
NADH dehydrogenase (quinone)
Encyclopedia
In enzymology, a NADH dehydrogenase (quinone) is an enzyme
that catalyzes
the chemical reaction
The 3 substrates
of this enzyme are NADH
, H+
, and acceptor
, whereas its two products
are NAD+
and reduced acceptor.
This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductase
s, specifically those acting on NADH or NADPH with other acceptors. The systematic name of this enzyme class is NADH:(quinone-acceptor) oxidoreductase. Other names in common use include reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (quinone) dehydrogenase, NADH-quinone oxidoreductase, NADH ubiquinone oxidoreductase, DPNH-menadione reductase, D-diaphorase, and NADH2 dehydrogenase (quinone), and mitochondrial (mt) complex I. This enzyme participates in oxidative phosphorylation
. Several compounds are known to inhibit this enzyme
, including AMP
, and 2,4-Dinitrophenol
.
has been solved for this class of enzymes, with the PDB
accession code .
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that catalyzes
Catalysis
Catalysis is the change in rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of a substance called a catalyst. Unlike other reagents that participate in the chemical reaction, a catalyst is not consumed by the reaction itself. A catalyst may participate in multiple chemical transformations....
the chemical reaction
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
- NADH + H+ + acceptor
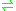 NAD+ + reduced acceptor
NAD+ + reduced acceptor
The 3 substrates
Substrate (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a substrate is a molecule upon which an enzyme acts. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions involving the substrate. In the case of a single substrate, the substrate binds with the enzyme active site, and an enzyme-substrate complex is formed. The substrate is transformed into one or...
of this enzyme are NADH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, abbreviated NAD, is a coenzyme found in all living cells. The compound is a dinucleotide, since it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine base and the other nicotinamide.In metabolism, NAD is involved...
, H+
Hydrogen ion
Hydrogen ion is recommended by IUPAC as a general term for all ions of hydrogen and its isotopes.Depending on the charge of the ion, two different classes can be distinguished: positively charged ions and negatively charged ions....
, and acceptor
Electron acceptor
An electron acceptor is a chemical entity that accepts electrons transferred to it from another compound. It is an oxidizing agent that, by virtue of its accepting electrons, is itself reduced in the process....
, whereas its two products
Product (chemistry)
Product are formed during chemical reactions as reagents are consumed. Products have lower energy than the reagents and are produced during the reaction according to the second law of thermodynamics. The released energy comes from changes in chemical bonds between atoms in reagent molecules and...
are NAD+
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, abbreviated NAD, is a coenzyme found in all living cells. The compound is a dinucleotide, since it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine base and the other nicotinamide.In metabolism, NAD is involved...
and reduced acceptor.
This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductase
Oxidoreductase
In biochemistry, an oxidoreductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from one molecule to another...
s, specifically those acting on NADH or NADPH with other acceptors. The systematic name of this enzyme class is NADH:(quinone-acceptor) oxidoreductase. Other names in common use include reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (quinone) dehydrogenase, NADH-quinone oxidoreductase, NADH ubiquinone oxidoreductase, DPNH-menadione reductase, D-diaphorase, and NADH2 dehydrogenase (quinone), and mitochondrial (mt) complex I. This enzyme participates in oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation is a metabolic pathway that uses energy released by the oxidation of nutrients to produce adenosine triphosphate . Although the many forms of life on earth use a range of different nutrients, almost all aerobic organisms carry out oxidative phosphorylation to produce ATP,...
. Several compounds are known to inhibit this enzyme
Enzyme inhibitor
An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to enzymes and decreases their activity. Since blocking an enzyme's activity can kill a pathogen or correct a metabolic imbalance, many drugs are enzyme inhibitors. They are also used as herbicides and pesticides...
, including AMP
Adenosine monophosphate
Adenosine monophosphate , also known as 5'-adenylic acid, is a nucleotide that is used as a monomer in RNA. It is an ester of phosphoric acid and the nucleoside adenosine. AMP consists of a phosphate group, the sugar ribose, and the nucleobase adenine...
, and 2,4-Dinitrophenol
2,4-Dinitrophenol
2,4-Dinitrophenol , C6H4N2O5, is a cellular metabolic poison. It uncouples oxidative phosphorylation by carrying protons across the mitochondrial membrane, leading to a rapid consumption of energy without generation of ATP....
.
Structural studies
As of late 2007, only one structureTertiary structure
In biochemistry and molecular biology, the tertiary structure of a protein or any other macromolecule is its three-dimensional structure, as defined by the atomic coordinates.-Relationship to primary structure:...
has been solved for this class of enzymes, with the PDB
Protein Data Bank
The Protein Data Bank is a repository for the 3-D structural data of large biological molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids....
accession code .

