
Group contribution method
Encyclopedia
A group contribution method is a technique to estimate and predict thermodynamic and other properties from molecular structures.
registry lists 33 million substances, but many of these are only of scientific interest.
Process designers need to know some basic chemical properties of the components and their mixtures. Experimental measurement is often too expensive.
Predictive methods can replace measurements if they provide sufficiently good estimations. The estimated properties cannot be as precise as well-made measurements but for many purposes the quality of estimated properties is sufficient. Predictive methods can also be used to check the results of experimental work.
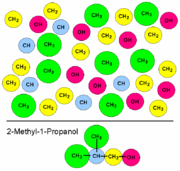 A group contribution method uses the principle that some simple aspects of the structures of chemical components are always the same in many different molecules. The smallest common constituents are the atoms and the bonds. All organic component for example are built of carbon
A group contribution method uses the principle that some simple aspects of the structures of chemical components are always the same in many different molecules. The smallest common constituents are the atoms and the bonds. All organic component for example are built of carbon
, hydrogen
, oxygen
, nitrogen
, halogen
s, and maybe sulfur
. Together with a single, a double, and a triple bond there are only ten atom types and three bond types to build thousands, of components. The next slightly more complex building blocks of components are functional group
s which are themselves built of few atoms and bonds.
A group contribution method is used to predict properties of pure components and mixtures by using group or atom properties. This reduces the number of needed data dramatically. Instead of needing to know the properties of thousands or millions components only data for a few dozens or few hundreds groups have to be known.
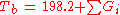
This simple form assumes that the property (normal boiling point in the example) is strictly linear dependent from the number of groups and additionally no interaction between groups and molecules are assumed. This simple approach is used for example in the Joback method
for some properties and it works well in a limited range of components and property ranges but leads to quite large errors if used outside the applicable ranges.
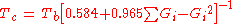
This approach often gives better results than pure additive equations because the relation with a known property introduces some knowledge about the molecule. Commonly used additional properties are the molecular weight, the number of atoms, chain length, and ring sizes and counts.
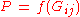
where P stands for property and Gij for group interaction value.
A typical group contribution method using group interaction values is the UNIFAC
method which estimates activity coefficients. A big disadvantage of the group interaction model is the need for many more model parameters. Where a simple additive model only needs ten parameters for ten groups a group interaction model needs already needs 45 parameters. Therefore a group interaction model has normally not parameter for all possible combinations.
, Beilstein database
, or the DIPPR data bank (from AIChE). The given pure component and mixture properties are then assigned to the groups by statistical correlations like e. g. (multi-)linear regression.
Important steps during the development of a new method are the
The reliability of a method mainly relies on a comprehensive data bank where sufficient source data have been available for all groups. A small data base may lead to a precise reproduction of the used data but will lead to significant errors when the model is used for the prediction of other systems.
Introduction
In today's chemical processes hundreds of thousands of components are used. The Chemical Abstracts ServiceChemical Abstracts Service
Chemical Abstracts is a periodical index that provides summaries and indexes of disclosures in recently published scientific documents. Approximately 8,000 journals, technical reports, dissertations, conference proceedings, and new books, in any of 50 languages, are monitored yearly, as are patent...
registry lists 33 million substances, but many of these are only of scientific interest.
Process designers need to know some basic chemical properties of the components and their mixtures. Experimental measurement is often too expensive.
Predictive methods can replace measurements if they provide sufficiently good estimations. The estimated properties cannot be as precise as well-made measurements but for many purposes the quality of estimated properties is sufficient. Predictive methods can also be used to check the results of experimental work.
Principles

Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
, hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
, oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
, nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
, halogen
Halogen
The halogens or halogen elements are a series of nonmetal elements from Group 17 IUPAC Style of the periodic table, comprising fluorine , chlorine , bromine , iodine , and astatine...
s, and maybe sulfur
Sulfur
Sulfur or sulphur is the chemical element with atomic number 16. In the periodic table it is represented by the symbol S. It is an abundant, multivalent non-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow...
