
Phosphoketolase
Encyclopedia
In enzymology, a phosphoketolase is an enzyme
that catalyzes
the chemical reaction
Thus, the two substrates
of this enzyme are D-xylulose 5-phosphate and phosphate
, whereas its 3 products
are acetyl phosphate, D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, and H2O
.
This enzyme belongs to the family of lyase
s, specifically the aldehyde-lyases, which cleave carbon-carbon bonds. The systematic name of this enzyme class is D-xylulose-5-phosphate D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-lyase (adding phosphate; acetyl-phosphate-forming). Other names in common use include D-xylulose-5-phosphate D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-lyase, and (phosphate-acetylating). This enzyme participates in 3 metabolic pathways
: pentose phosphate pathway
, methane metabolism, and carbon fixation
. It employs one cofactor
, thiamin diphosphate.
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that catalyzes
Catalysis
Catalysis is the change in rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of a substance called a catalyst. Unlike other reagents that participate in the chemical reaction, a catalyst is not consumed by the reaction itself. A catalyst may participate in multiple chemical transformations....
the chemical reaction
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
- D-xylulose 5-phosphate + phosphate
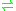 acetyl phosphate + D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate + H2O
acetyl phosphate + D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate + H2O
Thus, the two substrates
Substrate (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a substrate is a molecule upon which an enzyme acts. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions involving the substrate. In the case of a single substrate, the substrate binds with the enzyme active site, and an enzyme-substrate complex is formed. The substrate is transformed into one or...
of this enzyme are D-xylulose 5-phosphate and phosphate
Phosphate
A phosphate, an inorganic chemical, is a salt of phosphoric acid. In organic chemistry, a phosphate, or organophosphate, is an ester of phosphoric acid. Organic phosphates are important in biochemistry and biogeochemistry or ecology. Inorganic phosphates are mined to obtain phosphorus for use in...
, whereas its 3 products
Product (chemistry)
Product are formed during chemical reactions as reagents are consumed. Products have lower energy than the reagents and are produced during the reaction according to the second law of thermodynamics. The released energy comes from changes in chemical bonds between atoms in reagent molecules and...
are acetyl phosphate, D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, and H2O
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
.
This enzyme belongs to the family of lyase
Lyase
In biochemistry, a lyase is an enzyme that catalyzes the breaking of various chemical bonds by means other than hydrolysis and oxidation, often forming a new double bond or a new ring structure...
s, specifically the aldehyde-lyases, which cleave carbon-carbon bonds. The systematic name of this enzyme class is D-xylulose-5-phosphate D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-lyase (adding phosphate; acetyl-phosphate-forming). Other names in common use include D-xylulose-5-phosphate D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-lyase, and (phosphate-acetylating). This enzyme participates in 3 metabolic pathways
Metabolism
Metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that happen in the cells of living organisms to sustain life. These processes allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. Metabolism is usually divided into two categories...
: pentose phosphate pathway
Pentose phosphate pathway
The pentose phosphate pathway is a process that generates NADPH and pentoses . There are two distinct phases in the pathway. The first is the oxidative phase, in which NADPH is generated, and the second is the non-oxidative synthesis of 5-carbon sugars...
, methane metabolism, and carbon fixation
Carbon fixation
In biology, carbon fixation is the reduction of carbon dioxide to organic compounds by living organisms. The obvious example is photosynthesis. Carbon fixation requires both a source of energy such as sunlight, and an electron donor such as water. All life depends on fixed carbon. Organisms that...
. It employs one cofactor
Cofactor (biochemistry)
A cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound that is bound to a protein and is required for the protein's biological activity. These proteins are commonly enzymes, and cofactors can be considered "helper molecules" that assist in biochemical transformations....
, thiamin diphosphate.

