
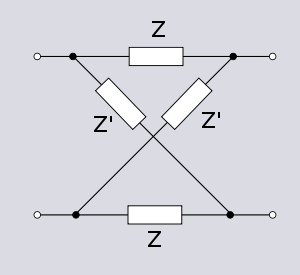
Lattice phase equaliser
Encyclopedia
All-pass filter
An all-pass filter is a signal processing filter that passes all frequencies equally, but changes the phase relationship between various frequencies. It does this by varying its propagation delay with frequency...
. That is, the attenuation
Attenuation
In physics, attenuation is the gradual loss in intensity of any kind of flux through a medium. For instance, sunlight is attenuated by dark glasses, X-rays are attenuated by lead, and light and sound are attenuated by water.In electrical engineering and telecommunications, attenuation affects the...
of the filter is constant at all frequencies
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
but the relative phase
Phase (waves)
Phase in waves is the fraction of a wave cycle which has elapsed relative to an arbitrary point.-Formula:The phase of an oscillation or wave refers to a sinusoidal function such as the following:...
between input and output varies with frequency. The lattice filter topology
Electronic filter topology
Electronic filter topology defines electronic filter circuits without taking note of the values of the components used but only the manner in which those components are connected....
has the particular property of being a constant-resistance network and for this reason is often used in combination with other constant resistance filters such as bridge-T equalisers. The topology
Topology (electronics)
The topology of an electronic circuit is the form taken by the network of interconnections of the circuit components. Different specific values or ratings of the components are regarded as being the same topology....
of a lattice filter, also called an X-section is identical to bridge topology
Bridge circuit
A bridge circuit is a type of electrical circuit in which two circuit branches are "bridged" by a third branch connected between the first two branches at some intermediate point along them. The bridge was originally developed for laboratory measurement purposes and one of the intermediate...
. The lattice phase equaliser was invented by Otto Zobel. using a filter topology proposed by George Campbell
George Ashley Campbell
George Ashley Campbell was a pioneer in developing and applying quantitative mathematical methods to the problems of long-distance telegraphy and telephony. His most important contributions were to the theory and implementation of the use of loading coils and the first wave filters designed to...
.
The characteristic impedance of this structure is given by;
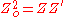
and the transfer function is given by;
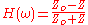
Applications
The lattice filter has an important application on linesTransmission line
In communications and electronic engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable designed to carry alternating current of radio frequency, that is, currents with a frequency high enough that its wave nature must be taken into account...
used by broadcasters for stereo audio
Stereophonic sound
The term Stereophonic, commonly called stereo, sound refers to any method of sound reproduction in which an attempt is made to create an illusion of directionality and audible perspective...
feeds. Phase distortion
Phase distortion
In signal processing, phase distortion or phase-frequency distortion is distortion that occurs when a filter's phase response is not linear over the frequency range of interest, that is, the phase shift introduced by a circuit or device is not directly proportional to frequency, or the...
on a monophonic
Monophony
In music, monophony is the simplest of textures, consisting of melody without accompanying harmony. This may be realized as just one note at a time, or with the same note duplicated at the octave . If the entire melody is sung by two voices or a choir with an interval between the notes or in...
line does not have a serious effect on the quality of the sound unless it is very large. The same is true of the absolute phase distortion on each leg (left and right channels) of a stereo pair of lines. However, the differential phase between legs has a very dramatic effect on the stereo image. This is because the formation of the stereo image in the brain relies on the phase difference information from the two ears. A phase difference translates to a delay, which in turn can be interpreted as a direction the sound came from. Consequently, landline
Landline
A landline was originally an overland telegraph wire, as opposed to an undersea cable. Currently, landline refers to a telephone line which travels through a solid medium, either metal wire or optical fibre, as distinguished from a mobile cellular line, where transmission is via radio waves...
s used by broadcasters for stereo transmissions are equalised to very tight differential phase specifications.
Another property of the lattice filter is that it is an intrinsically balanced
Balanced line
In telecommunications and professional audio, a balanced line or balanced signal pair is a transmission line consisting of two conductors of the same type, each of which have equal impedances along their lengths and equal impedances to ground and to other circuits. The chief advantage of the...
topology. This is useful when used with landlines which invariably use a balanced format. Many other types of filter section are intrinsically unbalanced and have to be transformed into a balanced implementation in these applications which increases the component count. This is not required in the case of lattice filters.
Design
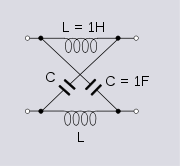
Characteristic impedance
The characteristic impedance or surge impedance of a uniform transmission line, usually written Z_0, is the ratio of the amplitudes of a single pair of voltage and current waves propagating along the line in the absence of reflections. The SI unit of characteristic impedance is the ohm...
. That is,
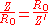
Such a network, when terminated in R0, will have an input resistance of R0 at all frequencies. If the impedance Z is purely reactive such that Z = iX then the phase shift, φ, inserted by the filter is given by,