. Together with a single, a double, and a triple bond there are only ten atom types and three bond types to build thousands, of components. The next slightly more complex building blocks of components are functional group
Functional group
In organic chemistry, functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reaction regardless of the size of the molecule it is a part of...
s which are themselves built of few atoms and bonds.
A group contribution method is used to predict properties of pure components and mixtures by using group or atom properties. This reduces the number of needed data dramatically. Instead of needing to know the properties of thousands or millions components only data for a few dozens or few hundreds groups have to be known.
Additive group contribution method
The simplest form of a group contribution method is the determination of a component property by summing up the group contribution.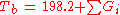
This simple form assumes that the property (normal boiling point in the example) is strictly linear dependent from the number of groups and additionally no interaction between groups and molecules are assumed. This simple approach is used for example in the Joback method
Joback method
The Joback method predicts eleven important and commonly used pure component thermodynamic properties from molecular structure only.- Group Contribution Method :The Joback method is a group contribution method...
for some properties and it works well in a limited range of components and property ranges but leads to quite large errors if used outside the applicable ranges.
Additive group contributions and correlations
This technique uses the pure additive group contributions to correlate the wanted property with an easy accessible property. This is often done for the critical temperature, where the Guldberg rule implies that Tc is 3/2 of the normal boiling point and the group contributions are used to give a more precise value than 3/2.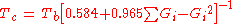
This approach often gives better results than pure additive equations because the relation with a known property introduces some knowledge about the molecule. Commonly used additional properties are the molecular weight, the number of atoms, chain length, and ring sizes and counts.
Group interactions
For the prediction of mixture properties it is in most cases not sufficient to use a purely additive method. Instead the property is determined from group interaction parameters.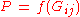
where P stands for property and Gij for group interaction value.
A typical group contribution method using group interaction values is the UNIFAC
UNIFAC
The UNIversal Functional Activity Coefficient method is a semi-empirical system for the prediction of non-electrolyte activity estimation in non-ideal mixtures. UNIFAC uses the functional groups present on the molecules that make up the liquid mixture to calculate activity coefficients...
method which estimates activity coefficients. A big disadvantage of the group interaction model is the need for many more model parameters. Where a simple additive model only needs ten parameters for ten groups a group interaction model needs already needs 45 parameters. Therefore a group interaction model has normally not parameter for all possible combinations.
Group contributions of higher orders
Some newer methods introduce second-order groups. The second-order order groups can be super-groups containing several first-order (standard) groups. This allows the introduction of new parameters for the position of groups. Another possibility is to modify first-order group contributions if specific other groups are also present.Determination of group contributions
Group contributions are obtained from known experimental data of well defined pure components and mixtures. Common sources are thermophysical data banks like the Dortmund Data BankDortmund Data Bank
The Dortmund Data Bank is a factual data bank for thermodynamic and thermophysical data. Its main usage is the data supply for process simulation where experimental data are the basis for the design, analysis, synthesis, and optimization of chemical processes...
, Beilstein database
Beilstein database
The Beilstein database is the largest database in the field of organic chemistry, in which compounds are uniquely identified by their Beilstein Registry Number. The database covers the scientific literature from 1771 to the present and contains experimentally validated information on millions of...
, or the DIPPR data bank (from AIChE). The given pure component and mixture properties are then assigned to the groups by statistical correlations like e. g. (multi-)linear regression.
Important steps during the development of a new method are the
- evaluation of the quality of available experimental data, elimination of wrong data, finding of outliers
- construction of groups
- searching additional simple and easily accessible properties that can be used to correlate the sum of group contributions with the examined property
- finding a good but simple mathematical equation for the relation of the group contribution sum with the wanted property. The critical pressures, for example, is often determined as Pc=f(ΣGi2)
- fitting the group contribution
The reliability of a method mainly relies on a comprehensive data bank where sufficient source data have been available for all groups. A small data base may lead to a precise reproduction of the used data but will lead to significant errors when the model is used for the prediction of other systems.

