
Rock processor
Encyclopedia
Rock was a multithreading, multicore
, SPARC
microprocessor
developed at Sun Microsystems
. Now canceled, it was a separate development from the CoolThreads/Niagara (UltraSPARC T1
, T2
, and SPARC T3) family of processors.
Rock aimed at higher per-thread performance, higher floating-point performance, and greater SMP
scalability than the Niagara family. The Rock processor targeted traditional high-end data-facing workloads, such as back-end database servers, as well as floating-point intensive high-performance computing
workloads, whereas the Niagara family targets network-facing workloads such as web servers.
 The Rock processor implements the 64-bit SPARC V9 instruction set and the VIS
The Rock processor implements the 64-bit SPARC V9 instruction set and the VIS
3.0 SIMD
multimedia instruction set extension. Each Rock processor has 16 cores, with each core capable of running two threads simultaneously, yielding 32 threads per chip. Servers built with Rock use FB-DIMMs to increase reliability, speed and density of memory systems. The Rock processor uses a 65 nm manufacturing process for a design frequency of 2.3 GHz. The maximum power consumption of the Rock processor chip is approximately 250 W.
s. Sun designed the chip this way because server workloads usually have high re-utilization in data and instruction across processes and threads but low number of floating-point operations in general. Thus sharing hardware resources among the four cores in a cluster leads to significant savings in area and power but low impact to performance.
. Hardware scout uses otherwise idle chip execution resources to perform prefetching during cache misses.
In March 2006, Marc Tremblay
, Vice President and Chief Architect for Sun's Scalable Systems Group, gave a presentation at the Xerox Palo Alto Research Center (PARC) on thread-level parallelism, hardware scouting, and thread-level speculation
. These multithreading technologies were expected to be included in the Rock processor.
In August 2007, Sun confirmed that Rock would be the first production processor to support transactional memory
. To provide the functionality, two new instructions were introduced (chkpt, commit) with one new status register (cps). The instruction chkpt <fail_pc> is used to begin a transaction and commit to commit the transaction. If transaction abort condition is detected, jump to <fail_pc> is issued and cps can be used to determine the reason. The support is best-effort based, as in addition to data conflicts, transactions can be aborted by other reasons. These include TLB misses, interrupts, certain commonly used function call sequences and "difficult" instructions (e.g., division). Nevertheless, many (arguably fine-grained) code blocks requiring synchronization could have benefited from transactional memory support of the Rock processor.
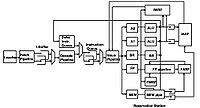
In February 2008, Marc Tremblay announced a unique feature called "out-of-order retirement" at the ISSCC. The benefits include replacing the "traditional instruction window with this much smaller deferred queue".
In April 2008, Sun engineers presented the transactional memory interface at Transact 2008, and the Adaptive Transactional Memory Test Platform simulator was announced to be made available to the general public shortly after.
line. Details of the server specifications were released in OpenSolaris
Architecture Review case FWARC/2008/761.
(LDOMs), independent system controller (SC), and Fault Management Architecture (FMA) Domain Services. The FMA feature was originally referenced to FWARC/2006/141, but this was closed and extended in FWARC/2008/455 "to successfully diagnose PCI fabric errors that occur in root domains."
(PCIe) hot-pluggable slots as well as a bridge to older PCI eXtended (PCI-X
)).
multithreaded 10 Gigabit Ethernet chip.
discussed the "taping out" of Rock to be on schedule for later in 2005.
In January 2007, Sun announced the tape-out
of Rock.
In April 2007, Sun CEO Jonathan I. Schwartz
blogged an image of a BGA
-packaged Rock chip, labeled UltraSPARC RK, and disclosed that it could address 256 terabyte
s of virtual memory in a single system running Solaris.
In May 2007, Sun announced the first silicon of Rock booting Solaris successfully.
In August 2007, Sun released details on the use of transactional memory in the Rock architecture.
In December 2007, Sun announced that Rock would be delayed from 2008 until 2009 due to "entirely new design and given its uniqueness and complexity".
In 2008, Mark Moir presented "Rock's Transactional Memory and How to Exploit It" at Sun Labs Open House 2008, discussing transactional memory as well as scouting threads and how these mitigated the computing problems not solved by innovative use of massive thread counts of slower processors.
