
Runic transliteration and transcription
Encyclopedia
Runic transliteration and transcription are part of analysing a runic inscription
which involves transliteration
of the runes into Latin letters
, transcription
into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation
of the inscription into a modern language. In machine-processed text, there is a long-standing practice of formatting transliterations in boldface and transcriptions in Italic type
, as the two forms of rendering a runic text have to be kept distinct.
inscriptions are quite easy to interpret. Most Scandinavians can learn to read runic inscriptions with a little training. The Elder Futhark
inscriptions, however, are much more challenging and they demand a great deal of knowledge in historical linguistics. Standard works such as Sveriges runinskrifter
contain extensive presentations of the ways inscriptions have been interpreted throughout the centuries.
 It is practically impossible to render the runes in all the various ways that they appear in the inscriptions, and so the way they look has to be presented in pictures and in drawings.
It is practically impossible to render the runes in all the various ways that they appear in the inscriptions, and so the way they look has to be presented in pictures and in drawings.
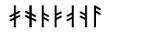
 Transliteration means that the runes are represented by a corresponding Latin letter in bold. No consideration is given to the sound the rune represented in the actual inscription, and a good example of this is the ansuz rune , which could vary greatly in shape. In the oldest Younger Futhark inscriptions, it always represented a nasal a, as in French an, but later it came to represent other phonemes such as /o/. However, some runemaster
Transliteration means that the runes are represented by a corresponding Latin letter in bold. No consideration is given to the sound the rune represented in the actual inscription, and a good example of this is the ansuz rune , which could vary greatly in shape. In the oldest Younger Futhark inscriptions, it always represented a nasal a, as in French an, but later it came to represent other phonemes such as /o/. However, some runemaster
s continued to use the ansuz rune for an a phoneme. The ansuz rune is always transliterated as o from the Younger Futhark, and consequently, the transliteration mon represents Old Norse man in a runestone from Bällsta, and hon represents Old Norse han in the Frösö Runestone
, while forþom represents Old Norse forðom in an inscription from Replösa.
Sometimes the runes are "dotted" which means that a dot has been added, and in transliterations dotted runes are treated differently from ordinary runes. Dotted u, k and i are transliterated as y, g and e though they are rather variations of the non-dotted runes than runes in their own right.
Bind rune
s are marked with an arch. Some bind runes look in a way that makes it impossible to know which rune preceded the other, and then the scholar has to test the various combinations that give a comprehensible word. Thus all transliterations of bind runes are scholarly interpretations.
Runes that are known from older depictions but that have since disappeared are rendered within square brackets.
Runic alphabet
The runic alphabets are a set of related alphabets using letters known as runes to write various Germanic languages before the adoption of the Latin alphabet and for specialized purposes thereafter...
which involves transliteration
Transliteration
Transliteration is a subset of the science of hermeneutics. It is a form of translation, and is the practice of converting a text from one script into another...
of the runes into Latin letters
Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet, also called the Roman alphabet, is the most recognized alphabet used in the world today. It evolved from a western variety of the Greek alphabet called the Cumaean alphabet, which was adopted and modified by the Etruscans who ruled early Rome...
, transcription
Transcription (linguistics)
Transcription in the linguistic sense is the systematic representation of language in written form. The source can either be utterances or preexisting text in another writing system, although some linguists only consider the former as transcription.Transcription should not be confused with...
into a normalized spelling in the language of the inscription, and translation
Translation
Translation is the communication of the meaning of a source-language text by means of an equivalent target-language text. Whereas interpreting undoubtedly antedates writing, translation began only after the appearance of written literature; there exist partial translations of the Sumerian Epic of...
of the inscription into a modern language. In machine-processed text, there is a long-standing practice of formatting transliterations in boldface and transcriptions in Italic type
Italic type
In typography, italic type is a cursive typeface based on a stylized form of calligraphic handwriting. Owing to the influence from calligraphy, such typefaces often slant slightly to the right. Different glyph shapes from roman type are also usually used—another influence from calligraphy...
, as the two forms of rendering a runic text have to be kept distinct.
Overview
By not only showing the original inscription, but also transliterating, transcribing and translating, scholars present the analysis in a way that allows the reader to follow their interpretation of the runes. Every step has its challenges, but most Younger FutharkYounger Futhark
The Younger Futhark, also called Scandinavian runes, is a runic alphabet, a reduced form of the Elder Futhark, consisting of only 16 characters, in use from ca. 800 CE...
inscriptions are quite easy to interpret. Most Scandinavians can learn to read runic inscriptions with a little training. The Elder Futhark
Elder Futhark
The Elder Futhark is the oldest form of the runic alphabet, used by Germanic tribes for Northwest Germanic and Migration period Germanic dialects of the 2nd to 8th centuries for inscriptions on artifacts such as jewellery, amulets, tools, weapons and runestones...
inscriptions, however, are much more challenging and they demand a great deal of knowledge in historical linguistics. Standard works such as Sveriges runinskrifter
Sveriges runinskrifter
Sveriges runinskrifter is a multi-volume catalog of rune inscriptions found in various Swedish provinces. The earliest volume of this ongoing series dates to 1900, and as of 1981, 15 volumes had been published.Sveriges runinskrifter established the standard cataloging system for Swedish rune...
contain extensive presentations of the ways inscriptions have been interpreted throughout the centuries.
Runes

Transliteration
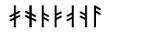

Runemaster
A runemaster or runecarver is a specialist in making runestones.Most early medieval Scandinavians were probably literate in runes, and most people probably carved messages on pieces of bone and wood. However, it was difficult to make runestones, and in order to master it one also needed to be a...
s continued to use the ansuz rune for an a phoneme. The ansuz rune is always transliterated as o from the Younger Futhark, and consequently, the transliteration mon represents Old Norse man in a runestone from Bällsta, and hon represents Old Norse han in the Frösö Runestone
Frösö Runestone
Frösöstenen is the northern-most raised runestone in the World and Jämtland's only runestone. It originally stood at the tip of ferry terminal on the sound between the island of Frösön and Östersund.On it is inscribed:...
, while forþom represents Old Norse forðom in an inscription from Replösa.
Sometimes the runes are "dotted" which means that a dot has been added, and in transliterations dotted runes are treated differently from ordinary runes. Dotted u, k and i are transliterated as y, g and e though they are rather variations of the non-dotted runes than runes in their own right.
Bind rune
Bind rune
A bind rune is a ligature of two or more runes. They are extremely rare in Viking Age inscriptions, but are common in pre-Viking Age and in post-Viking Age inscriptions....
s are marked with an arch. Some bind runes look in a way that makes it impossible to know which rune preceded the other, and then the scholar has to test the various combinations that give a comprehensible word. Thus all transliterations of bind runes are scholarly interpretations.
Runes that are known from older depictions but that have since disappeared are rendered within square brackets.

