamine derivative which is produced by the enzyme thiamine pyrophosphatase. Thiamine pyrophosphate is a coenzyme that is present in all living systems, in which it catalyzes several biochemical reactions...
(TPP), covalently bound lipoamide
Lipoamide
Lipoamide is a trivial name for 6,8-dithiooctanoic amide. It is 6,8-dithiooctanoic acid's functional form where the carboxyl group is attached to protein by an amide linkage . Sometimes lipoamide is used to refer to protein bound lipoic acid, but this can be misleading as this is technically...
and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), and the cosubstrates nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, abbreviated NAD, is a coenzyme found in all living cells. The compound is a dinucleotide, since it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine base and the other nicotinamide.In metabolism, NAD is involved...
(NAD+) and coenzyme A
Coenzyme A
Coenzyme A is a coenzyme, notable for its role in the synthesis and oxidation of fatty acids, and the oxidation of pyruvate in the citric acid cycle. All sequenced genomes encode enzymes that use coenzyme A as a substrate, and around 4% of cellular enzymes use it as a substrate...
(CoA), and a metal ion (Mg2+).
Organic cofactors are often vitamin
Vitamin
A vitamin is an organic compound required as a nutrient in tiny amounts by an organism. In other words, an organic chemical compound is called a vitamin when it cannot be synthesized in sufficient quantities by an organism, and must be obtained from the diet. Thus, the term is conditional both on...
s or are made from vitamins. Many contain the nucleotide
Nucleotide
Nucleotides are molecules that, when joined together, make up the structural units of RNA and DNA. In addition, nucleotides participate in cellular signaling , and are incorporated into important cofactors of enzymatic reactions...
adenosine monophosphate
Adenosine monophosphate
Adenosine monophosphate , also known as 5'-adenylic acid, is a nucleotide that is used as a monomer in RNA. It is an ester of phosphoric acid and the nucleoside adenosine. AMP consists of a phosphate group, the sugar ribose, and the nucleobase adenine...
(AMP) as part of their structures, such as ATP
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine-5'-triphosphate is a multifunctional nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme. It is often called the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism...
, coenzyme A
Coenzyme A
Coenzyme A is a coenzyme, notable for its role in the synthesis and oxidation of fatty acids, and the oxidation of pyruvate in the citric acid cycle. All sequenced genomes encode enzymes that use coenzyme A as a substrate, and around 4% of cellular enzymes use it as a substrate...
, FAD
FAD
In biochemistry, flavin adenine dinucleotide is a redox cofactor involved in several important reactions in metabolism. FAD can exist in two different redox states, which it converts between by accepting or donating electrons. The molecule consists of a riboflavin moiety bound to the phosphate...
, and NAD+. This common structure may reflect a common evolutionary origin as part of ribozyme
Ribozyme
A ribozyme is an RNA molecule with a well defined tertiary structure that enables it to catalyze a chemical reaction. Ribozyme means ribonucleic acid enzyme. It may also be called an RNA enzyme or catalytic RNA. Many natural ribozymes catalyze either the hydrolysis of one of their own...
s in an ancient RNA world
RNA world hypothesis
The RNA world hypothesis proposes that life based on ribonucleic acid pre-dates the current world of life based on deoxyribonucleic acid , RNA and proteins. RNA is able both to store genetic information, like DNA, and to catalyze chemical reactions, like an enzyme protein...
. It has been suggested that the AMP part of the molecule can be considered a kind of "handle" by which the enzyme can "grasp" the coenzyme to switch it between different catalytic centers.
Classification
Cofactors can be divided into two broad groups: organic cofactors, such as flavin or hemeHeme
A heme or haem is a prosthetic group that consists of an iron atom contained in the center of a large heterocyclic organic ring called a porphyrin. Not all porphyrins contain iron, but a substantial fraction of porphyrin-containing metalloproteins have heme as their prosthetic group; these are...
, and inorganic cofactors, such as the metal ions Mg2+, Cu+, Mn2+, or iron-sulfur clusters
Iron-sulfur protein
Iron-sulfur proteins are proteins characterized by the presence of iron-sulfur clusters containing sulfide-linked di-, tri-, and tetrairon centers in variable oxidation states...
.
Organic cofactors are sometimes further divided into coenzymes and prosthetic groups. The term coenzyme refers specifically to enzymes and, as such, to the functional properties of a protein. On the other hand, "prosthetic group" emphasizes the nature of the binding of a cofactor to a protein (tight or covalent) and, thus, refers to a structural property. Different sources give slightly different definitions of coenzymes, cofactors, and prosthetic groups. Some consider tightly-bound organic molecules as prosthetic groups and not as coenzymes, while others define all non-protein organic molecules needed for enzyme activity as coenzymes, and classify those that are tightly bound as coenzyme prosthetic groups. It should be noted that these terms are often used loosely.
A 1979 letter in Trends in Biochemical Sciences noted the confusion in the literature and the essentially arbitrary distinction made between prosthetic groups and coenzymes and proposed the following scheme. Here, cofactors were defined as an additional substance apart from protein and substrate that is required for enzyme activity and a prosthetic group as a substance that undergoes its whole catalytic cycle
Catalytic cycle
A catalytic cycle in chemistry is a term for a multistep reaction mechanism that involves a catalyst . The catalytic cycle is the main method for describing the role of catalysts in biochemistry, organometallic chemistry, materials science, etc. Often such cycles show the conversion of a...
attached to a single enzyme molecule. However, the author could not arrive at a single all-encompassing definition of a "coenzyme" and proposed that this term be dropped from use in the literature.
Metal ions
MetalMetal
A metal , is an element, compound, or alloy that is a good conductor of both electricity and heat. Metals are usually malleable and shiny, that is they reflect most of incident light...
ion
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
s are common cofactors. The study of these cofactors falls under the area of bioinorganic chemistry
Bioinorganic chemistry
Bioinorganic chemistry is a field that examines the role of metals in biology. Bioinorganic chemistry includes the study of both natural phenomena such as the behavior of metalloproteins as well artificially introduced metals, including those that are non-essential, in medicine and toxicology...
. In nutrition
Nutrition
Nutrition is the provision, to cells and organisms, of the materials necessary to support life. Many common health problems can be prevented or alleviated with a healthy diet....
, the list of essential trace element
Trace element
In analytical chemistry, a trace element is an element in a sample that has an average concentration of less than 100 parts per million measured in atomic count, or less than 100 micrograms per gram....
s reflects their role as cofactors. In humans this list commonly includes iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
, magnesium
Magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg, atomic number 12, and common oxidation number +2. It is an alkaline earth metal and the eighth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and ninth in the known universe as a whole...