In September 2008, the OpenSolaris
project started to organize patches for the Rock-based SuperNova platforms.
In January 2009, Sun CEO Jonathan Schwartz announced Rock was still on track for a 2009 release.
On 10 March 2009 Dave Dice, Yossi Lev, Mark Moir and Dan Nussbaum presented "Early Experience with a Commercial Hardware Transactional Memory Implementation" at the Fourteenth International Conference on Architectural Support for Programming Languages and Operating Systems (ASPLOS '09). They published their "experience with the hardware transactional memory (HTM) feature of two pre-production revisions of a new commercial multicore processor", Rock, by Sun. This paper was published in May 2009.
On April 20, 2009, Sun and Oracle Corporation
announced that they had entered into a definitive agreement
under which Oracle would acquire Sun.
On 12 June 2009, a posting on a Sun blog announced a technical NDA-only presentation on ROCK on July 14, 2009 at the Hamburg, Germany OpenSolaris Users Group Meeting.
On 15 June 2009, the New York Times reported that "two people briefed on Sun’s plans" said the Rock project was canceled. Sun did not comment.
On 17 June 2009, The EE Times
reported that "Sun did not submit a paper on Rock... leading to speculation the company may have canceled the chip."
On Wednesday, 24 June 2009, a presentation on "Speculative Threading & Parallelization" featured "A Novel Pipeline Architecture Implemented in Sun's ROCK Processor" at The 36th International Symposium on Computer Architecture
.
On 6 August 2009, support for Rock was removed from the OpenSolaris Project.
On 13 August 2009, a presentation on "NZTM: Nonblocking Zero-indirection Transactional Memory" written by Fuad Tabba, Mark Moir, James Goodman, Andrew Hay, and Cong Wang, was presented at the 21st ACM Symposium on Parallelism in Algorithms and Architectures in Calgary, Canada. The NZSTM algorithm performance was evaluated on Sun’s forthcoming Rock processor.
On 11 September 2009, The Register
reported that the Rock processor was left out of the SPARC processor roadmap then being shown to Sun's customers and partners.
On 15 September 2009, the paper "tm_db: A Generic Debugging Library for Transactional Programs" written by Yossi Lev and Maurice Herlihy, was presented at The Eighteenth International Conference on Parallel Architectures and Compilation Techniques (PACT) Raleigh, North Carolina.
On 26 October 2009, Dave Dice, Yossi Lev, Mark Moir and Dan Nussbaum expanded a formerly published paper "Early Experience with a Commercial Hardware Transactional Memory Implementation" which was presented at the Fourteenth International Conference on Architectural Support for Programming Languages and Operating Systems (ASPLOS '09).
On January 27, 2010, Oracle announced it had completed its acquisition of Sun.
On 5 April 2010, Dave Dice, Yossi Lev, Virendra Marathe, Mark Moir, Marek Olszewski and Dan Nussbaum released a paper "Simplifying Concurrent Algorithms by Exploiting Hardware Transactional Memory" to be presented at the 22nd ACM
Symposium on Parallelism in Algorithms and Architectures
(SPAA 2010).
On 5 April 2010, Dave Dice and Nir Shavit released a paper "TLRW: Return of the Read-Write Lock" to be presented at SPAA 2010.
On 12 May 2010, Reuters
reported that Oracle CEO Larry Ellison
shut down the Rock project when Oracle acquired Sun, quoting him as saying, "It was just madness to continue that project."
Multicore
Multicore may refer to:* Multi-core processor ** Multicore Association, founded in 2005, a non-profit, industry consortium focused on multicore technology* multicore cable, a generic term for an electrical cable that has multiple cores...
, SPARC
SPARC
SPARC is a RISC instruction set architecture developed by Sun Microsystems and introduced in mid-1987....
microprocessor
Microprocessor
A microprocessor incorporates the functions of a computer's central processing unit on a single integrated circuit, or at most a few integrated circuits. It is a multipurpose, programmable device that accepts digital data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory, and...
developed at Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems, Inc. was a company that sold :computers, computer components, :computer software, and :information technology services. Sun was founded on February 24, 1982...