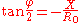
The prototype
Prototype filter
Prototype filters are electronic filter designs that are used as a template to produce a modified filter design for a particular application. They are an example of a nondimensionalised design from which the desired filter can be scaled or transformed. They are most often seen in regards to...
lattice filter shown here passes low frequencies without modification but phase shifts high frequencies. That is, it is phase correction for the high end of the band. At low frequencies the phase shift is 0° but as the frequency increases the phase shift approaches 180°. It can be seen qualitatively that this is so by replacing the inductors with open circuits and the capacitors with short circuits, which is what they become at high frequency. At high frequency the lattice filter is a cross-over network and will produce 180° phase shift. A 180° phase shift is the same as an inversion in the frequency domain, but is a delay in the time domain. At an angular frequency
Angular frequency
In physics, angular frequency ω is a scalar measure of rotation rate. Angular frequency is the magnitude of the vector quantity angular velocity...
of ω = 1 rad
Radian
Radian is the ratio between the length of an arc and its radius. The radian is the standard unit of angular measure, used in many areas of mathematics. The unit was formerly a SI supplementary unit, but this category was abolished in 1995 and the radian is now considered a SI derived unit...
/s the phase shift is exactly 90° and this is the mid-point of the filter's transfer function.
Low-in-phase section

Prototype filter
Prototype filters are electronic filter designs that are used as a template to produce a modified filter design for a particular application. They are an example of a nondimensionalised design from which the desired filter can be scaled or transformed. They are most often seen in regards to...
transforms. A filter which is in-phase at low frequencies (that is, one that is correcting phase at high frequencies) can be obtained from the prototype with simple scaling factors.
The phase response of a scaled filter is given by,
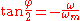
where ωm is the mid-point frequency and is given by,
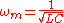
High-in-phase section
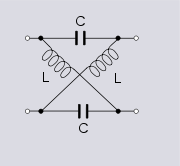
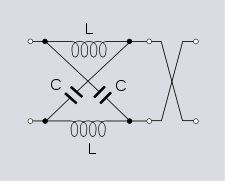
Band equalise section
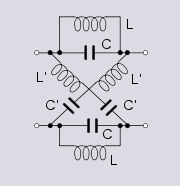
An alternative, and possibly more accurate, view of this filter's response is to describe it as a phase change that varies from 0° to 360° with increasing frequency. At 360° phase shift, of course, the input and output are now back in phase with each other.
Resistance compensation

In the example diagram, the resistors placed in series with the capacitors, R1, are made equal to the unwanted stray resistance present in the inductors. This ensures that the attenuation at high frequency is the same as the attenuation at low frequency and brings the filter back to a flat response. The purpose of the shunt resistors, R2, is to bring the image impedance
Image impedance
Image impedance is a concept used in electronic network design and analysis and most especially in filter design. The term image impedance applies to the impedance seen looking in to the ports of a network. Usually a two-port network is implied but the concept is capable of being extended to...
of the filter back to the original design R0. The resulting filter is the equivalent of a box attenuator formed from the R1's and R2's connected in cascade with an ideal lattice filter as shown in the diagram.
Unbalanced topology
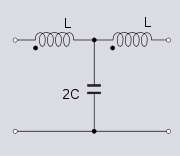
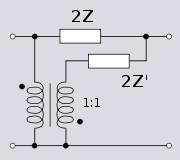
The lattice phase equaliser cannot be directly transformed into T-section topology without introducing active components. However, a T-section is possible if ideal transformers are introduced. Transformer action can be conveniently achieved in the low-in-phase T-section by winding both inductors on a common core. The response of this section is identical to the original lattice, however, the input is no longer constant resistance. This circuit was first used by George Washington Pierce who needed a delay line as part of the improved sonar he developed between the world wars. Pierce used a cascade of these sections to provide the required delay. The circuit can be considered a low-pass m-derived filter
M-derived filter
m-derived filters or m-type filters are a type of electronic filter designed using the image method. They were invented by Otto Zobel in the early 1920s. This filter type was originally intended for use with telephone multiplexing and was an improvement on the existing constant k type filter...
with m>1 which puts the transmission zero on the jω axis of the complex frequency plane. Other unbalanced transformations utilising ideal transformers are possible, one such is shown on the right.
See also
- All-pass filterAll-pass filterAn all-pass filter is a signal processing filter that passes all frequencies equally, but changes the phase relationship between various frequencies. It does this by varying its propagation delay with frequency...
- Image impedanceImage impedanceImage impedance is a concept used in electronic network design and analysis and most especially in filter design. The term image impedance applies to the impedance seen looking in to the ports of a network. Usually a two-port network is implied but the concept is capable of being extended to...
- Zobel networkZobel networkZobel networks are a type of filter section based on the image impedance design principle. They are named after Otto Zobel of Bell Labs who published a much referenced paper on image filters in 1923. The distinguishing feature of Zobel networks is that the input impedance is fixed in the design...
- Bartlett's bisection theoremBartlett's bisection theoremBartlett's Bisection Theorem is an electrical theorem in network analysis due to Albert Charles Bartlett. The theorem shows that any symmetrical two-port network can be transformed into a lattice network...
- Bridged T delay equaliserBridged T delay equaliserthumbThe bridged-T delay equaliser is an electrical all-pass filter circuit utilising bridged-T topology whose purpose is to insert an, ideally, constant delay at all frequencies in the signal path. It is a class of image filter.-Applications:...