, manganese
Manganese
Manganese is a chemical element, designated by the symbol Mn. It has the atomic number 25. It is found as a free element in nature , and in many minerals...
, cobalt
Cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element with symbol Co and atomic number 27. It is found naturally only in chemically combined form. The free element, produced by reductive smelting, is a hard, lustrous, silver-gray metal....
, copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
, zinc
Zinc
Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2...
, selenium
Selenium
Selenium is a chemical element with atomic number 34, chemical symbol Se, and an atomic mass of 78.96. It is a nonmetal, whose properties are intermediate between those of adjacent chalcogen elements sulfur and tellurium...
, and molybdenum
Molybdenum
Molybdenum , is a Group 6 chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42. The name is from Neo-Latin Molybdaenum, from Ancient Greek , meaning lead, itself proposed as a loanword from Anatolian Luvian and Lydian languages, since its ores were confused with lead ores...
. Although chromium
Chromium
Chromium is a chemical element which has the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6. It is a steely-gray, lustrous, hard metal that takes a high polish and has a high melting point. It is also odorless, tasteless, and malleable...
deficiency causes impaired glucose tolerance
Impaired glucose tolerance
Impaired glucose tolerance is a pre-diabetic state of dysglycemia that is associated with insulin resistance and increased risk of cardiovascular pathology. IGT may precede type 2 diabetes mellitus by many years...
, no human enzyme that uses this metal as a cofactor has been identified. Iodine
Iodine
Iodine is a chemical element with the symbol I and atomic number 53. The name is pronounced , , or . The name is from the , meaning violet or purple, due to the color of elemental iodine vapor....
is also an essential trace element, but this element is used as part of the structure of thyroid hormone
Thyroid hormone
The thyroid hormones, thyroxine and triiodothyronine , are tyrosine-based hormones produced by the thyroid gland primarily responsible for regulation of metabolism. An important component in the synthesis of thyroid hormones is iodine. The major form of thyroid hormone in the blood is thyroxine ,...
s rather than as an enzyme cofactor. Calcium
Calcium
Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
is another special case, in that it is required as a component of the human diet, and it is needed for the full activity of many enzymes, such as nitric oxide synthase
Nitric oxide synthase
Nitric oxide synthases are a family of enzymes that catalyze the production of nitric oxide from L-arginine. NO is an important cellular signaling molecule, having a vital role in many biological processes...
, protein phosphatases
Phosphatase
A phosphatase is an enzyme that removes a phosphate group from its substrate by hydrolysing phosphoric acid monoesters into a phosphate ion and a molecule with a free hydroxyl group . This action is directly opposite to that of phosphorylases and kinases, which attach phosphate groups to their...
, and adenylate kinase
Adenylate kinase
Adenylate kinase is a phosphotransferase enzyme that catalyzes the interconversion of adenine nucleotides, and plays an important role in cellular energy homeostasis.-Substrate and products:...
, but calcium activates these enzymes in allosteric regulation
Allosteric regulation
In biochemistry, allosteric regulation is the regulation of an enzyme or other protein by binding an effector molecule at the protein's allosteric site . Effectors that enhance the protein's activity are referred to as allosteric activators, whereas those that decrease the protein's activity are...
, often binding to these enzymes in a complex with calmodulin
Calmodulin
Calmodulin is a calcium-binding protein expressed in all eukaryotic cells...
. Calcium is, therefore, a cell signaling
Cell signaling
Cell signaling is part of a complex system of communication that governs basic cellular activities and coordinates cell actions. The ability of cells to perceive and correctly respond to their microenvironment is the basis of development, tissue repair, and immunity as well as normal tissue...
molecule, and not usually considered a cofactor of the enzymes it regulates.
Other organisms require additional metals as enzyme cofactors, such as vanadium
Vanadium
Vanadium is a chemical element with the symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery gray, ductile and malleable transition metal. The formation of an oxide layer stabilizes the metal against oxidation. The element is found only in chemically combined form in nature...
in the nitrogenase
Nitrogenase
Nitrogenases are enzymes used by some organisms to fix atmospheric nitrogen gas . It is the only known family of enzymes that accomplish this process. Dinitrogen is quite inert because of the strength of its N-N triple bond...
of the nitrogen-fixing
Nitrogen fixation
Nitrogen fixation is the natural process, either biological or abiotic, by which nitrogen in the atmosphere is converted into ammonia . This process is essential for life because fixed nitrogen is required to biosynthesize the basic building blocks of life, e.g., nucleotides for DNA and RNA and...
bacteria of the genus Azotobacter
Azotobacter
Azotobacter is a genus of usually motile, oval or spherical bacteria that form thick-walled cysts and may produce large quantities of capsular slime. They are aerobic, free-living soil microbes which play an important role in the nitrogen cycle in nature, binding atmospheric nitrogen, which is...
, tungsten
Tungsten
Tungsten , also known as wolfram , is a chemical element with the chemical symbol W and atomic number 74.A hard, rare metal under standard conditions when uncombined, tungsten is found naturally on Earth only in chemical compounds. It was identified as a new element in 1781, and first isolated as...
in the aldehyde ferredoxin oxidoreductase
Aldehyde ferredoxin oxidoreductase
In enzymology, an aldehyde ferredoxin oxidoreductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactionThe 3 substrates of this enzyme are aldehyde, H2O, and oxidized ferredoxin, whereas its 3 products are acid, H+, and reduced ferredoxin....
of the thermophilic archaea
Archaea
The Archaea are a group of single-celled microorganisms. A single individual or species from this domain is called an archaeon...
n Pyrococcus furiosus
Pyrococcus furiosus
Pyrococcus furiosus is an extremophilic species of Archaea. It can be classified as a hyperthermophile because it thrives best under extremely high temperatures—higher than those preferred of a thermophile...
, and even cadmium
Cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element with the symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, bluish-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12, zinc and mercury. Similar to zinc, it prefers oxidation state +2 in most of its compounds and similar to mercury it shows a low...
in the carbonic anhydrase
Carbonic anhydrase
The carbonic anhydrases form a family of enzymes that catalyze the rapid interconversion of carbon dioxide and water to bicarbonate and protons , a reversible reaction that occurs rather slowly in the absence of a catalyst...
from the marine diatom
Diatom
Diatoms are a major group of algae, and are one of the most common types of phytoplankton. Most diatoms are unicellular, although they can exist as colonies in the shape of filaments or ribbons , fans , zigzags , or stellate colonies . Diatoms are producers within the food chain...
Thalassiosira weissflogii.
