
Fructosamine
Encyclopedia
Fructosamine is a compound that can be considered the result of a reaction between fructose
and ammonia
or an amine
(with a molecule of water being released). A fructosamine is also formed when carbonyl
group of glucose
reacts with an amino group of a protein, as the double bond
to oxygen moves from the end carbon atom to the next carbon atom and water is released. Fructosamines formed from serum proteins such as albumin
are known as glycated serum protein (GSP), and are used to identify the plasma
glucose
concentration
over time and so assess diabetic control over an intermediate period of time.
(HbA1c) measurement that indicates average glucose levels over the preceding 12 weeks, as reflected by the permanent glycosylation of a small fraction of the hemoglobin
molecules in the person's blood. However, this is not appropriate where there has been a recent change in diet or treatment within 6 weeks, or if there are abnormalities of red blood cell aging or mix of hemoglobin subtypes (predominantly HbA in normal adults). Hence, people with recent blood loss or hemolytic anemia
, or hemoglobinopathy
such as sickle-cell disease
, are not suitable for some glycosylated hemoglobin methods that do not account for higher-turnover hemoglobin. Fructosamine is used in these circumstances, as it also reflects an average of blood glucose levels, but over a shorter period of 2 to 3 weeks. Fructosamine is also of use in conditions, such as pregnancy
, in which hormonal changes cause greater short-term fluctuation in glucose concentrations.
An increase in fructosamine in lab testing results usually means an increase in glucose in the blood.
On average, each change of 3.3 mmol (60 mg/dl) in average blood sugar levels will give rise to changes of 2% HbA1c and 75 µmol fructosamine values. However, this overemphasizes the upper-limit of many laboratories' reference ranges of 285 umol/L as equivalent to HbA1c 7.5% rather than 6.5%. A comparative study, which has been used in official advice for Quality and Outcomes Framework
guidance in the UK and summaried by the United States' National Quality Measures Clearinghouse: gives the following formula and resulting values:
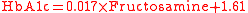
Fructose
Fructose, or fruit sugar, is a simple monosaccharide found in many plants. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and galactose, that are absorbed directly into the bloodstream during digestion. Fructose was discovered by French chemist Augustin-Pierre Dubrunfaut in 1847...
and ammonia
Ammonia
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
or an amine
Amine
Amines are organic compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines,...
(with a molecule of water being released). A fructosamine is also formed when carbonyl
Carbonyl
In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom: C=O. It is common to several classes of organic compounds, as part of many larger functional groups....
group of glucose
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar and an important carbohydrate in biology. Cells use it as the primary source of energy and a metabolic intermediate...
reacts with an amino group of a protein, as the double bond
Double bond
A double bond in chemistry is a chemical bond between two chemical elements involving four bonding electrons instead of the usual two. The most common double bond, that between two carbon atoms, can be found in alkenes. Many types of double bonds between two different elements exist, for example in...
to oxygen moves from the end carbon atom to the next carbon atom and water is released. Fructosamines formed from serum proteins such as albumin
Albumin
Albumin refers generally to any protein that is water soluble, which is moderately soluble in concentrated salt solutions, and experiences heat denaturation. They are commonly found in blood plasma, and are unique to other blood proteins in that they are not glycosylated...
are known as glycated serum protein (GSP), and are used to identify the plasma
Blood plasma
Blood plasma is the straw-colored liquid component of blood in which the blood cells in whole blood are normally suspended. It makes up about 55% of the total blood volume. It is the intravascular fluid part of extracellular fluid...
glucose
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar and an important carbohydrate in biology. Cells use it as the primary source of energy and a metabolic intermediate...
concentration
Concentration
In chemistry, concentration is defined as the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Four types can be distinguished: mass concentration, molar concentration, number concentration, and volume concentration...
over time and so assess diabetic control over an intermediate period of time.
Indications
Glucose control is usually assessed in diabetes with the Glycosylated hemoglobinGlycosylated hemoglobin
Glycated hemoglobin is a form of hemoglobin that is measured primarily to identify the average plasma glucose concentration over prolonged periods of time. It is formed in a non-enzymatic glycation pathway by hemoglobin's exposure to plasma glucose...
(HbA1c) measurement that indicates average glucose levels over the preceding 12 weeks, as reflected by the permanent glycosylation of a small fraction of the hemoglobin
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein in the red blood cells of all vertebrates, with the exception of the fish family Channichthyidae, as well as the tissues of some invertebrates...
molecules in the person's blood. However, this is not appropriate where there has been a recent change in diet or treatment within 6 weeks, or if there are abnormalities of red blood cell aging or mix of hemoglobin subtypes (predominantly HbA in normal adults). Hence, people with recent blood loss or hemolytic anemia
Hemolytic anemia
Hemolytic anemia is a form of anemia due to hemolysis, the abnormal breakdown of red blood cells , either in the blood vessels or elsewhere in the human body . It has numerous possible causes, ranging from relatively harmless to life-threatening...
, or hemoglobinopathy
Hemoglobinopathy
Hemoglobinopathy is a kind of genetic defect that results in abnormal structure of one of the globin chains of the hemoglobin molecule. Hemoglobinopathies are inherited single-gene disorders; in most cases, they are inherited as autosomal co-dominant traits. Common hemoglobinopathies include...
such as sickle-cell disease
Sickle-cell disease
Sickle-cell disease , or sickle-cell anaemia or drepanocytosis, is an autosomal recessive genetic blood disorder with overdominance, characterized by red blood cells that assume an abnormal, rigid, sickle shape. Sickling decreases the cells' flexibility and results in a risk of various...
, are not suitable for some glycosylated hemoglobin methods that do not account for higher-turnover hemoglobin. Fructosamine is used in these circumstances, as it also reflects an average of blood glucose levels, but over a shorter period of 2 to 3 weeks. Fructosamine is also of use in conditions, such as pregnancy
Pregnancy
Pregnancy refers to the fertilization and development of one or more offspring, known as a fetus or embryo, in a woman's uterus. In a pregnancy, there can be multiple gestations, as in the case of twins or triplets...
, in which hormonal changes cause greater short-term fluctuation in glucose concentrations.
Interpretation of results
There is no standard reference range available for this test. The reference values depends upon the factors of patient age, gender, sample population, and test method. Hence, each laboratory reports will include the patient's specific reference range for the test.An increase in fructosamine in lab testing results usually means an increase in glucose in the blood.
On average, each change of 3.3 mmol (60 mg/dl) in average blood sugar levels will give rise to changes of 2% HbA1c and 75 µmol fructosamine values. However, this overemphasizes the upper-limit of many laboratories' reference ranges of 285 umol/L as equivalent to HbA1c 7.5% rather than 6.5%. A comparative study, which has been used in official advice for Quality and Outcomes Framework
Quality and Outcomes Framework
The Quality and Outcomes Framework is a system for the performance management and payment of general practitioners in the National Health Service in England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland...
guidance in the UK and summaried by the United States' National Quality Measures Clearinghouse: gives the following formula and resulting values:
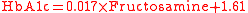
- Hence:

| Fructosamine (µmol) |
HbA1c % |
|---|---|
| 200 | 5 |
| 258 | 6 |
| 288 | 6.5 |
| 317 | 7 |
| 346 | 7.5 |
| 375 | 8 |
| 435 | 9 |
| 494 | 10 |
| 552 | 11 |
| 611 | 12 |