. Now canceled, it was a separate development from the CoolThreads/Niagara (UltraSPARC T1
UltraSPARC T1
|right|262px|UltraSPARC T1 processorSun Microsystems' UltraSPARC T1 microprocessor, known until its 14 November 2005 announcement by its development codename "Niagara", is a multithreading, multicore CPU...
, T2
UltraSPARC T2
Sun Microsystems' UltraSPARC T2 microprocessor is a multithreading, multi-core CPU. It is a member of the SPARC family, and the successor to the UltraSPARC T1. The chip is sometimes referred to by its codename, Niagara 2...
, and SPARC T3) family of processors.
Rock aimed at higher per-thread performance, higher floating-point performance, and greater SMP
Symmetric multiprocessing
In computing, symmetric multiprocessing involves a multiprocessor computer hardware architecture where two or more identical processors are connected to a single shared main memory and are controlled by a single OS instance. Most common multiprocessor systems today use an SMP architecture...
scalability than the Niagara family. The Rock processor targeted traditional high-end data-facing workloads, such as back-end database servers, as well as floating-point intensive high-performance computing
High-performance computing
High-performance computing uses supercomputers and computer clusters to solve advanced computation problems. Today, computer systems approaching the teraflops-region are counted as HPC-computers.-Overview:...
workloads, whereas the Niagara family targets network-facing workloads such as web servers.
Processor core



Visual Instruction Set
Visual Instruction Set, or VIS, is a SIMD instruction set for SPARC V9 microprocessors developed by Sun Microsystems. There are three versions of VIS: VIS 1, VIS 2 and VIS 2+...
3.0 SIMD
SIMD
Single instruction, multiple data , is a class of parallel computers in Flynn's taxonomy. It describes computers with multiple processing elements that perform the same operation on multiple data simultaneously...
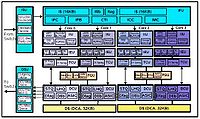
multimedia instruction set extension. Each Rock processor has 16 cores, with each core capable of running two threads simultaneously, yielding 32 threads per chip. Servers built with Rock use FB-DIMMs to increase reliability, speed and density of memory systems. The Rock processor uses a 65 nm manufacturing process for a design frequency of 2.3 GHz. The maximum power consumption of the Rock processor chip is approximately 250 W.
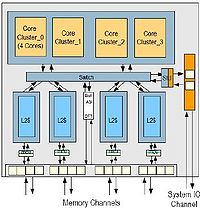
Core cluster
The 16 cores in Rock are arranged in four core clusters. The cores in a cluster share a 32 KB instruction cache, two 32 KB data caches, and two floating point unitFloating point unit
A floating-point unit is a part of a computer system specially designed to carry out operations on floating point numbers. Typical operations are addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and square root...
s. Sun designed the chip this way because server workloads usually have high re-utilization in data and instruction across processes and threads but low number of floating-point operations in general. Thus sharing hardware resources among the four cores in a cluster leads to significant savings in area and power but low impact to performance.
Unconventional features
In 2005, Sun publicly disclosed a feature in the Rock processor called hardware scoutHardware scout
Hardware scout is a technique that uses otherwise idle processor execution resources to perform prefetching during cache misses. When a thread is stalled by a cache miss, the processor pipeline checkpoints the register file, switches to runahead mode, and continues to issue instructions from the...
. Hardware scout uses otherwise idle chip execution resources to perform prefetching during cache misses.
In March 2006, Marc Tremblay
Marc Tremblay
Marc Tremblay is a distinguished engineer at Microsoft. Prior to joining Microsoft in April 2009, he was senior vice president and chief technology officer of the microelectronics business unit at Sun Microsystems. He was instrumental in the design of various microprocessors at Sun, including the...
, Vice President and Chief Architect for Sun's Scalable Systems Group, gave a presentation at the Xerox Palo Alto Research Center (PARC) on thread-level parallelism, hardware scouting, and thread-level speculation
Speculative multithreading
Speculative multithreading , also known as thread level speculation , is a dynamic parallelization technique that depends on out-of-order execution to achieve speedup on multiprocessor CPUs. It is a kind of speculative execution that occurs at the thread level as opposed to the instruction level....
. These multithreading technologies were expected to be included in the Rock processor.
