
HD 181433
Encyclopedia
HD 181433 is a star
located approximately 87 light-year
s awayCalculated from parallax: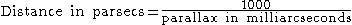 in the constellation
in the constellation
of Pavo
(the Peacock). According to SIMBAD
, it has a stellar classification of K3III-IV, which puts it on the borderline between being a red giant
and a subgiant this is inconsistent with its luminosity properties: it has a luminosity of only 0.308 times that of the Sun. Its entry in the Hipparcos catalogue lists a spectral type of K5V, classifying it as a dwarf star
. , three extrasolar planet
s are thought to be orbiting within the system. There is currently little information on these planets. The name of this star comes from its identifier in the Henry Draper catalogue
.
(this classification is based solely on the mass of the planet and should not be taken to imply that the planet could support Earthlike conditions). The middle planet and the outer planet are gas giant
s. The orbital period
s for three planets are 9.3743 days for a 7.56 ME planet, 962 days for a 0.64 MJ
planet, and 2172 days for a 0.54 MJ planet.
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
located approximately 87 light-year
Light-year
A light-year, also light year or lightyear is a unit of length, equal to just under 10 trillion kilometres...
s awayCalculated from parallax:
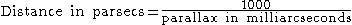 in the constellation
in the constellationConstellation
In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky....
of Pavo
Pavo (constellation)
Pavo is a constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for peacock. It is one of twelve constellations created by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman and it first appeared on a 35-cm diameter celestial globe published in 1597 in...
(the Peacock). According to SIMBAD
SIMBAD
SIMBAD is an astronomical database of objects beyond the Solar System...
, it has a stellar classification of K3III-IV, which puts it on the borderline between being a red giant
Red giant
A red giant is a luminous giant star of low or intermediate mass in a late phase of stellar evolution. The outer atmosphere is inflated and tenuous, making the radius immense and the surface temperature low, somewhere from 5,000 K and lower...
and a subgiant this is inconsistent with its luminosity properties: it has a luminosity of only 0.308 times that of the Sun. Its entry in the Hipparcos catalogue lists a spectral type of K5V, classifying it as a dwarf star
Dwarf star
The term dwarf star refers to a variety of distinct classes of stars.* Dwarf star alone generally refers to any main sequence star, a star of luminosity class V.** Red dwarfs are low-mass main sequence stars....
. , three extrasolar planet
Extrasolar planet
An extrasolar planet, or exoplanet, is a planet outside the Solar System. A total of such planets have been identified as of . It is now known that a substantial fraction of stars have planets, including perhaps half of all Sun-like stars...
s are thought to be orbiting within the system. There is currently little information on these planets. The name of this star comes from its identifier in the Henry Draper catalogue
Henry Draper Catalogue
The Henry Draper Catalogue is an astronomical star catalogue published between 1918 and 1924, giving spectroscopic classifications for 225,300 stars; it was later expanded by the Henry Draper Extension , published between 1925 and 1936, which gave classifications for 46,850 more stars, and by the...
.
Planetary system
Orbiting the star are three planets, the discovery was announced in 2008 and the discovery paper was published in 2009. The inner planet has a mass at least 7.5 times that of Earth, and is termed a super-EarthSuper-Earth
A super-Earth is an extrasolar planet with a mass higher than Earth's, but substantially below the mass of the Solar System's gas giants. The term super-Earth refers only to the mass of the planet, and does not imply anything about the surface conditions or habitability...
(this classification is based solely on the mass of the planet and should not be taken to imply that the planet could support Earthlike conditions). The middle planet and the outer planet are gas giant
Gas giant
A gas giant is a large planet that is not primarily composed of rock or other solid matter. There are four gas giants in the Solar System: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune...
s. The orbital period
Orbital period
The orbital period is the time taken for a given object to make one complete orbit about another object.When mentioned without further qualification in astronomy this refers to the sidereal period of an astronomical object, which is calculated with respect to the stars.There are several kinds of...
s for three planets are 9.3743 days for a 7.56 ME planet, 962 days for a 0.64 MJ
Jupiter mass
Jupiter mass , is the unit of mass equal to the total mass of the planet Jupiter . Jupiter mass is used to describe masses of the gas giants, such as the outer planets and extrasolar planets. It is also used in describing brown dwarfs....
planet, and 2172 days for a 0.54 MJ planet.