In many cases, the cofactor includes both an inorganic and organic component. One diverse set of examples is the haem proteins, which consist of a porphyrin
Porphyrin
Porphyrins are a group of organic compounds, many naturally occurring. One of the best-known porphyrins is heme, the pigment in red blood cells; heme is a cofactor of the protein hemoglobin. Porphyrins are heterocyclic macrocycles composed of four modified pyrrole subunits interconnected at...
ring coordinated to iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
.
| Ion | Examples of enzymes containing this ion |
|---|---|
| Cupric Copper Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish... |
Cytochrome oxidase |
| Ferrous or Ferric Iron Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust... |
Catalase Catalase Catalase is a common enzyme found in nearly all living organisms that are exposed to oxygen, where it catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen... Cytochrome Cytochrome Cytochromes are, in general, membrane-bound hemoproteins that contain heme groups and carry out electron transport.They are found either as monomeric proteins or as subunits of bigger enzymatic complexes that catalyze redox reactions.... (via Heme Heme A heme or haem is a prosthetic group that consists of an iron atom contained in the center of a large heterocyclic organic ring called a porphyrin. Not all porphyrins contain iron, but a substantial fraction of porphyrin-containing metalloproteins have heme as their prosthetic group; these are... ) Nitrogenase Nitrogenase Nitrogenases are enzymes used by some organisms to fix atmospheric nitrogen gas . It is the only known family of enzymes that accomplish this process. Dinitrogen is quite inert because of the strength of its N-N triple bond... Hydrogenase Hydrogenase A hydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyses the reversible oxidation of molecular hydrogen . Hydrogenases play a vital role in anaerobic metabolism.... |
| Magnesium Magnesium Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg, atomic number 12, and common oxidation number +2. It is an alkaline earth metal and the eighth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and ninth in the known universe as a whole... |
Glucose 6-phosphatase Glucose 6-phosphatase Glucose 6-phosphatase is an enzyme that hydrolyzes glucose-6-phosphate resulting in the creation of a phosphate group and free glucose. Glucose is then exported from the cell via glucose transporter membrane proteins... Hexokinase Hexokinase A hexokinase is an enzyme that phosphorylates a six-carbon sugar, a hexose, to a hexose phosphate. In most tissues and organisms, glucose is the most important substrate of hexokinases, and glucose-6-phosphate the most important product.... DNA polymerase DNA polymerase A DNA polymerase is an enzyme that helps catalyze in the polymerization of deoxyribonucleotides into a DNA strand. DNA polymerases are best known for their feedback role in DNA replication, in which the polymerase "reads" an intact DNA strand as a template and uses it to synthesize the new strand.... |
| Manganese Manganese Manganese is a chemical element, designated by the symbol Mn. It has the atomic number 25. It is found as a free element in nature , and in many minerals... |
Arginase Arginase Arginase is a manganese-containing enzyme. The reaction catalyzed by this enzyme is: arginine + H2O → ornithine + urea. It is the final enzyme of the urea cycle.- Structure and function :Arginase belong to the ureohydrolase family of enzymes.... |
| Molybdenum Molybdenum Molybdenum , is a Group 6 chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42. The name is from Neo-Latin Molybdaenum, from Ancient Greek , meaning lead, itself proposed as a loanword from Anatolian Luvian and Lydian languages, since its ores were confused with lead ores... |
Nitrate reductase Nitrate reductase Nitrate reductases are molybdoenzymes that reduce nitrate to nitrite .* Eukaryotic nitrate reductases are part of the sulfite oxidase family of molybdoenzymes.... Nitrogenase Nitrogenase Nitrogenases are enzymes used by some organisms to fix atmospheric nitrogen gas . It is the only known family of enzymes that accomplish this process. Dinitrogen is quite inert because of the strength of its N-N triple bond... |
| Nickel Nickel Nickel is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel belongs to the transition metals and is hard and ductile... |
Urease Urease Urease is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of urea into carbon dioxide and ammonia. The reaction occurs as follows:In 1926, James Sumner showed that urease is a protein. Urease is found in bacteria, yeast, and several higher plants. The structure of urease was first solved by P.A... |
| Selenium Selenium Selenium is a chemical element with atomic number 34, chemical symbol Se, and an atomic mass of 78.96. It is a nonmetal, whose properties are intermediate between those of adjacent chalcogen elements sulfur and tellurium... |
Glutathione peroxidase Glutathione peroxidase Glutathione peroxidase is the general name of an enzyme family with peroxidase activity whose main biological role is to protect the organism from oxidative damage... |
| Zinc Zinc Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2... |
Alcohol dehydrogenase Alcohol dehydrogenase Alcohol dehydrogenases are a group of dehydrogenase enzymes that occur in many organisms and facilitate the interconversion between alcohols and aldehydes or ketones with the reduction of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide... Carbonic anhydrase Carbonic anhydrase The carbonic anhydrases form a family of enzymes that catalyze the rapid interconversion of carbon dioxide and water to bicarbonate and protons , a reversible reaction that occurs rather slowly in the absence of a catalyst... DNA polymerase DNA polymerase A DNA polymerase is an enzyme that helps catalyze in the polymerization of deoxyribonucleotides into a DNA strand. DNA polymerases are best known for their feedback role in DNA replication, in which the polymerase "reads" an intact DNA strand as a template and uses it to synthesize the new strand.... |
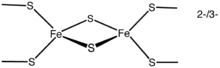
Iron-sulfur clusters
Iron-sulfur clusters are complexes of iron and sulfur atoms held within proteins by cysteinyl residues. They play both structural and functional roles, including electron transfer, redox sensing, and as structural modules.Organic
Organic cofactors are small organic molecules (typically a molecular mass less than 1000 Da) that can be either loosely or tightly bound to the enzyme and directly participate in the reaction. In the latter case, when it is difficult to remove without denaturing the enzyme, it can be called a prosthetic group. It is important to emphasize that there is no sharp division between loosely and tightly bound cofactors. Indeed, many such as NAD+ can be tightly bound in some enzymes, while it is loosely bound in others. Another example is thiamine pyrophosphateThiamine pyrophosphate
Thiamine pyrophosphate , or thiamine diphosphate , is a thiamine derivative which is produced by the enzyme thiamine pyrophosphatase. Thiamine pyrophosphate is a coenzyme that is present in all living systems, in which it catalyzes several biochemical reactions...
(TPP), which is tightly bound in transketolase
Transketolase
Transketolase, an enzyme of both the pentose phosphate pathway in animals and the Calvin cycle of photosynthesis, catalyzes two important reactions, which operate in opposite directions in these two pathways...
or pyruvate decarboxylase
Pyruvate decarboxylase
Not to be confused with pyruvate dehydrogenase, the enzyme which catalyses the link reaction.Pyruvate decarboxylase is a homotetrameric enzyme that catalyses the decarboxylation of pyruvic acid to acetaldehyde and carbon dioxide in the cytoplasm. It is also called 2-oxo-acid carboxylase,...
