.gif)
Mass (mass spectrometry)
Encyclopedia
The mass recorded by a mass spectrometer can refer to different physical quantities depending on the characteristics of the instrument and the manner in which the mass spectrum
is displayed.
, a 5 ppm
accuracy is sufficient to uniquely determine the elemental composition.
with formula H2O is 1.00794 + 1.00794 + 15.9994 = 18.01528.
, containing two hydrogen-2 (deuterium
or 2H) and one oxygen-16 (16O) is 2.0141 + 2.0141 + 15.9949 = 20.0229.
having the same number of each isotopic
atom but differing in their positions. For example, CH3CHDCH3 and CH3CH2CH2D are a pair of constitutional isotopomers. An isotopomer should not be confused with isotopologue
s, which are chemical species that differ only in the isotopic
composition of their molecule
s or ion
s. An example is water
, where three of its hydrogen-related isotopologues are: HOH, HOD and DOD, where D stands for deuterium (2H).
is a mass obtained by multiplying the measured mass by a numeric factor. The Kendrick mass is used to aid in the identification of molecules of similar chemical structure from peaks in mass spectra. The method of stating mass was suggested in 1963 by the chemist
Edward Kendrick.
According to the procedure outlined by Kendrick, the mass of CH2 is defined as 14.000 Da, instead of 14.01565 Da.
The Kendrick mass for a family of compounds F is given by
 .
.
For hydrocarbon analysis, F=CH2.
number, is the number of proton
s and neutron
s in an atomic nucleus
. The mass number is unique for each isotope
of an element and is written either after the element name or as a superscript to the left of an element's symbol. For example, carbon-12
(12C) has 6 protons and 6 neutrons.
