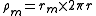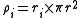Length constant
Encyclopedia
Length constant is a constant used in neurobiology signified by the Greek letter lambda
(λ). The longer a length constant is, the bigger the effect a potential (either an action potential or a current injected at the site) will have along the cell. A long length constant can result in spatial summation, or the algebraic summation of one potential with other potentials from other areas of the cell.
In an action potential
(or in a passive spread of signal) in a neuron
, the constant λ is
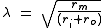
where rm is the resistance across the membrane, ri is the resistance inside the membrane, and ro is the resistance outside the membrane. In calculation, the effects of ro are negligible, so the equation becomes
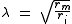
The resistance across the membrane is a function of the number of open ion channels and the resistance inside the membrane is generally a function of the diameter
of the axon
. A large diameter is related to a lower ri.
The length constant is used to describe the rise of potential difference across the membrane
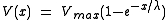
The fall of voltage is described by
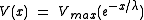
Where voltage
is typically in millivolts, x is distance in millimeters, and λ is in millimeters.
Vmax is defined as the maximum voltage attained in the action potential, where
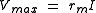
where rm is the resistance across the membrane and I is the current flow.
Setting for x= λ for the rise of voltage sets V(x) equal to .63 Vmax. This means that the length constant is the distance at which 63% of Vmax has been reached during the rise of voltage.
Setting for x= λ for the fall of voltage sets V(x) equal to .37 Vmax, meaning that the length constant is the distance at which 37% of Vmax has been reached during the fall of voltage.
rather than resistance, the constant λ is (with negligible ro):
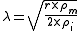
Where is the radius of the neuron.
is the radius of the neuron.
The radius and number 2 come from that:
Expressed in this way, it can be seen that the length constant increases with increasing radius of the neuron.
Lambda
Lambda is the 11th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals lambda has a value of 30. Lambda is related to the Phoenician letter Lamed . Letters in other alphabets that stemmed from lambda include the Roman L and the Cyrillic letter El...
(λ). The longer a length constant is, the bigger the effect a potential (either an action potential or a current injected at the site) will have along the cell. A long length constant can result in spatial summation, or the algebraic summation of one potential with other potentials from other areas of the cell.
In an action potential
Action potential
In physiology, an action potential is a short-lasting event in which the electrical membrane potential of a cell rapidly rises and falls, following a consistent trajectory. Action potentials occur in several types of animal cells, called excitable cells, which include neurons, muscle cells, and...
(or in a passive spread of signal) in a neuron
Neuron
A neuron is an electrically excitable cell that processes and transmits information by electrical and chemical signaling. Chemical signaling occurs via synapses, specialized connections with other cells. Neurons connect to each other to form networks. Neurons are the core components of the nervous...
, the constant λ is
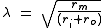
where rm is the resistance across the membrane, ri is the resistance inside the membrane, and ro is the resistance outside the membrane. In calculation, the effects of ro are negligible, so the equation becomes
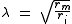
The resistance across the membrane is a function of the number of open ion channels and the resistance inside the membrane is generally a function of the diameter
Diameter
In geometry, a diameter of a circle is any straight line segment that passes through the center of the circle and whose endpoints are on the circle. The diameters are the longest chords of the circle...
of the axon
Axon
An axon is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body or soma....
. A large diameter is related to a lower ri.
The length constant is used to describe the rise of potential difference across the membrane
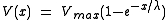
The fall of voltage is described by
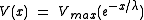
Where voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
is typically in millivolts, x is distance in millimeters, and λ is in millimeters.
Vmax is defined as the maximum voltage attained in the action potential, where
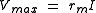
where rm is the resistance across the membrane and I is the current flow.
Setting for x= λ for the rise of voltage sets V(x) equal to .63 Vmax. This means that the length constant is the distance at which 63% of Vmax has been reached during the rise of voltage.
Setting for x= λ for the fall of voltage sets V(x) equal to .37 Vmax, meaning that the length constant is the distance at which 37% of Vmax has been reached during the fall of voltage.
By resistivity
Expressed with resistivityResistivity
Electrical resistivity is a measure of how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allows the movement of electric charge. The SI unit of electrical resistivity is the ohm metre...
rather than resistance, the constant λ is (with negligible ro):
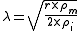
Where
 is the radius of the neuron.
is the radius of the neuron.The radius and number 2 come from that:
Expressed in this way, it can be seen that the length constant increases with increasing radius of the neuron.