, while it is less tightly bound in pyruvate dehydrogenase
Pyruvate dehydrogenase
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is a complex of three enzymes that transform pyruvate into acetyl-CoA by a process called pyruvate decarboxylation. Acetyl-CoA may then be used in the citric acid cycle to carry out cellular respiration, and this complex links the glycolysis metabolic pathway to the...
. Other coenzymes, flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), biotin
Biotin
Biotin, also known as Vitamin H or Coenzyme R, is a water-soluble B-complex vitamin discovered by Bateman in 1916. It is composed of a ureido ring fused with a tetrahydrothiophene ring. A valeric acid substituent is attached to one of the carbon atoms of the tetrahydrothiophene ring...
, and lipoamide
Lipoamide
Lipoamide is a trivial name for 6,8-dithiooctanoic amide. It is 6,8-dithiooctanoic acid's functional form where the carboxyl group is attached to protein by an amide linkage . Sometimes lipoamide is used to refer to protein bound lipoic acid, but this can be misleading as this is technically...
, for instance, are covalently bound. Tightly-bound cofactors are, in general, regenerated during the same reaction cycle, while loosely-bound cofactors can be regenerated in a subsequent reaction catalyzed by a different enzyme. In the latter case, the cofactor can also be considered a substrate or cosubstrate.
Vitamin
Vitamin
A vitamin is an organic compound required as a nutrient in tiny amounts by an organism. In other words, an organic chemical compound is called a vitamin when it cannot be synthesized in sufficient quantities by an organism, and must be obtained from the diet. Thus, the term is conditional both on...
s can serve as precursors to many organic cofactors (e.g., vitamins B1, B2, B6
Vitamin B6
Vitamin B6 is a water-soluble vitamin and is part of the vitamin B complex group. Several forms of the vitamin are known, but pyridoxal phosphate is the active form and is a cofactor in many reactions of amino acid metabolism, including transamination, deamination, and decarboxylation...
, B12
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12, vitamin B12 or vitamin B-12, also called cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin with a key role in the normal functioning of the brain and nervous system, and for the formation of blood. It is one of the eight B vitamins...
, niacin
Niacin
"Niacin" redirects here. For the neo-fusion band, see Niacin .Niacin is an organic compound with the formula and, depending on the definition used, one of the forty to eighty essential human nutrients.Niacin is one of five vitamins associated with a pandemic deficiency disease: niacin deficiency...
, folic acid
Folic acid
Folic acid and folate , as well as pteroyl-L-glutamic acid, pteroyl-L-glutamate, and pteroylmonoglutamic acid are forms of the water-soluble vitamin B9...
) or as coenzymes themselves (e.g., vitamin C
Vitamin C
Vitamin C or L-ascorbic acid or L-ascorbate is an essential nutrient for humans and certain other animal species. In living organisms ascorbate acts as an antioxidant by protecting the body against oxidative stress...
). However, vitamins do have other functions in the body. Many organic cofactors also contain a nucleotide
Nucleotide
Nucleotides are molecules that, when joined together, make up the structural units of RNA and DNA. In addition, nucleotides participate in cellular signaling , and are incorporated into important cofactors of enzymatic reactions...
, such as the electron carriers NAD
NAD
NAD may refer to:* No abnormality detected, a medical status description* No apparent distress, a status description in childbirth* NAD Electronics, a Canadian audio equipment manufacturer...
and FAD
FAD
In biochemistry, flavin adenine dinucleotide is a redox cofactor involved in several important reactions in metabolism. FAD can exist in two different redox states, which it converts between by accepting or donating electrons. The molecule consists of a riboflavin moiety bound to the phosphate...
, and coenzyme A
Coenzyme A
Coenzyme A is a coenzyme, notable for its role in the synthesis and oxidation of fatty acids, and the oxidation of pyruvate in the citric acid cycle. All sequenced genomes encode enzymes that use coenzyme A as a substrate, and around 4% of cellular enzymes use it as a substrate...
, which carries acyl
Acyl
An acyl group is a functional group derived by the removal of one or more hydroxyl groups from an oxoacid, including inorganic acids.In organic chemistry, the acyl group is usually derived from a carboxylic acid . Therefore, it has the formula RCO-, where R represents an alkyl group that is...
groups. Most of these cofactors are found in a huge variety of species, and some are universal to all forms of life. An exception to this wide distribution is a group of unique cofactors that evolved in methanogen
Methanogen
Methanogens are microorganisms that produce methane as a metabolic byproduct in anoxic conditions. They are classified as archaea, a group quite distinct from bacteria...
s, which are restricted to this group of archaea
Archaea
The Archaea are a group of single-celled microorganisms. A single individual or species from this domain is called an archaeon...
.