In August 2007, Sun confirmed that Rock would be the first production processor to support transactional memory
Transactional memory
Transactional memory attempts to simplify parallel programming by allowing a group of load and store instructions to execute in an atomic way. It is a concurrency control mechanism analogous to database transactions for controlling access to shared memory in concurrent computing.-Hardware vs...
. To provide the functionality, two new instructions were introduced (chkpt, commit) with one new status register (cps). The instruction chkpt <fail_pc> is used to begin a transaction and commit to commit the transaction. If transaction abort condition is detected, jump to <fail_pc> is issued and cps can be used to determine the reason. The support is best-effort based, as in addition to data conflicts, transactions can be aborted by other reasons. These include TLB misses, interrupts, certain commonly used function call sequences and "difficult" instructions (e.g., division). Nevertheless, many (arguably fine-grained) code blocks requiring synchronization could have benefited from transactional memory support of the Rock processor.
In February 2008, Marc Tremblay announced a unique feature called "out-of-order retirement" at the ISSCC. The benefits include replacing the "traditional instruction window with this much smaller deferred queue".
In April 2008, Sun engineers presented the transactional memory interface at Transact 2008, and the Adaptive Transactional Memory Test Platform simulator was announced to be made available to the general public shortly after.
Server platforms
The Rock processor was intended to be used in Sun's proposed Supernova (server)Supernova (server)
The Supernova server line is under development at Sun Microsystems.The UltraSPARC Rock slots into this line of servers retaining this code name...
line. Details of the server specifications were released in OpenSolaris
OpenSolaris
OpenSolaris was an open source computer operating system based on Solaris created by Sun Microsystems. It was also the name of the project initiated by Sun to build a developer and user community around the software...
Architecture Review case FWARC/2008/761.
Physical resources
The Physical Resource Inventory (PRI) specification of ARC 2008/761 indicates the Supernova platforms would support: IEEE 1275 OpenFirmware, platform virtualization through Logical DomainsLogical Domains
Logical Domains is the server virtualization and partitioning technology from Sun Microsystems released in April 2007. It has been re-branded as Oracle VM Server for SPARC since Oracle Corporation completed the acquisition of Sun in January 2010. Each domain is a full virtual machine with a...
(LDOMs), independent system controller (SC), and Fault Management Architecture (FMA) Domain Services. The FMA feature was originally referenced to FWARC/2006/141, but this was closed and extended in FWARC/2008/455 "to successfully diagnose PCI fabric errors that occur in root domains."
Input/output description
The iodevice Machine Description (MD) Node Specification of ARC 2008/761 indicates support for both PCI ExpressPCI Express
PCI Express , officially abbreviated as PCIe, is a computer expansion card standard designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X, and AGP bus standards...
(PCIe) hot-pluggable slots as well as a bridge to older PCI eXtended (PCI-X
PCI-X
PCI-X, short for PCI-eXtended, is a computer bus and expansion card standard that enhances the 32-bit PCI Local Bus for higher bandwidth demanded by servers. It is a double-wide version of PCI, running at up to four times the clock speed, but is otherwise similar in electrical implementation and...
)).
Input/output expandability
Hitendra Zhangada, in the SPS Common Software Features Engineering group, at Sun described a variety of PCIe parameters in software which support the hardware platforms. "Bronze" servers would support PCIe slots 0-5. "Silver" servers would support I/O boards 0-1 and PCIe slots 0-7 for each board. "Platinum" servers would support I/O boards 0-3 and PCIe slots 0-7 for each board. "Silver-II" servers would support PCIe slots 00-19. "Platinum-II" servers would support boards 0-7 and slots 0-3 for each board.Common features
Zhangada sponsored a fast-track software ARC case describing Supernova platforms AT480 and AT880. Ravi Subbarao, Director of Enterprise Systems Software at Sun, sponsored ARC 2008/761, describing platforms bindings and interface changes for MD, PRI and OpenBoot devices.AT7180
The SPARC Enterprise AT7180 was speculated to be a single socket model handling as many as 32 hardware threads.AT7280
The SPARC Enterprise AT7280 was speculated to be a dual socket model handling as many as 64 hardware threads.AT7480
The Supernova Silver-II was proposed to be named the SPARC Enterprise AT7480, a quad socket model reported to handle as many as 128 hardware threads, based on the PCI Express bus architecture with Open Boot firmware.AT7880
The Supernova Platinum-II was proposed to be named the SPARC Enterprise AT7880, an eight-socket model reported to handle as many as 256 hardware threads, based on the PCI Express bus architecture with Open Boot firmware. Pingchung Lee explained in a December 10, 2008 email for ARC case 2008/761 that the AT7880 would have eight individual CPU boards, each with one Sun NeptuneSun Neptune
Neptune, also known as Sun Multithreaded 10 GbE, is a dual 10 Gbit/s, multithreaded, PCIe x8-based network card. It was developed and originally produced by Sun Microsystems, and later licensed to Marvell....