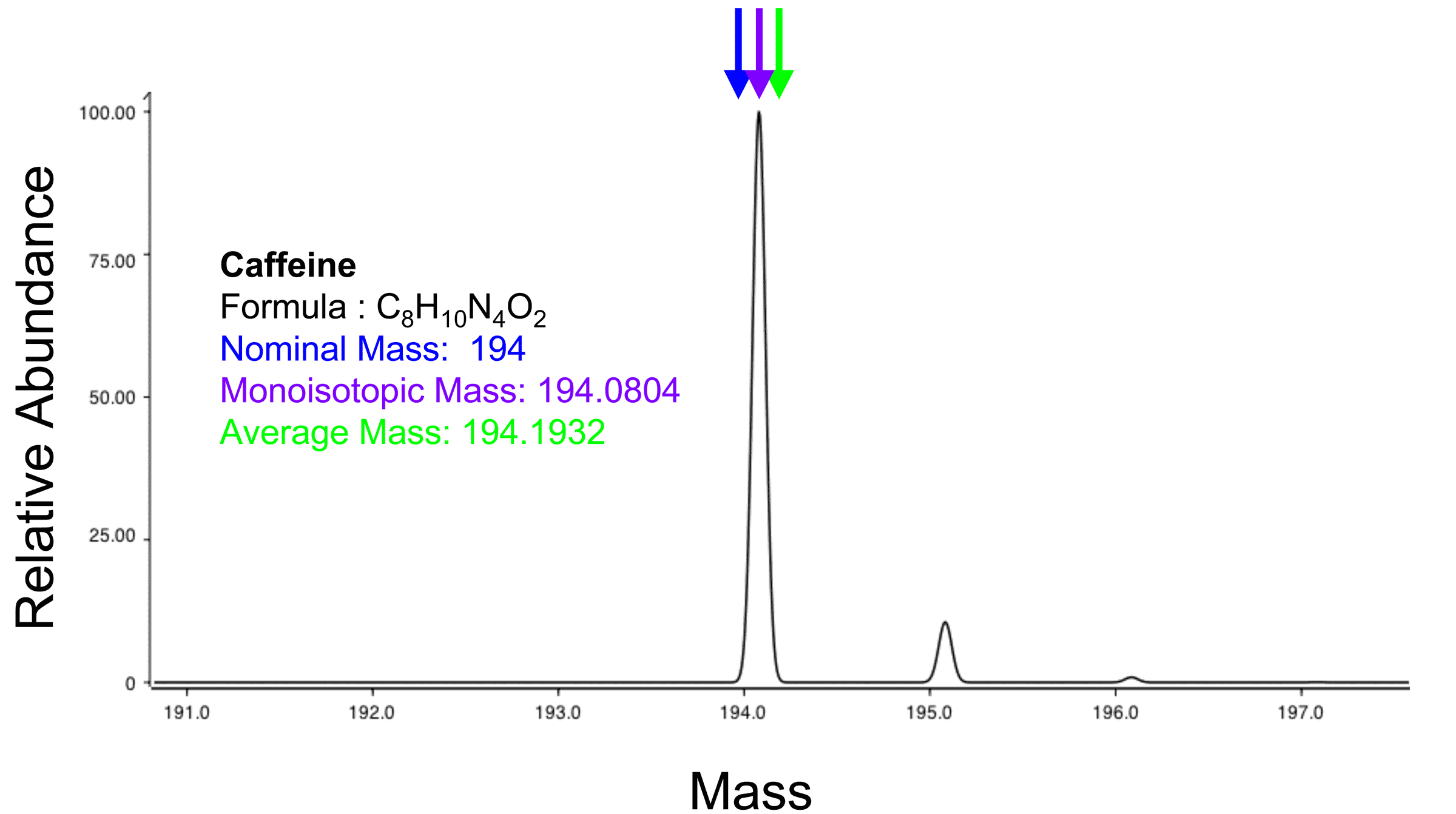 The molecular mass (abbreviated Mr) of a substance
The molecular mass (abbreviated Mr) of a substance
, formerly also called molecular weight and abbreviated as MW, is the mass
of one molecule
of that substance, relative to the unified atomic mass unit u (equal to 1/12 the mass of one atom
of 12C
). Due to this relativity, the molecular mass of a substance is commonly referred to as the relative molecular mass, and abbreviated to Mr.
es of the atom
s in a molecule
using the unbound, ground-state, rest mass of the principal (most abundant) isotope for each element instead of the isotopic average mass. For typical organic compounds, where the monoisotopic mass is most commonly used, this also results in the lightest isotope being selected. For some heavier atoms such as iron
and argon
the principal isotope is not the lightest isotope. The term is designed for measurements in mass spectrometry
primarily with smaller molecules. It is not typically useful as a concept in physics or general chemistry. Monoisotopic mass is typically expressed in unified atomic mass units
(u), also called daltons (Da).
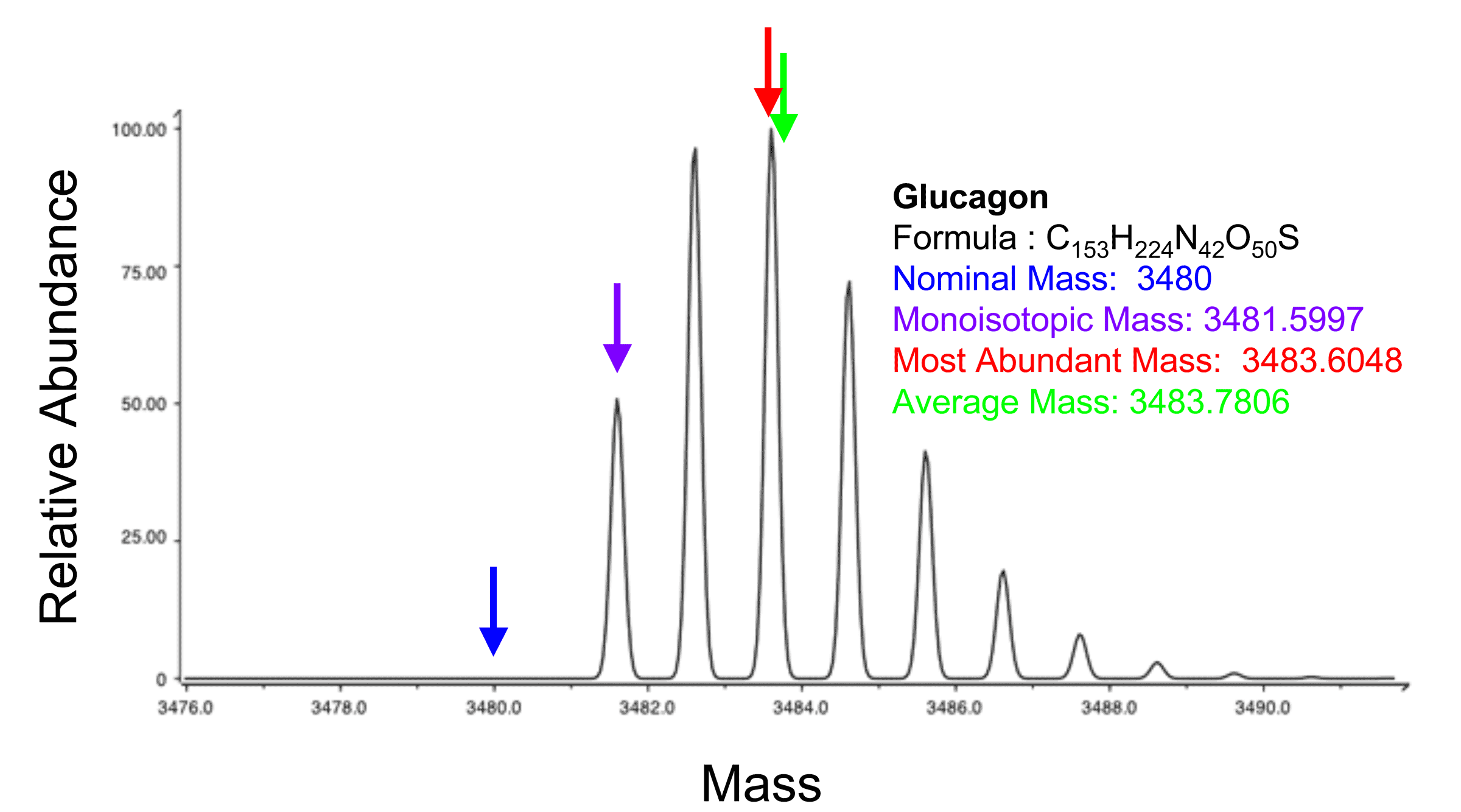 This refers to the mass of the molecule with the most highly represented isotope distribution, based on the natural abundance
This refers to the mass of the molecule with the most highly represented isotope distribution, based on the natural abundance
of the isotopes.
s of all constituent atoms. For example H = 1, C = 12, O = 16, etc. The nominal mass of H2O is 18, for example.
Mass spectrum
A mass spectrum is an intensity vs. m/z plot representing a chemical analysis. Hence, the mass spectrum of a sample is a pattern representing the distribution of ions by mass in a sample. It is a histogram usually acquired using an instrument called a mass spectrometer...
