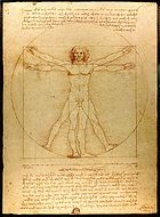
Science and inventions of Leonardo da Vinci
Overview
Leonardo da Vinci was an Italian polymath
, regarded as the epitome of the "Renaissance Man", displaying skills in numerous diverse areas of study. Whilst most famous for his paintings such as the Mona Lisa
and the Last Supper, Leonardo is also renowned as a scientist, engineer and inventor. The areas of his scientific study included aeronautics
, anatomy
, astronomy
, botany
, cartography
, civil engineering
, chemistry
, geology
, geometry
, hydrodynamics, mathematics
, mechanical engineering
, optics
, physics
, pyrotechnics
and zoology
.
While the full extent of his scientific studies has only become recognized in the last 150 years, he was, during his lifetime, employed for his engineering and skill of invention.
Polymath
A polymath is a person whose expertise spans a significant number of different subject areas. In less formal terms, a polymath may simply be someone who is very knowledgeable...
, regarded as the epitome of the "Renaissance Man", displaying skills in numerous diverse areas of study. Whilst most famous for his paintings such as the Mona Lisa
Mona Lisa
Mona Lisa is a portrait by the Italian artist Leonardo da Vinci. It is a painting in oil on a poplar panel, completed circa 1503–1519...
and the Last Supper, Leonardo is also renowned as a scientist, engineer and inventor. The areas of his scientific study included aeronautics
Aeronautics
Aeronautics is the science involved with the study, design, and manufacturing of airflight-capable machines, or the techniques of operating aircraft and rocketry within the atmosphere...
, anatomy
Anatomy
Anatomy is a branch of biology and medicine that is the consideration of the structure of living things. It is a general term that includes human anatomy, animal anatomy , and plant anatomy...
, astronomy
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
, botany
Botany
Botany, plant science, or plant biology is a branch of biology that involves the scientific study of plant life. Traditionally, botany also included the study of fungi, algae and viruses...
, cartography
Cartography
Cartography is the study and practice of making maps. Combining science, aesthetics, and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality can be modeled in ways that communicate spatial information effectively.The fundamental problems of traditional cartography are to:*Set the map's...
, civil engineering
Civil engineering
Civil engineering is a professional engineering discipline that deals with the design, construction, and maintenance of the physical and naturally built environment, including works like roads, bridges, canals, dams, and buildings...
, chemistry
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
, geology
Geology
Geology is the science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which it evolves. Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth, as it provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates...
, geometry
Geometry
Geometry arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers ....
, hydrodynamics, mathematics
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, mechanical engineering
Mechanical engineering
Mechanical engineering is a discipline of engineering that applies the principles of physics and materials science for analysis, design, manufacturing, and maintenance of mechanical systems. It is the branch of engineering that involves the production and usage of heat and mechanical power for the...
, optics
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
, physics
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, pyrotechnics
Pyrotechnics
Pyrotechnics is the science of using materials capable of undergoing self-contained and self-sustained exothermic chemical reactions for the production of heat, light, gas, smoke and/or sound...
and zoology
Zoology
Zoology |zoölogy]]), is the branch of biology that relates to the animal kingdom, including the structure, embryology, evolution, classification, habits, and distribution of all animals, both living and extinct...
.
While the full extent of his scientific studies has only become recognized in the last 150 years, he was, during his lifetime, employed for his engineering and skill of invention.