Vitamins and derivatives
| Cofactor | Vitamin | Additional component | Chemical group(s) transferred | Distribution | |||||||||||||
| Thiamine pyrophosphate Thiamine pyrophosphate Thiamine pyrophosphate , or thiamine diphosphate , is a thiamine derivative which is produced by the enzyme thiamine pyrophosphatase. Thiamine pyrophosphate is a coenzyme that is present in all living systems, in which it catalyzes several biochemical reactions... |
Thiamine Thiamine Thiamine or thiamin or vitamin B1 , named as the "thio-vitamine" is a water-soluble vitamin of the B complex. First named aneurin for the detrimental neurological effects if not present in the diet, it was eventually assigned the generic descriptor name vitamin B1. Its phosphate derivatives are... (B1) |
None | 2-carbon groups, α cleavage | Bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals... , archaea Archaea The Archaea are a group of single-celled microorganisms. A single individual or species from this domain is called an archaeon... and eukaryote Eukaryote A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear... s >- | NAD+ Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, abbreviated NAD, is a coenzyme found in all living cells. The compound is a dinucleotide, since it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine base and the other nicotinamide.In metabolism, NAD is involved... and NADP+ Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP or TPN in older notation , is a coenzyme used in anabolic reactions, such as lipid and nucleic acid synthesis, which require NADPH as a reducing agent.... |
Niacin Niacin "Niacin" redirects here. For the neo-fusion band, see Niacin .Niacin is an organic compound with the formula and, depending on the definition used, one of the forty to eighty essential human nutrients.Niacin is one of five vitamins associated with a pandemic deficiency disease: niacin deficiency... (B3) |
ADP | Electron Electron The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton... s |
Bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals... , archaea Archaea The Archaea are a group of single-celled microorganisms. A single individual or species from this domain is called an archaeon... and eukaryote Eukaryote A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear... s >- | Pyridoxal phosphate |
Pyridoxine Pyridoxine Pyridoxine is one of the compounds that can be called vitamin B6, along with pyridoxal and pyridoxamine. It differs from pyridoxamine by the substituent at the '4' position. It is often used as 'pyridoxine hydrochloride'.-Chemistry:... (B6) |
None | Amino and carboxyl groups | Bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals... , archaea Archaea The Archaea are a group of single-celled microorganisms. A single individual or species from this domain is called an archaeon... and eukaryote Eukaryote A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear... s >- |
Lipoamide Lipoamide Lipoamide is a trivial name for 6,8-dithiooctanoic amide. It is 6,8-dithiooctanoic acid's functional form where the carboxyl group is attached to protein by an amide linkage . Sometimes lipoamide is used to refer to protein bound lipoic acid, but this can be misleading as this is technically... |
Lipoic acid Lipoic acid Lipoic acid , also known as α-lipoic acid and Alpha Lipoic Acid is an organosulfur compound derived from octanoic acid. LA contains two vicinal sulfur atoms attached via a disulfide bond and is thus considered to be oxidized... |
None | electrons, acyl groups Acyl An acyl group is a functional group derived by the removal of one or more hydroxyl groups from an oxoacid, including inorganic acids.In organic chemistry, the acyl group is usually derived from a carboxylic acid . Therefore, it has the formula RCO-, where R represents an alkyl group that is... |
Bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals... , archaea Archaea The Archaea are a group of single-celled microorganisms. A single individual or species from this domain is called an archaeon... and eukaryote Eukaryote A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear... s |
| Vitamin B12 Vitamin B12 Vitamin B12, vitamin B12 or vitamin B-12, also called cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin with a key role in the normal functioning of the brain and nervous system, and for the formation of blood. It is one of the eight B vitamins... |
Methyl group | acyl groups Acyl An acyl group is a functional group derived by the removal of one or more hydroxyl groups from an oxoacid, including inorganic acids.In organic chemistry, the acyl group is usually derived from a carboxylic acid . Therefore, it has the formula RCO-, where R represents an alkyl group that is... |
Bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals... , archaea Archaea The Archaea are a group of single-celled microorganisms. A single individual or species from this domain is called an archaeon... and eukaryote Eukaryote A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear... s >- |
Cobalamine | Cobalamine (B12) | None | hydrogen Hydrogen Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly... , alkyl groups |
Bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals... , archaea Archaea The Archaea are a group of single-celled microorganisms. A single individual or species from this domain is called an archaeon... and eukaryote Eukaryote A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear... s >- | Biotin Biotin Biotin, also known as Vitamin H or Coenzyme R, is a water-soluble B-complex vitamin discovered by Bateman in 1916. It is composed of a ureido ring fused with a tetrahydrothiophene ring. A valeric acid substituent is attached to one of the carbon atoms of the tetrahydrothiophene ring... |
Biotin Biotin Biotin, also known as Vitamin H or Coenzyme R, is a water-soluble B-complex vitamin discovered by Bateman in 1916. It is composed of a ureido ring fused with a tetrahydrothiophene ring. A valeric acid substituent is attached to one of the carbon atoms of the tetrahydrothiophene ring... (H) |
None | CO2 | Bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals... , archaea Archaea The Archaea are a group of single-celled microorganisms. A single individual or species from this domain is called an archaeon... and eukaryote Eukaryote A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear... s >- | Coenzyme A Coenzyme A Coenzyme A is a coenzyme, notable for its role in the synthesis and oxidation of fatty acids, and the oxidation of pyruvate in the citric acid cycle. All sequenced genomes encode enzymes that use coenzyme A as a substrate, and around 4% of cellular enzymes use it as a substrate... |
Pantothenic acid Pantothenic acid Pantothenic acid, also called pantothenate or vitamin B5 , is a water-soluble vitamin. For many animals, pantothenic acid is an essential nutrient. Animals require pantothenic acid to synthesize coenzyme-A , as well as to synthesize and metabolize proteins, carbohydrates, and fats.Pantothenic acid... (B5) |
ADP | Acetyl group Acetyl In organic chemistry, acetyl is a functional group, the acyl with chemical formula COCH3. It is sometimes represented by the symbol Ac . The acetyl group contains a methyl group single-bonded to a carbonyl... and other acyl groups Acyl An acyl group is a functional group derived by the removal of one or more hydroxyl groups from an oxoacid, including inorganic acids.In organic chemistry, the acyl group is usually derived from a carboxylic acid . Therefore, it has the formula RCO-, where R represents an alkyl group that is... |
Bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals... , archaea Archaea The Archaea are a group of single-celled microorganisms. A single individual or species from this domain is called an archaeon... and eukaryote Eukaryote A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear... s >- | Tetrahydrofolic acid Tetrahydrofolic acid Tetrahydrofolic acid, or tetrahydrofolate, is a folic acid derivative.-Metabolism:-Human synthesis:It is produced from dihydrofolic acid by dihydrofolate reductase... |
Folic acid Folic acid Folic acid and folate , as well as pteroyl-L-glutamic acid, pteroyl-L-glutamate, and pteroylmonoglutamic acid are forms of the water-soluble vitamin B9... (B9) |
Glutamate Glutamic acid Glutamic acid is one of the 20 proteinogenic amino acids, and its codons are GAA and GAG. It is a non-essential amino acid. The carboxylate anions and salts of glutamic acid are known as glutamates... residues |
Methyl, formyl Aldehyde An aldehyde is an organic compound containing a formyl group. This functional group, with the structure R-CHO, consists of a carbonyl center bonded to hydrogen and an R group.... , methylene and formimino groups |
Bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals... , archaea Archaea The Archaea are a group of single-celled microorganisms. A single individual or species from this domain is called an archaeon... and eukaryote Eukaryote A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear... s >- |Menaquinone Vitamin K Vitamin K is a group of structurally similar, fat soluble vitamins that are needed for the posttranslational modification of certain proteins required for blood coagulation and in metabolic pathways in bone and other tissue. They are 2-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone derivatives... |
Vitamin K | None | Carbonyl group Carbonyl In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom: C=O. It is common to several classes of organic compounds, as part of many larger functional groups.... and electron Electron The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton... s |
Bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals... , archaea Archaea The Archaea are a group of single-celled microorganisms. A single individual or species from this domain is called an archaeon... and eukaryote Eukaryote A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear... s >- |Ascorbic acid Ascorbic acid Ascorbic acid is a naturally occurring organic compound with antioxidant properties. It is a white solid, but impure samples can appear yellowish. It dissolves well in water to give mildly acidic solutions. Ascorbic acid is one form of vitamin C. The name is derived from a- and scorbutus , the... |
Vitamin C | None | Electron Electron The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton... s |
Bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals... , archaea Archaea The Archaea are a group of single-celled microorganisms. A single individual or species from this domain is called an archaeon... and eukaryote Eukaryote A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear... s >- |
Flavin mononucleotide Flavin mononucleotide Flavin mononucleotide , or riboflavin-5′-phosphate, is a biomolecule produced from riboflavin by the enzyme riboflavin kinase and functions as prosthetic group of various oxidoreductases including NADH dehydrogenase as well as cofactor in biological blue-light photo receptors... |
Riboflavin Riboflavin Riboflavin, also known as vitamin B2 or additive E101, is an easily absorbed micronutrient with a key role in maintaining health in humans and animals. It is the central component of the cofactors FAD and FMN, and is therefore required by all flavoproteins. As such, vitamin B2 is required for a... (B2) |
None | Electron Electron The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton... s |
Bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals... , archaea Archaea The Archaea are a group of single-celled microorganisms. A single individual or species from this domain is called an archaeon... and eukaryote Eukaryote A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear... s >- | Flavin adenine dinucleotide |
Riboflavin Riboflavin Riboflavin, also known as vitamin B2 or additive E101, is an easily absorbed micronutrient with a key role in maintaining health in humans and animals. It is the central component of the cofactors FAD and FMN, and is therefore required by all flavoproteins. As such, vitamin B2 is required for a... (B2) |
None | Electron Electron The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton... s |
Bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals... , archaea Archaea The Archaea are a group of single-celled microorganisms. A single individual or species from this domain is called an archaeon... and eukaryote Eukaryote A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear... s >- |Coenzyme F420 Coenzyme F420 Coenzyme F420 or 8-hydroxy-5-deazaflavin is a coenzyme involved in redox reactions in methanogens , in many Actinobacteria, and sporadically in other bacterial lineages. It is a flavin derivative... |
Riboflavin Riboflavin Riboflavin, also known as vitamin B2 or additive E101, is an easily absorbed micronutrient with a key role in maintaining health in humans and animals. It is the central component of the cofactors FAD and FMN, and is therefore required by all flavoproteins. As such, vitamin B2 is required for a... (B2) |
Amino acids | Electron Electron The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton... s |
Methanogen Methanogen Methanogens are microorganisms that produce methane as a metabolic byproduct in anoxic conditions. They are classified as archaea, a group quite distinct from bacteria... s and some bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals... >- |
Non-vitamins
| Cofactor | Chemical group(s) transferred | Distribution >- |Adenosine triphosphate Adenosine triphosphate Adenosine-5'-triphosphate is a multifunctional nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme. It is often called the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism... |
Phosphate group Phosphate A phosphate, an inorganic chemical, is a salt of phosphoric acid. In organic chemistry, a phosphate, or organophosphate, is an ester of phosphoric acid. Organic phosphates are important in biochemistry and biogeochemistry or ecology. Inorganic phosphates are mined to obtain phosphorus for use in... |
Bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals... , archaea Archaea The Archaea are a group of single-celled microorganisms. A single individual or species from this domain is called an archaeon... and eukaryote Eukaryote A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear... s >- |S-Adenosyl methionine S-Adenosyl methionine S-Adenosyl methionine is a common cosubstrate involved in methyl group transfers. SAM was first discovered in Italy by G. L. Cantoni in 1952. It is made from adenosine triphosphate and methionine by methionine adenosyltransferase . Transmethylation, transsulfuration, and aminopropylation are the... |
Methyl group Methyl group Methyl group is a functional group derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms —CH3. The group is often abbreviated Me. Such hydrocarbon groups occur in many organic compounds. The methyl group can be found in three forms: anion, cation and radical. The anion... |
Bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals... , archaea Archaea The Archaea are a group of single-celled microorganisms. A single individual or species from this domain is called an archaeon... and eukaryote Eukaryote A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear... s >- |Coenzyme B Coenzyme B Coenzyme B is a coenzyme required for redox reactions in methanogens. The full chemical name of coenzyme B is 7-mercaptoheptanoylthreoninephosphate... |
Electron Electron The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton... s |
Methanogen Methanogen Methanogens are microorganisms that produce methane as a metabolic byproduct in anoxic conditions. They are classified as archaea, a group quite distinct from bacteria... s >- | Coenzyme M Coenzyme M Coenzyme M is a coenzyme required for methyl-transfer reactions in the metabolism of methanogens. The coenzyme is an anion with the formula . It is named 2-mercaptoethanesulfonate and abbreviated HS–CoM. The cation is unimportant, but the sodium salt is most available... |
Methyl group Methyl group Methyl group is a functional group derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms —CH3. The group is often abbreviated Me. Such hydrocarbon groups occur in many organic compounds. The methyl group can be found in three forms: anion, cation and radical. The anion... |
Methanogen Methanogen Methanogens are microorganisms that produce methane as a metabolic byproduct in anoxic conditions. They are classified as archaea, a group quite distinct from bacteria... s >- | Coenzyme Q Coenzyme Q Coenzyme Q10, also known as ubiquinone, ubidecarenone, coenzyme Q, and abbreviated at times to CoQ10 , CoQ, Q10, or Q, is a 1,4-benzoquinone, where Q refers to the quinone chemical group, and 10 refers to the number of isoprenyl chemical subunits in its tail.This oil-soluble, vitamin-like substance... |
Electron Electron The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton... s |
Bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals... , archaea Archaea The Archaea are a group of single-celled microorganisms. A single individual or species from this domain is called an archaeon... and eukaryote Eukaryote A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear... s >- |Cytidine triphosphate Cytidine triphosphate Cytidine triphosphate is a pyrimidine nucleoside triphosphate.CTP is a substrate in the synthesis of RNA.CTP is a high-energy molecule equal to ATP, but its role in the organism is more specific than that of ATP.... |
Diacylglycerols and lipid head groups | Bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals... , archaea Archaea The Archaea are a group of single-celled microorganisms. A single individual or species from this domain is called an archaeon... and eukaryote Eukaryote A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear... s >- |Glutathione Glutathione Glutathione is a tripeptide that contains an unusual peptide linkage between the amine group of cysteine and the carboxyl group of the glutamate side-chain... |