is displayed.
Accurate mass
The accurate mass (more appropriately, the measured accurate mass) is an experimentally determined mass that allows the elemental composition to be determined. For molecules with mass below 200 uAtomic mass unit
The unified atomic mass unit or dalton is a unit that is used for indicating mass on an atomic or molecular scale. It is defined as one twelfth of the rest mass of an unbound neutral atom of carbon-12 in its nuclear and electronic ground state, and has a value of...
, a 5 ppm
Parts-per notation
In science and engineering, the parts-per notation is a set of pseudo units to describe small values of miscellaneous dimensionless quantities, e.g. mole fraction or mass fraction. Since these fractions are quantity-per-quantity measures, they are pure numbers with no associated units of measurement...
accuracy is sufficient to uniquely determine the elemental composition.
Average mass
The average mass of a molecule is obtained by summing the average atomic masses of the constituent elements. For example, the average mass of natural waterWater
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
with formula H2O is 1.00794 + 1.00794 + 15.9994 = 18.01528.
Exact mass
The exact mass (more appropriately, the calculated exact mass) is obtained by summing the masses of the individual isotopes of the molecule. For example, the exact mass of water containing two hydrogen-1 (1H) and one oxygen-16 (16O) is 1.0078 + 1.0078 + 15.9949 = 18.0105. The exact mass of heavy waterHeavy water
Heavy water is water highly enriched in the hydrogen isotope deuterium; e.g., heavy water used in CANDU reactors is 99.75% enriched by hydrogen atom-fraction...
