
Klincewicz method
Encyclopedia
Correlation
In statistics, dependence refers to any statistical relationship between two random variables or two sets of data. Correlation refers to any of a broad class of statistical relationships involving dependence....
with some basic molecular properties. The method estimates the critical temperature, the critical pressure, and the critical volume of pure components.
Model description
As a group contribution methodGroup contribution method
A group contribution method is a technique to estimate and predict thermodynamic and other properties from molecular structures.- Introduction :In today's chemical processes hundreds of thousands of components are used...
the Klincewicz method correlates some structural information of a chemical molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
with the critical data. The used structural information are small functional group
Functional group
In organic chemistry, functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reaction regardless of the size of the molecule it is a part of...
s which are assumed to have no interactions. This assumption makes it possible to calculate the thermodynamic properties directly from the sums of the group contributions. The correlation method does not even use these functional groups, only the molecular weight and the number of atoms are used as molecular descriptor
Descriptor
Descriptor may refer to*file descriptor, an abstract key for accessing a file*index term, also known as a "descriptor" in information retrieval*molecular descriptor, which helps characterize a chemical compound...
s.
The prediction of the critical temperature relies on the knowledge of the normal boiling point because the method only predicts the relation of the normal boiling point and the critical temperature and not directly the critical temperature. The critical volume and pressure however are directly predicted.
Model Quality
The quality of the Klincewicz method is not superior to older methods, especially the method of Ambrose gives somewhat better results as stated by the original authors and by Reid et al. The advantage of the Klincewicz method is that it is less complex.The quality and complexity of the Klincewicz method is comparable to the Lydersen method from 1955 which has been used widely in chemical engineering.
The aspect where the Klincewicz method is unique and useful are the alternative equations where only very basic molecular data like the molecular weight and the atom count are used.
Deviation diagrams
The diagrams show estimated critical data of hydrocarbonHydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons from which one hydrogen atom has been removed are functional groups, called hydrocarbyls....
s together with experimental data. An estimation would be perfect if all data points would lie directly on the diagonal line. Only the simple correlation of the Klincewicz method with the moelcular weight and the atom count have been used in this example.
Equations
Klincewicz published two sets of equations. The first uses contributions of 35 different groups. These group contribution based equations are giving somewhat better results than the very simple equations based only on correlations with the molecular weight and the atom count.Group-contribution-based equations
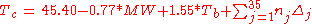

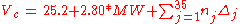
Equations based on correlation with molecular weight and atom count only

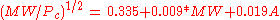

with
| MW: | Molecular weight in g/mol |
| Tb: | Normal boiling point in K |
| A: | Number of atoms |
Group contributions
| |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| |
|
|
|
| -CH3 | |||
| -CH2 | |||
| -CH2- (Ring) | |||
| >CH | |||
| >CH- (Ring) | |||
| |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
| >C=;=C= | |||
| >C= (Ring) | |||
| |
|||
| |
|||
| -OH | |||
| -O | |||
| -O- (Ring) | |||
| >CO;-CHO | |||
| -COOH | |||
| -CO-O | |||
| -NH2 | |||
| >NH | |||
| >NH (Ring) | |||
| >N | |||
| |
|||
| -CN | |||
| -SH | |||
| -S | |||
| -S- (Ring) | |||
| -F | |||
| -Cl | |||
| -Br | |||
| -I | |||
| -XCX (X = halogen) | |||
| -NO2 |
The group XCX is used to take the pairwise interaction of halogens connected to a single carbon into account. Its contribution has to be added once for two halogens but three times for three halogens (interactions between the halogens 1-2, 1-3, and 2-3).
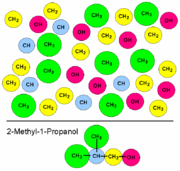
Example calculation with group contributions
| |
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Property | No. of groups | Group value | No. of groups | Group value | 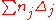 |
Estimated Value | Unit |
| Tc | |||||||
| Pc | |||||||
| Vc | |||||||
*used normal boiling point Tb= 329.250 K
Example calculation with molecular weight and atom count only
Used molecular weight: 58.080 g/molUsed atom count: 10
| Property | Estimated Value | Unit |
| Tc | ||
| Pc | ||
| Vc | ||

