Oxazolidine
Encyclopedia
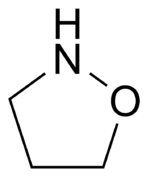
Oxazolidine is a five-membered ring compound consisting of three carbon
s, a nitrogen
, a hydrogen
, and an oxygen
. The oxygen and NH are the 1 and 3 positions, respectively. In oxazolidine derivatives, there is always a carbon between the oxygen and the nitrogen (or it would be an isoxazolidine). All of the carbons in oxazolidines are reduced (compare to oxazole
and oxazoline
). Some of their derivatives, the oxazolidinedione
s, are used as anticonvulsant
s.
paints. The rings hydrolyze
in the presence of moisture into amine
and hydroxyl
groups, which can then bind with diisocyanates to form the coating.
It is the saturated relative of Isoxazole
.
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
s, a nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
, a hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
, and an oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
. The oxygen and NH are the 1 and 3 positions, respectively. In oxazolidine derivatives, there is always a carbon between the oxygen and the nitrogen (or it would be an isoxazolidine). All of the carbons in oxazolidines are reduced (compare to oxazole
Oxazole
Oxazole is the parent compound for a vast class of heterocyclic aromatic organic compounds. These are azoles with an oxygen and a nitrogen separated by one carbon. Oxazoles are aromatic compounds but less so than the thiazoles...
and oxazoline
Oxazoline
Oxazoline is both the five-membered ring heterocyclic chemical compound with the formula C3H5NO and the class of compounds containing this ring.- See also :* Desoxazoline * Oxazole* Oxazolidine* Oxazolidinedione...
). Some of their derivatives, the oxazolidinedione
Oxazolidinedione
Oxazolidinedione is a heterocyclic chemical compound that forms the core structure of a variety anticonvulsant drugs including:* Ethadione* Paramethadione* Trimethadione...
s, are used as anticonvulsant
Anticonvulsant
The anticonvulsants are a diverse group of pharmaceuticals used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of bipolar disorder, since many seem to act as mood stabilizers, and in the treatment of neuropathic pain. The goal of an...
s.
Bisoxazolidines
Bisoxazolidines have two oxazolidine rings, and they are used as reactive diluents in polyurethanePolyurethane
A polyurethane is any polymer composed of a chain of organic units joined by carbamate links. Polyurethane polymers are formed through step-growth polymerization, by reacting a monomer with another monomer in the presence of a catalyst.Polyurethanes are...
paints. The rings hydrolyze
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction during which molecules of water are split into hydrogen cations and hydroxide anions in the process of a chemical mechanism. It is the type of reaction that is used to break down certain polymers, especially those made by condensation polymerization...
in the presence of moisture into amine
Amine
Amines are organic compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines,...
and hydroxyl
Hydroxyl
A hydroxyl is a chemical group containing an oxygen atom covalently bonded with a hydrogen atom. In inorganic chemistry, the hydroxyl group is known as the hydroxide ion, and scientists and reference works generally use these different terms though they refer to the same chemical structure in...
groups, which can then bind with diisocyanates to form the coating.
Isoxazolidines
In an isoxazolidine nitrogen and oxygen occupy positions 1 and 2 in the ring:It is the saturated relative of Isoxazole
Isoxazole
Isoxazole is an azole with an oxygen atom next to the nitrogen. It is also the class of compounds containing this ring.Isoxazole rings are found in some natural products, such as ibotenic acid. Isoxazoles also form the basis for a number of drugs, including the COX-2 inhibitor valdecoxib...
.
See also
- ImidazoleImidazoleImidazole is an organic compound with the formula C3H4N2. This aromatic heterocyclic is a diazole and is classified as an alkaloid. Imidazole refers to the parent compound, whereas imidazoles are a class of heterocycles with similar ring structure, but varying substituents...
, an analog with the oxygenOxygenOxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
replaced by a nitrogen. - ThiazoleThiazoleThiazole, or 1,3-thiazole, is a heterocyclic compound that contains both sulfur and nitrogen; the term 'thiazole' also refers to a large family of derivatives. Thiazole itself is a pale yellow liquid with a pyridine-like odor and the molecular formula C3H3NS...
, an analog with the oxygen replaced by a sulfur. - BenzoxazoleBenzoxazoleBenzoxazole is an aromatic organic compound with a molecular formula C7H5NO, a benzene-fused oxazole ring structure, and an odor similar to pyridine. Benzoxazole is used primarily in industry and research, and has no household use....
, where the oxazole is fused to another aromatic ring. - PyrrolePyrrolePyrrole is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound, a five-membered ring with the formula C4H4NH. It is a colourless volatile liquid that darkens readily upon exposure to air. Substituted derivatives are also called pyrroles, e.g., N-methylpyrrole, C4H4NCH3...
, an analog without the oxygen atom. - FuranFuranFuran is a heterocyclic organic compound, consisting of a five-membered aromatic ring with four carbon atoms and one oxygen. The class of compounds containing such rings are also referred to as furans....
, an analog without the nitrogen atom. - OxazolineOxazolineOxazoline is both the five-membered ring heterocyclic chemical compound with the formula C3H5NO and the class of compounds containing this ring.- See also :* Desoxazoline * Oxazole* Oxazolidine* Oxazolidinedione...
, which has only one double bond reduced. - OxazolidinedioneOxazolidinedioneOxazolidinedione is a heterocyclic chemical compound that forms the core structure of a variety anticonvulsant drugs including:* Ethadione* Paramethadione* Trimethadione...
, which has two in-cycle keto groups (a carbamate and a lactam). - Oxazolidinone, which has an in-cycle carbamate.