, containing two hydrogen-2 (deuterium
Deuterium
Deuterium, also called heavy hydrogen, is one of two stable isotopes of hydrogen. It has a natural abundance in Earth's oceans of about one atom in of hydrogen . Deuterium accounts for approximately 0.0156% of all naturally occurring hydrogen in Earth's oceans, while the most common isotope ...
or 2H) and one oxygen-16 (16O) is 2.0141 + 2.0141 + 15.9949 = 20.0229.
Isotopomer
An isotopomer (isotopic isomer) is an isomerIsomer
In chemistry, isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. Isomers do not necessarily share similar properties, unless they also have the same functional groups. There are many different classes of isomers, like stereoisomers, enantiomers, geometrical...
having the same number of each isotopic
Isotope
Isotopes are variants of atoms of a particular chemical element, which have differing numbers of neutrons. Atoms of a particular element by definition must contain the same number of protons but may have a distinct number of neutrons which differs from atom to atom, without changing the designation...
atom but differing in their positions. For example, CH3CHDCH3 and CH3CH2CH2D are a pair of constitutional isotopomers. An isotopomer should not be confused with isotopologue
Isotopologue
Isotopologues are molecules that differ only in their isotopic composition. Simply, the isotopologue of a chemical species has at least one atom with a different number of neutrons than the parent....
s, which are chemical species that differ only in the isotopic
Isotope
Isotopes are variants of atoms of a particular chemical element, which have differing numbers of neutrons. Atoms of a particular element by definition must contain the same number of protons but may have a distinct number of neutrons which differs from atom to atom, without changing the designation...
composition of their molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
s or ion
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
s. An example is water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
, where three of its hydrogen-related isotopologues are: HOH, HOD and DOD, where D stands for deuterium (2H).
Kendrick mass
The Kendrick massKendrick mass
The Kendrick mass is a mass obtained by multiplying the measured mass by a numeric factor. The Kendrick mass is used to aid in the identification of molecules of similar chemical structure from peaks in mass spectra...
is a mass obtained by multiplying the measured mass by a numeric factor. The Kendrick mass is used to aid in the identification of molecules of similar chemical structure from peaks in mass spectra. The method of stating mass was suggested in 1963 by the chemist
Chemist
A chemist is a scientist trained in the study of chemistry. Chemists study the composition of matter and its properties such as density and acidity. Chemists carefully describe the properties they study in terms of quantities, with detail on the level of molecules and their component atoms...
Edward Kendrick.
According to the procedure outlined by Kendrick, the mass of CH2 is defined as 14.000 Da, instead of 14.01565 Da.
The Kendrick mass for a family of compounds F is given by
 .
.For hydrocarbon analysis, F=CH2.
Mass number
The mass number, also called the nucleonNucleon
In physics, a nucleon is a collective name for two particles: the neutron and the proton. These are the two constituents of the atomic nucleus. Until the 1960s, the nucleons were thought to be elementary particles...
number, is the number of proton
Proton
The proton is a subatomic particle with the symbol or and a positive electric charge of 1 elementary charge. One or more protons are present in the nucleus of each atom, along with neutrons. The number of protons in each atom is its atomic number....
s and neutron
Neutron
The neutron is a subatomic hadron particle which has the symbol or , no net electric charge and a mass slightly larger than that of a proton. With the exception of hydrogen, nuclei of atoms consist of protons and neutrons, which are therefore collectively referred to as nucleons. The number of...
s in an atomic nucleus
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the very dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. It was discovered in 1911, as a result of Ernest Rutherford's interpretation of the famous 1909 Rutherford experiment performed by Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden, under the direction of Rutherford. The...
. The mass number is unique for each isotope
Isotope
Isotopes are variants of atoms of a particular chemical element, which have differing numbers of neutrons. Atoms of a particular element by definition must contain the same number of protons but may have a distinct number of neutrons which differs from atom to atom, without changing the designation...
of an element and is written either after the element name or as a superscript to the left of an element's symbol. For example, carbon-12
Carbon-12
Carbon-12 is the more abundant of the two stable isotopes of the element carbon, accounting for 98.89% of carbon; it contains 6 protons, 6 neutrons, and 6 electrons....