multithreaded 10 Gigabit Ethernet chip.
Product pre-release history
In February 2005, Sun CEO Scott McNealyScott McNealy
Scott McNealy is an American business executive. He co-founded computer technology company Sun Microsystems in 1982 along with Vinod Khosla, Bill Joy, and Andy Bechtolsheim.-Biography:...
discussed the "taping out" of Rock to be on schedule for later in 2005.
In January 2007, Sun announced the tape-out
Tape-out
In electronics design, tape-out or tapeout is the final result of the design cycle for integrated circuits or printed circuit boards, the point at which the artwork for the photomask of a circuit is sent for manufacture....
of Rock.
In April 2007, Sun CEO Jonathan I. Schwartz
Jonathan I. Schwartz
Jonathan Ian Schwartz is the co-founder and Chief Executive Officer of Picture of Health. He was formerly the President and CEO of Sun Microsystems prior to its acquisition by Oracle, and previously the founder and Chief Executive Officer of Lighthouse Design, Ltd., a software company focused on...
blogged an image of a BGA
Ball grid array
A ball grid array is a type of surface-mount packaging used for integrated circuits.- Description :The BGA is descended from the pin grid array , which is a package with one face covered with pins in a grid pattern. These pins conduct electrical signals from the integrated circuit to the printed...
-packaged Rock chip, labeled UltraSPARC RK, and disclosed that it could address 256 terabyte
Terabyte
The terabyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. The prefix tera means 1012 in the International System of Units , and therefore 1 terabyte is , or 1 trillion bytes, or 1000 gigabytes. 1 terabyte in binary prefixes is 0.9095 tebibytes, or 931.32 gibibytes...
s of virtual memory in a single system running Solaris.
In May 2007, Sun announced the first silicon of Rock booting Solaris successfully.
In August 2007, Sun released details on the use of transactional memory in the Rock architecture.
In December 2007, Sun announced that Rock would be delayed from 2008 until 2009 due to "entirely new design and given its uniqueness and complexity".
In 2008, Mark Moir presented "Rock's Transactional Memory and How to Exploit It" at Sun Labs Open House 2008, discussing transactional memory as well as scouting threads and how these mitigated the computing problems not solved by innovative use of massive thread counts of slower processors.
In September 2008, the OpenSolaris
OpenSolaris
OpenSolaris was an open source computer operating system based on Solaris created by Sun Microsystems. It was also the name of the project initiated by Sun to build a developer and user community around the software...
project started to organize patches for the Rock-based SuperNova platforms.
In January 2009, Sun CEO Jonathan Schwartz announced Rock was still on track for a 2009 release.
On 10 March 2009 Dave Dice, Yossi Lev, Mark Moir and Dan Nussbaum presented "Early Experience with a Commercial Hardware Transactional Memory Implementation" at the Fourteenth International Conference on Architectural Support for Programming Languages and Operating Systems (ASPLOS '09). They published their "experience with the hardware transactional memory (HTM) feature of two pre-production revisions of a new commercial multicore processor", Rock, by Sun. This paper was published in May 2009.
On April 20, 2009, Sun and Oracle Corporation
Oracle Corporation
Oracle Corporation is an American multinational computer technology corporation that specializes in developing and marketing hardware systems and enterprise software products – particularly database management systems...
announced that they had entered into a definitive agreement
Sun acquisition by Oracle
The acquisition of Sun Microsystems by Oracle Corporation was completed by Oracle on January 27, 2010. Significantly, Oracle, previously only a software vendor, now owned both hardware and software product lines from Sun The acquisition of Sun Microsystems by Oracle Corporation was completed by...
under which Oracle would acquire Sun.
