
IC50
Encyclopedia
The half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) is a measure of the effectiveness of a compound in inhibiting biological or biochemical function. This quantitative measure indicates how much of a particular drug or other substance (inhibitor
) is needed to inhibit a given biological process (or component of a process, i.e. an enzyme
, cell
, cell receptor or microorganism
) by half. In other words, it is the half maximal (50%) inhibitory concentration (IC) of a substance (50% IC, or IC50). It is commonly used as a measure of antagonist drug potency
in pharmacological research. Sometimes, it is also converted to the pIC50 scale (-log IC50), in which higher values indicate exponentially greater potency. According to the FDA
, IC50 represents the concentration of a drug that is required for 50% inhibition in vitro.
It is comparable to an EC50 for agonist drugs
. EC50 also represents the plasma concentration required for obtaining 50% of a maximum effect in vivo.
and examining the effect of different concentrations of antagonist on reversing agonist activity. IC50 values can be calculated for a given antagonist by determining the concentration needed to inhibit half of the maximum biological response of the agonist.
IC50 values are very dependent on conditions under which they are measured. In general, the higher the concentration of inhibitor, the more agonist activity will be lowered. IC50 value increases as enzyme concentration increases. Furthermore depending on the type of inhibition other factors may influence IC50 value; for ATP
dependent enzymes IC50 value has an interdependency with concentration of ATP, especially so if inhibition is all of it competitive
. IC50 values can be used to compare the potency of two antagonists.
value. The level of specific binding of the radioligand is then determined in the presence of a range of concentrations of other competing non-radioactive compounds (usually antagonists), in order to measure the potency with which they compete for the binding of the radioligand. Competition curves may also be computer-fitted to a logistic function as described under direct fit.
In this situation the IC50 is the concentration of competing ligand which displaces 50% of the specific binding of the radioligand. The IC50 value is converted to an absolute inhibition constant Ki using the Cheng-Prusoff equation (see Ki).
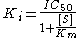
where Ki is the binding affinity of the inhibitor, IC50 is the functional strength of the inhibitor, [S] is substrate concentration and Km is the concentration of substrate at which enzyme activity is at half maximal (but is frequently confused with substrate affinity for the enzyme, which it is not). Whereas the IC50 value for a compound may vary between experiments depending on experimental conditions, the Ki is an absolute value. Ki is the inhibition constant for a drug; the concentration of competing ligand in a competition assay which would occupy 50% of the receptors if no ligand were present.
Enzyme inhibitor
An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to enzymes and decreases their activity. Since blocking an enzyme's activity can kill a pathogen or correct a metabolic imbalance, many drugs are enzyme inhibitors. They are also used as herbicides and pesticides...
) is needed to inhibit a given biological process (or component of a process, i.e. an enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
, cell
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
, cell receptor or microorganism
Microorganism
A microorganism or microbe is a microscopic organism that comprises either a single cell , cell clusters, or no cell at all...
) by half. In other words, it is the half maximal (50%) inhibitory concentration (IC) of a substance (50% IC, or IC50). It is commonly used as a measure of antagonist drug potency
Potency (pharmacology)
In the field of pharmacology, potency is a measure of drug activity expressed in terms of the amount required to produce an effect of given intensity. A highly potent drug evokes a larger response at low concentrations, while a drug of lower potency evokes a small response at low concentrations...
in pharmacological research. Sometimes, it is also converted to the pIC50 scale (-log IC50), in which higher values indicate exponentially greater potency. According to the FDA
Food and Drug Administration
The Food and Drug Administration is an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, one of the United States federal executive departments...
, IC50 represents the concentration of a drug that is required for 50% inhibition in vitro.
It is comparable to an EC50 for agonist drugs
Agonist
An agonist is a chemical that binds to a receptor of a cell and triggers a response by that cell. Agonists often mimic the action of a naturally occurring substance...
. EC50 also represents the plasma concentration required for obtaining 50% of a maximum effect in vivo.
Functional antagonist assay
The IC50 of a drug can be determined by constructing a dose-response curveDose-response relationship
The dose-response relationship, or exposure-response relationship, describes the change in effect on an organism caused by differing levels of exposure to a stressor after a certain exposure time...
and examining the effect of different concentrations of antagonist on reversing agonist activity. IC50 values can be calculated for a given antagonist by determining the concentration needed to inhibit half of the maximum biological response of the agonist.
IC50 values are very dependent on conditions under which they are measured. In general, the higher the concentration of inhibitor, the more agonist activity will be lowered. IC50 value increases as enzyme concentration increases. Furthermore depending on the type of inhibition other factors may influence IC50 value; for ATP
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine-5'-triphosphate is a multifunctional nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme. It is often called the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism...
dependent enzymes IC50 value has an interdependency with concentration of ATP, especially so if inhibition is all of it competitive
Competitive inhibition
Competitive inhibition is a form of enzyme inhibition where binding of the inhibitor to the active site on the enzyme prevents binding of the substrate and vice versa.-Mechanism:...
. IC50 values can be used to compare the potency of two antagonists.
Competition binding assays
In this type of assay, a single concentration of radioligand (usually an agonist) is used in every assay tube. The ligand is used at a low concentration, usually at or below its KdDissociation constant
In chemistry, biochemistry, and pharmacology, a dissociation constant is a specific type of equilibrium constant that measures the propensity of a larger object to separate reversibly into smaller components, as when a complex falls apart into its component molecules, or when a salt splits up into...
value. The level of specific binding of the radioligand is then determined in the presence of a range of concentrations of other competing non-radioactive compounds (usually antagonists), in order to measure the potency with which they compete for the binding of the radioligand. Competition curves may also be computer-fitted to a logistic function as described under direct fit.
In this situation the IC50 is the concentration of competing ligand which displaces 50% of the specific binding of the radioligand. The IC50 value is converted to an absolute inhibition constant Ki using the Cheng-Prusoff equation (see Ki).
IC50 and affinity
IC50 is not a direct indicator of affinity although the two can be related at least for competitive agonists and antagonists by the Cheng-Prusoff equation.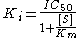
where Ki is the binding affinity of the inhibitor, IC50 is the functional strength of the inhibitor, [S] is substrate concentration and Km is the concentration of substrate at which enzyme activity is at half maximal (but is frequently confused with substrate affinity for the enzyme, which it is not). Whereas the IC50 value for a compound may vary between experiments depending on experimental conditions, the Ki is an absolute value. Ki is the inhibition constant for a drug; the concentration of competing ligand in a competition assay which would occupy 50% of the receptors if no ligand were present.
Behavioral Assays
The IC50 terminology is also used for some behavioral measures in vivo, such as a two bottle fluid consumption test. When animals decrease consumption from the drug-laced water bottle, the concentration of the drug that results in a 50% decrease in consumption is considered the IC50 for fluid consumption of that drug.See also
- Certain safety factorCertain safety factorThe Certain Safety Factor is the ratio of the lethal dose to 1% of population to the effective dose to 99% of the population . This is a better safety index than the LD50 for materials that have both desirable and undesirable effects, because it factors in the ends of the spectrum where doses may...
- Dose-response relationshipDose-response relationshipThe dose-response relationship, or exposure-response relationship, describes the change in effect on an organism caused by differing levels of exposure to a stressor after a certain exposure time...
- EC50EC50The term half maximal effective concentration refers to the concentration of a drug, antibody or toxicant which induces a response halfway between the baseline and maximum after some specified exposure time...
- LD50LD50In toxicology, the median lethal dose, LD50 , LC50 or LCt50 of a toxin, radiation, or pathogen is the dose required to kill half the members of a tested population after a specified test duration...