Electron Electron The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton... s |
bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals... and most eukaryote Eukaryote A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear... s >- |Heme Heme A heme or haem is a prosthetic group that consists of an iron atom contained in the center of a large heterocyclic organic ring called a porphyrin. Not all porphyrins contain iron, but a substantial fraction of porphyrin-containing metalloproteins have heme as their prosthetic group; these are... |
Electron Electron The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton... s |
Bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals... , archaea Archaea The Archaea are a group of single-celled microorganisms. A single individual or species from this domain is called an archaeon... and eukaryote Eukaryote A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear... s >- |Methanofuran Methanofuran Methanofuran describes a family of chemical compounds found in methanogenic archaea. These species feature a 2-aminomethylfuran linked to phenoxy group... |
Formyl group Aldehyde An aldehyde is an organic compound containing a formyl group. This functional group, with the structure R-CHO, consists of a carbonyl center bonded to hydrogen and an R group.... |
Methanogen Methanogen Methanogens are microorganisms that produce methane as a metabolic byproduct in anoxic conditions. They are classified as archaea, a group quite distinct from bacteria... s |
| Molybdopterin Molybdopterin Molybdopterins, when reacted with molybdenum or tungsten in the form of molybdate or tungstate, are a class of cofactors found in most molybdenum and all tungsten enzymes... |
Oxygen Oxygen Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition... atoms |
Bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals... , archaea Archaea The Archaea are a group of single-celled microorganisms. A single individual or species from this domain is called an archaeon... and eukaryote Eukaryote A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear... s >- |Nucleotide sugar Nucleotide sugar Nucleotide sugars are the activated forms of monosaccharides. Nucleotide sugars act as glycosyl donors in glycosylation reactions. Those reactions are catalyzed by a group of enzymes called glycosyltransferases.-History:... s |
Monosaccharide Monosaccharide Monosaccharides are the most basic units of biologically important carbohydrates. They are the simplest form of sugar and are usually colorless, water-soluble, crystalline solids. Some monosaccharides have a sweet taste. Examples of monosaccharides include glucose , fructose , galactose, xylose... s |
Bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals... , archaea Archaea The Archaea are a group of single-celled microorganisms. A single individual or species from this domain is called an archaeon... and eukaryote Eukaryote A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear... s >- |3'-Phosphoadenosine-5'-phosphosulfate 3'-Phosphoadenosine-5'-phosphosulfate 3'-Phosphoadenosine-5'-phosphosulfate is a derivative of adenosine monophosphate that is phosphorylated at the 3' position and has a sulfate group attached to the 5' phosphate. This anion, abbreviated PAPS, serves as a coenzyme in sulfotransferase reactions... |
Sulfate group Sulfate In inorganic chemistry, a sulfate is a salt of sulfuric acid.-Chemical properties:... |
Bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals... , archaea Archaea The Archaea are a group of single-celled microorganisms. A single individual or species from this domain is called an archaeon... and eukaryote Eukaryote A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear... s |
| Electron Electron The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton... s |
Bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals... >- |Tetrahydrobiopterin Tetrahydrobiopterin Tetrahydrobiopterin or sapropterin is a naturally occurring essential cofactor of the three aromatic amino acid hydroxylase enzymes, used in the degradation of amino acid phenylalanine and in the biosynthesis of the neurotransmitters serotonin , melatonin, dopamine, norepinephrine ,... |
Oxygen Oxygen Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition... atom and electron Electron The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton... s |
Bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals... , archaea Archaea The Archaea are a group of single-celled microorganisms. A single individual or species from this domain is called an archaeon... and eukaryote Eukaryote A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear... s >- |Tetrahydromethanopterin Tetrahydromethanopterin Tetrahydromethanopterin is a coenzyme in methanogenesis. It is the carrier of the C1 group as it is reduced to the methyl level, before transferring to the coenzyme M.... |
Methyl group Methyl group Methyl group is a functional group derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms —CH3. The group is often abbreviated Me. Such hydrocarbon groups occur in many organic compounds. The methyl group can be found in three forms: anion, cation and radical. The anion... |
Methanogen Methanogen Methanogens are microorganisms that produce methane as a metabolic byproduct in anoxic conditions. They are classified as archaea, a group quite distinct from bacteria... s |
Cofactors as metabolic intermediates

Functional group
In organic chemistry, functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reaction regardless of the size of the molecule it is a part of...
s. This common chemistry allows cells to use a small set of metabolic intermediates to carry chemical groups between different reactions. These group-transfer intermediates are the loosely-bound organic cofactors, often called coenzymes.
Each class of group-transfer reaction is carried out by a particular cofactor, which is the substrate for a set of enzymes that produce it, and a set of enzymes that consume it. An example of this are the dehydrogenase
Dehydrogenase
A dehydrogenase is an enzyme that oxidises a substrate by a reduction reaction that transfers one or more hydrides to an electron acceptor, usually NAD+/NADP+ or a flavin coenzyme such as FAD or FMN.-Examples:...
s that use nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, abbreviated NAD, is a coenzyme found in all living cells. The compound is a dinucleotide, since it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine base and the other nicotinamide.In metabolism, NAD is involved...
(NAD+) as a cofactor. Here, hundreds of separate types of enzymes remove electrons from their substrates and reduce
Redox
Redox reactions describe all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed....
NAD+ to NADH. This reduced cofactor is then a substrate for any of the reductase
Reductase
-Examples:* 5-alpha reductase* Dihydrofolate reductase* HMG-CoA reductase* Methemoglobin reductase* Ribonucleotide reductase* Thioredoxin reductase* E. coli nitroreductase* Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase...
s in the cell that require electrons to reduce their substrates.
Therefore, these cofactors are continuously recycled as part of metabolism. As an example, the total quantity of ATP in the human body is about 0.1 mole
Mole (unit)
The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value...
. This ATP is constantly being broken down into ADP, and then converted back into ATP. Thus, at any given time, the total amount of ATP + ADP remains fairly constant. The energy used by human cells requires the hydrolysis
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction during which molecules of water are split into hydrogen cations and hydroxide anions in the process of a chemical mechanism. It is the type of reaction that is used to break down certain polymers, especially those made by condensation polymerization...
of 100 to 150 moles of ATP daily, which is around 50 to 75 kg. In typical situations, humans use up their body weight of ATP over the course of the day. This means that each ATP molecule is recycled 1000 to 1500 times daily.
Evolution
Organic cofactors, such as ATPAdenosine triphosphate
Adenosine-5'-triphosphate is a multifunctional nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme. It is often called the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism...
and NADH, are present in all known forms of life and form a core part of metabolism
Metabolism
Metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that happen in the cells of living organisms to sustain life. These processes allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. Metabolism is usually divided into two categories...
