
Ruthenium(III) acetylacetonate
Encyclopedia
Ruthenium acetylacetonate is a coordination complex with the formula Ru
(acac
)3, where acac is acetylacetonate. This compound exists as a dark violet solid that is soluble in most organic solvents. It is an example of a homoleptic
trisacetylacetonato complex, that is a complex that only has acac ligands.
and acetylacetone
in the presence of potassium bicarbonate
. Since then, alternative synthetic routes have been examined, but the original procedure remains useful with minor variations:
with five d-electrons. Because Ru(acac)3 is low spin, there is one unpaired d electron, causing this compound to be paramagnetic. Ru(acac)3 has a magnetic susceptibility, χM, of 3.032×10−6 cm3/mol with an effective magnetic moment, μeff, of 1.66 μB. As a solution in DMF
, the compound oxidizes at 0.593 and reduces at -1.223 V vs the ferrocene
/ferrocenium couple.
Reduction of Ru(acac)3 in the presence of alkenes affords the related diolefin complexes. Typically, such reactions are conducted with zinc
amalgam
in moist tetrahydrofuran
:
The resulting compounds are rare examples of metal-alkene complexes that reversibly sustain oxidation:
Ruthenium
Ruthenium is a chemical element with symbol Ru and atomic number 44. It is a rare transition metal belonging to the platinum group of the periodic table. Like the other metals of the platinum group, ruthenium is inert to most chemicals. The Russian scientist Karl Ernst Claus discovered the element...
(acac
Acac
ACAC may refer to:* American Council for Accredited Certification, a private, non-profit certifying body* Atlanta Contemporary Art Center, a contemporary art museum in Atlanta* ACAC consortium, a subsidiary of China Aviation Industry Corporation...
)3, where acac is acetylacetonate. This compound exists as a dark violet solid that is soluble in most organic solvents. It is an example of a homoleptic
Homoleptic
In inorganic chemistry, a homoleptic chemical compound is a metal compound with all ligands identical. The term uses a homo prefix to indicate that something is the same for all....
trisacetylacetonato complex, that is a complex that only has acac ligands.
Preparation
First described in 1914, tris(acetylacetonato)ruthenium (III) was first prepared by the reaction of ruthenium(III) chlorideRuthenium(III) chloride
Ruthenium chloride is the chemical compound with the formula RuCl3. "Ruthenium chloride" more commonly refers to the hydrate RuCl3·xH2O. Both the anhydrous and hydrated species are dark brown or black solids...
and acetylacetone
Acetylacetone
Acetylacetone is an organic compound that famously exists in two tautomeric forms that rapidly interconvert. The less stable tautomer is a diketone formally named pentane-2,4-dione. The more common tautomer is the enol form. The pair of tautomers rapidly interconvert and are treated as a single...
in the presence of potassium bicarbonate
Potassium bicarbonate
Potassium bicarbonate , is a colorless, odorless, slightly basic, salty substance...
. Since then, alternative synthetic routes have been examined, but the original procedure remains useful with minor variations:
- RuCl3•3H2O + MeCOCH2COMe → Ru(acac)3 + 3 HCl + 3 H2O
Structure and properties
This compound has idealized D3 symmetry. Six oxygen atoms surround the central ruthenium atom in an octahedral arrangement. The average Ru-O bond length in Ru(acac)3 is 2.00 Å. The complex is low spinCrystal field theory
Crystal field theory is a model that describes the electronic structure of transition metal compounds, all of which can be considered coordination complexes. CFT successfully accounts for some magnetic properties, colours, hydration enthalpies, and spinel structures of transition metal complexes,...
with five d-electrons. Because Ru(acac)3 is low spin, there is one unpaired d electron, causing this compound to be paramagnetic. Ru(acac)3 has a magnetic susceptibility, χM, of 3.032×10−6 cm3/mol with an effective magnetic moment, μeff, of 1.66 μB. As a solution in DMF
Dimethylformamide
Dimethylformamide is an organic compound with the formula 2NCH. Commonly abbreviated as DMF , this colourless liquid is miscible with water and the majority of organic liquids. DMF is a common solvent for chemical reactions...
, the compound oxidizes at 0.593 and reduces at -1.223 V vs the ferrocene
Ferrocene
Ferrocene is an organometallic compound with the formula Fe2. It is the prototypical metallocene, a type of organometallic chemical compound consisting of two cyclopentadienyl rings bound on opposite sides of a central metal atom. Such organometallic compounds are also known as sandwich compounds...
/ferrocenium couple.
Reduction of Ru(acac)3 in the presence of alkenes affords the related diolefin complexes. Typically, such reactions are conducted with zinc
Zinc
Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2...
amalgam
Amalgam (chemistry)
An amalgam is a substance formed by the reaction of mercury with another metal. Almost all metals can form amalgams with mercury, notable exceptions being iron and platinum. Silver-mercury amalgams are important in dentistry, and gold-mercury amalgam is used in the extraction of gold from ore.The...
in moist tetrahydrofuran
Tetrahydrofuran
Tetrahydrofuran is a colorless, water-miscible organic liquid with low viscosity at standard temperature and pressure. This heterocyclic compound has the chemical formula 4O. As one of the most polar ethers with a wide liquid range, it is a useful solvent. Its main use, however, is as a precursor...
:
- 2 Ru(acac)3 + 4 alkene + Zn → 2 Ru(acac)2(alkene)2 + Zn(acac)2
The resulting compounds are rare examples of metal-alkene complexes that reversibly sustain oxidation:
- Ru(acac)2(alkene)2
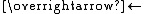 [Ru(acac)2(alkene)2]+ + e-
[Ru(acac)2(alkene)2]+ + e-