On 12 June 2009, a posting on a Sun blog announced a technical NDA-only presentation on ROCK on July 14, 2009 at the Hamburg, Germany OpenSolaris Users Group Meeting.
On 15 June 2009, the New York Times reported that "two people briefed on Sun’s plans" said the Rock project was canceled. Sun did not comment.
On 17 June 2009, The EE Times
EE Times
EE Times is an electronics industry newspaper published in the USA by UBM Electronics, a division of United Business Media. Launched in 1972 by Gerard G. Leeds of CMP Publishing. CMP was acquired by United in 1999...
reported that "Sun did not submit a paper on Rock... leading to speculation the company may have canceled the chip."
On Wednesday, 24 June 2009, a presentation on "Speculative Threading & Parallelization" featured "A Novel Pipeline Architecture Implemented in Sun's ROCK Processor" at The 36th International Symposium on Computer Architecture
International Symposium on Computer Architecture
The International Symposium on Computer Architecture is generally viewed as the top-tier academic conference on computer architecture.-External references:* in the ACM digital library.* in DBLP.* ....
.
On 6 August 2009, support for Rock was removed from the OpenSolaris Project.
On 13 August 2009, a presentation on "NZTM: Nonblocking Zero-indirection Transactional Memory" written by Fuad Tabba, Mark Moir, James Goodman, Andrew Hay, and Cong Wang, was presented at the 21st ACM Symposium on Parallelism in Algorithms and Architectures in Calgary, Canada. The NZSTM algorithm performance was evaluated on Sun’s forthcoming Rock processor.
On 11 September 2009, The Register
The Register
The Register is a British technology news and opinion website. It was founded by John Lettice, Mike Magee and Ross Alderson in 1994 as a newsletter called "Chip Connection", initially as an email service...
reported that the Rock processor was left out of the SPARC processor roadmap then being shown to Sun's customers and partners.
On 15 September 2009, the paper "tm_db: A Generic Debugging Library for Transactional Programs" written by Yossi Lev and Maurice Herlihy, was presented at The Eighteenth International Conference on Parallel Architectures and Compilation Techniques (PACT) Raleigh, North Carolina.
On 26 October 2009, Dave Dice, Yossi Lev, Mark Moir and Dan Nussbaum expanded a formerly published paper "Early Experience with a Commercial Hardware Transactional Memory Implementation" which was presented at the Fourteenth International Conference on Architectural Support for Programming Languages and Operating Systems (ASPLOS '09).
On January 27, 2010, Oracle announced it had completed its acquisition of Sun.
On 5 April 2010, Dave Dice, Yossi Lev, Virendra Marathe, Mark Moir, Marek Olszewski and Dan Nussbaum released a paper "Simplifying Concurrent Algorithms by Exploiting Hardware Transactional Memory" to be presented at the 22nd ACM
Association for Computing Machinery
The Association for Computing Machinery is a learned society for computing. It was founded in 1947 as the world's first scientific and educational computing society. Its membership is more than 92,000 as of 2009...
Symposium on Parallelism in Algorithms and Architectures
Symposium on Parallelism in Algorithms and Architectures
SPAA, the ACM Symposium on Parallelism in Algorithms and Architectures, is an academic conference in the fields of parallel computing and distributed computing...
(SPAA 2010).
On 5 April 2010, Dave Dice and Nir Shavit released a paper "TLRW: Return of the Read-Write Lock" to be presented at SPAA 2010.
On 12 May 2010, Reuters
Reuters
Reuters is a news agency headquartered in New York City. Until 2008 the Reuters news agency formed part of a British independent company, Reuters Group plc, which was also a provider of financial market data...
reported that Oracle CEO Larry Ellison
Larry Ellison
Lawrence Joseph "Larry" Ellison is the co-founder and chief executive officer of Oracle Corporation, one of the world's leading enterprise software companies. As of 2011, he is the third wealthiest American citizen, with an estimated worth of $33 billion.- Early life :Larry Ellison was born in the...
shut down the Rock project when Oracle acquired Sun, quoting him as saying, "It was just madness to continue that project."