. Such universal conservation indicates that these molecules evolved very early in the development of living things. At least some of the current set of cofactors may, therefore, have been present in the last universal ancestor
Last universal ancestor
The last universal ancestor , also called the last universal common ancestor , or the cenancestor, is the most recent organism from which all organisms now living on Earth descend. Thus it is the most recent common ancestor of all current life on Earth...
, which lived about 4 billion years ago.
Organic cofactors may have been present even earlier in the history of life
Timeline of evolution
This timeline of evolution of life outlines the major events in the development of life on planet Earth since it first originated until the present day. In biology, evolution is any change across successive generations in the heritable characteristics of biological populations...
on Earth. It is interesting to note that the nucleotide adenosine is present in cofactors that catalyse many basic metabolic reactions such as methyl, acyl, and phosphoryl group transfer, as well as redox
Redox
Redox reactions describe all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed....
reactions. This ubiquitous chemical scaffold has, therefore, been proposed to be a remnant of the RNA world
RNA world hypothesis
The RNA world hypothesis proposes that life based on ribonucleic acid pre-dates the current world of life based on deoxyribonucleic acid , RNA and proteins. RNA is able both to store genetic information, like DNA, and to catalyze chemical reactions, like an enzyme protein...
, with early ribozyme
Ribozyme
A ribozyme is an RNA molecule with a well defined tertiary structure that enables it to catalyze a chemical reaction. Ribozyme means ribonucleic acid enzyme. It may also be called an RNA enzyme or catalytic RNA. Many natural ribozymes catalyze either the hydrolysis of one of their own...
s evolving to bind a restricted set of nucleotides and related compounds. Adenosine-based cofactors are thought to have acted as interchangeable adaptors that allowed enzymes and ribozymes to bind new cofactors through small modifications in existing adenosine-binding domain
Protein domain
A protein domain is a part of protein sequence and structure that can evolve, function, and exist independently of the rest of the protein chain. Each domain forms a compact three-dimensional structure and often can be independently stable and folded. Many proteins consist of several structural...
s, which had originally evolved to bind a different cofactor. This process of adapting a pre-evolved structure for a novel use is referred to as exaptation
Exaptation
Exaptation, cooption, and preadaptation are related terms referring to shifts in the function of a trait during evolution. For example, a trait can evolve because it served one particular function, but subsequently it may come to serve another. Exaptations are common in both anatomy and behaviour...
.
A computational method, IPRO, recently predicted mutations that experimentally switched the cofactor specificity of Candida boidinii xylose reductase from NADPH to NADH. Details on how to download the software implemented in Python and experimental testing of predictions are outlined in the following paper.
History
The first organic cofactor to be discovered was NAD+, which was identified by Arthur HardenArthur Harden
Sir Arthur Harden FRS was an English biochemist. He shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1929 with Hans Karl August Simon von Euler-Chelpin for their investigations into the fermentation of sugar and fermentative enzymes....
and William Youndin 1906. They noticed that adding boiled and filtered yeast
Yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic micro-organisms classified in the kingdom Fungi, with 1,500 species currently described estimated to be only 1% of all fungal species. Most reproduce asexually by mitosis, and many do so by an asymmetric division process called budding...
extract greatly accelerated alcoholic fermentation in unboiled yeast extracts. They called the unidentified factor responsible for this effect a coferment. Through a long and difficult purification from yeast extracts, this heat-stable factor was identified as a nucleotide
Nucleotide
Nucleotides are molecules that, when joined together, make up the structural units of RNA and DNA. In addition, nucleotides participate in cellular signaling , and are incorporated into important cofactors of enzymatic reactions...
sugar phosphate by Hans von Euler-Chelpin
Hans von Euler-Chelpin
Hans Karl August Simon von Euler-Chelpin was a German-born Swedish biochemist. He won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1929 with Arthur Harden for their investigations on the fermentation of sugar and fermentative enzymes.He was professor of general and organic chemistry at Stockholm University...
. Other cofactors were identified throughout the early 20th century, with ATP being isolated in 1929 by Karl Lohmann, and coenzyme A being discovered in 1945 by Fritz Albert Lipmann
Fritz Albert Lipmann
Fritz Albert Lipmann FRS was a German-American biochemist and a co-discoverer in 1945 of coenzyme A. For this, together with other research on coenzyme A, he was awarded half the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1953 .Lipmann was born in Königsberg, Germany to a Jewish family.Lipmann...
.
The functions of these molecules were at first mysterious, but, in 1936, Otto Heinrich Warburg
Otto Heinrich Warburg
Otto Heinrich Warburg , son of physicist Emil Warburg, was a German physiologist, medical doctor and Nobel laureate. He served as an officer in the elite Uhlan during the First World War and won the Iron Cross for bravery. Warburg was one of the twentieth century's leading biochemists...
identified the function of NAD+ in hydride transfer. This discovery was followed in the early 1940s by the work of Herman Kalckar
Herman Kalckar
Herman Moritz Kalckar was a Danish biochemist who pioneered the study of cellular respiration. Trained as a medical doctor at the University of Copenhagen, Kalckar then conducted research for his Ph. D. in Ejnar Lundsgaard's physiology laboratory, work which helped establish a fundamental...
, who established the link between the oxidation of sugars and the generation of ATP. This confirmed the central role of ATP in energy transfer that had been proposed by Fritz Albert Lipmann in 1941. Later, in 1949, Morris Friedkin and Albert L. Lehninger
Albert L. Lehninger
Albert Lester Lehninger was an American biochemist in the field of bioenergetics. He made fundamental contributions to the current understanding of metabolism at a molecular level. In 1948, he discovered, with Eugene P...
proved that NAD+ linked metabolic pathways such as the citric acid cycle and the synthesis of ATP.
Non-enzymatic cofactors
The term is used in other areas of biology to refer more broadly to non-protein (or even protein) molecules that either activate, inhibit, or are required for the protein to function. For example, ligandsLigand (biochemistry)
In biochemistry and pharmacology, a ligand is a substance that forms a complex with a biomolecule to serve a biological purpose. In a narrower sense, it is a signal triggering molecule, binding to a site on a target protein.The binding occurs by intermolecular forces, such as ionic bonds, hydrogen...
such as hormones that bind to and activate receptor proteins
Receptor (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a receptor is a molecule found on the surface of a cell, which receives specific chemical signals from neighbouring cells or the wider environment within an organism...
are termed cofactors or coactivators, whereas molecules that inhibit receptor proteins are termed corepressors.
External links
- Cofactors lecture (Powerpoint file)
- The CoFactor Database