(12C) has 6 protons and 6 neutrons.
Molecular mass

Chemical compound
A chemical compound is a pure chemical substance consisting of two or more different chemical elements that can be separated into simpler substances by chemical reactions. Chemical compounds have a unique and defined chemical structure; they consist of a fixed ratio of atoms that are held together...
, formerly also called molecular weight and abbreviated as MW, is the mass
Mass
Mass can be defined as a quantitive measure of the resistance an object has to change in its velocity.In physics, mass commonly refers to any of the following three properties of matter, which have been shown experimentally to be equivalent:...
of one molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
of that substance, relative to the unified atomic mass unit u (equal to 1/12 the mass of one atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
of 12C
Carbon-12
Carbon-12 is the more abundant of the two stable isotopes of the element carbon, accounting for 98.89% of carbon; it contains 6 protons, 6 neutrons, and 6 electrons....
). Due to this relativity, the molecular mass of a substance is commonly referred to as the relative molecular mass, and abbreviated to Mr.
Monoisotopic mass
The monoisotopic mass is the sum of the massMass
Mass can be defined as a quantitive measure of the resistance an object has to change in its velocity.In physics, mass commonly refers to any of the following three properties of matter, which have been shown experimentally to be equivalent:...
es of the atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
s in a molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
using the unbound, ground-state, rest mass of the principal (most abundant) isotope for each element instead of the isotopic average mass. For typical organic compounds, where the monoisotopic mass is most commonly used, this also results in the lightest isotope being selected. For some heavier atoms such as iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
and argon
Argon
Argon is a chemical element represented by the symbol Ar. Argon has atomic number 18 and is the third element in group 18 of the periodic table . Argon is the third most common gas in the Earth's atmosphere, at 0.93%, making it more common than carbon dioxide...
the principal isotope is not the lightest isotope. The term is designed for measurements in mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique that measures the mass-to-charge ratio of charged particles.It is used for determining masses of particles, for determining the elemental composition of a sample or molecule, and for elucidating the chemical structures of molecules, such as peptides and...
primarily with smaller molecules. It is not typically useful as a concept in physics or general chemistry. Monoisotopic mass is typically expressed in unified atomic mass units
Atomic mass unit
The unified atomic mass unit or dalton is a unit that is used for indicating mass on an atomic or molecular scale. It is defined as one twelfth of the rest mass of an unbound neutral atom of carbon-12 in its nuclear and electronic ground state, and has a value of...
(u), also called daltons (Da).
Most abundant mass

Natural abundance
In chemistry, natural abundance refers to the abundance of isotopes of a chemical element as naturally found on a planet. The relative atomic mass of these isotopes is the atomic weight listed for the element in the periodic table...
of the isotopes.
Nominal mass
The nominal mass of an ion or molecule is calculated using the integer mass (ignoring the mass defect) of the most abundant isotope of each element. This is the equivalent of summing the mass numberMass number
The mass number , also called atomic mass number or nucleon number, is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atomic nucleus. Because protons and neutrons both are baryons, the mass number A is identical with the baryon number B as of the nucleus as of the whole atom or ion...
s of all constituent atoms. For example H = 1, C = 12, O = 16, etc. The nominal mass of H2O is 18, for example.
See also
- Francis William AstonFrancis William AstonFrancis William Aston was a British chemist and physicist who won the 1922 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his discovery, by means of his mass spectrograph, of isotopes, in a large number of non-radioactive elements, and for his enunciation of the whole-number rule...
- Atomic mass unitAtomic mass unitThe unified atomic mass unit or dalton is a unit that is used for indicating mass on an atomic or molecular scale. It is defined as one twelfth of the rest mass of an unbound neutral atom of carbon-12 in its nuclear and electronic ground state, and has a value of...
- Gram-molecular weight
- List of elements by atomic mass
- Nitrogen rule (mass spectrometry)

