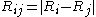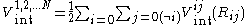Hamaker theory
Encyclopedia
After the explanation of van der Waals force
s by Fritz London
several scientists soon realised that his definition could be extended from the interaction of two molecule
s with induced dipole
s to macro-scale objects by summing all of the forces between the molecule
s in each of the bodies involved. The theory is named after H. C. Hamaker
who derived the interaction between two spheres, a sphere and a wall, and presented a general discussion in a heavily-cited 1937 paper.
The interaction of two bodies is then treated as the pairwise interaction of a set of N molecules at positions: Ri {i:1,2,... ...,N}. The distance between the molecules i and j is then:
The interaction energy of the system is taken to be:
where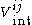 is the interaction of molecules i and j in the absence of the influence of other molecules.
is the interaction of molecules i and j in the absence of the influence of other molecules.
The theory is however only an approximation which assumes that the interactions can be treated independently, the theory must also be adjusted to take into account quantum perturbation theory
.
Van der Waals force
In physical chemistry, the van der Waals force , named after Dutch scientist Johannes Diderik van der Waals, is the sum of the attractive or repulsive forces between molecules other than those due to covalent bonds or to the electrostatic interaction of ions with one another or with neutral...
s by Fritz London
Fritz London
Fritz Wolfgang London was a German theoretical physicist. His fundamental contributions to the theories of chemical bonding and of intermolecular forces are today considered classic and are discussed in standard textbooks of physical chemistry.With his brother Heinz, he made a significant...
several scientists soon realised that his definition could be extended from the interaction of two molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
s with induced dipole
Dipole
In physics, there are several kinds of dipoles:*An electric dipole is a separation of positive and negative charges. The simplest example of this is a pair of electric charges of equal magnitude but opposite sign, separated by some distance. A permanent electric dipole is called an electret.*A...
s to macro-scale objects by summing all of the forces between the molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
s in each of the bodies involved. The theory is named after H. C. Hamaker
H. C. Hamaker
Hugo Christiaan Hamaker was a Dutch scientist, who was responsible for the Hamaker theory which explains the van der Waals forces between objects larger than molecules. His 1937 paper was heavily cited.He completed his doctorate at the Universiteit Utrecht in 1934...
who derived the interaction between two spheres, a sphere and a wall, and presented a general discussion in a heavily-cited 1937 paper.
The interaction of two bodies is then treated as the pairwise interaction of a set of N molecules at positions: Ri {i:1,2,... ...,N}. The distance between the molecules i and j is then:
The interaction energy of the system is taken to be:
where
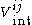 is the interaction of molecules i and j in the absence of the influence of other molecules.
is the interaction of molecules i and j in the absence of the influence of other molecules.The theory is however only an approximation which assumes that the interactions can be treated independently, the theory must also be adjusted to take into account quantum perturbation theory
Perturbation theory (quantum mechanics)
In quantum mechanics, perturbation theory is a set of approximation schemes directly related to mathematical perturbation for describing a complicated quantum system in terms of a simpler one. The idea is to start with a simple system for which a mathematical solution is known, and add an...
.