
F. R. Carrick Institute
Encyclopedia
The F. R. Carrick Institute for Clinical Ergonomics, Rehabilitation, and Applied Neuroscience (C.E.R.A.N.) of Leeds Metropolitan University
, England
consists of a faculty of world class scientists and clinical researchers in Biomedical Engineering
and Rehabilitation
, Experimental Psychology
and Adult and Developmental Neuropsychology
, Ergonomics
and Human Factors, Cognitive Neuroscience
, Linguistics
, Developmental Neuroscience
and research in Physical Therapy
and Occupational Therapy
. The participants have produced numerous patents and developments as well as translational research in fundamental biomedical technologies including applications of high temperature superconductivity, imaging science
, brain pacemaker
s, apnea
monitoring, laparoscopy
, pain management
systems, neural nets, treatments for decubitus ulcer, drug delivery systems, non-invasive anesthesia
, acoustic body parts identification, acoustic correlation transform, miniaturized MRI, and neurochemical modulation by weak magnetic fields.
The Institute is affiliated with Winthrop-University Hospital
in Mineola, N.Y., USA.
A doctoral program in Rehabilitation Sciences and in Clinical Rehabilitation Neuropsychology is offered by C.E.R.A.N. through the Faculty of Health of Leeds Metropolitan University
http://drgersh.googlepages.com/ph.dprogrammeinrehabilitationneuropsychohttp://www.leedsmet.ac.uk/health/psychology/features/crossboundaries.htmhttp://drgersh.googlepages.com/home
Neurocybernetics Group
Neuroscience Group
Rehabilitation and Applied Biosciences Group
Humanities in Biomedicine Group
Cognitive Neuroscience, Neuropsychology, Curriculum, and Human Factors Groups
The Central Model for Cognitive Neuroscience and Education in Rehabilitation
 Applied and Theoretical Linguistics Group
Applied and Theoretical Linguistics Group
Leeds Metropolitan University
Leeds Metropolitan University is a British University with three campuses. Two are situated in Leeds, West Yorkshire, England while the third is situated in Bhopal, India...
, England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
consists of a faculty of world class scientists and clinical researchers in Biomedical Engineering
Biomedical engineering
Biomedical Engineering is the application of engineering principles and design concepts to medicine and biology. This field seeks to close the gap between engineering and medicine: It combines the design and problem solving skills of engineering with medical and biological sciences to improve...
and Rehabilitation
Physical medicine and rehabilitation
Physical medicine and rehabilitation , physiatry or rehabilitation medicine, is a branch of medicine that aims to enhance and restore functional ability and quality of life to those with physical impairments or disabilities. A physician having completed training in this field is referred to as a...
, Experimental Psychology
Experimental psychology
Experimental psychology is a methodological approach, rather than a subject, and encompasses varied fields within psychology. Experimental psychologists have traditionally conducted research, published articles, and taught classes on neuroscience, developmental psychology, sensation, perception,...
and Adult and Developmental Neuropsychology
Neuropsychology
Neuropsychology studies the structure and function of the brain related to specific psychological processes and behaviors. The term neuropsychology has been applied to lesion studies in humans and animals. It has also been applied to efforts to record electrical activity from individual cells in...
, Ergonomics
Ergonomics
Ergonomics is the study of designing equipment and devices that fit the human body, its movements, and its cognitive abilities.The International Ergonomics Association defines ergonomics as follows:...
and Human Factors, Cognitive Neuroscience
Cognitive neuroscience
Cognitive neuroscience is an academic field concerned with the scientific study of biological substrates underlying cognition, with a specific focus on the neural substrates of mental processes. It addresses the questions of how psychological/cognitive functions are produced by the brain...
, Linguistics
Linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. Linguistics can be broadly broken into three categories or subfields of study: language form, language meaning, and language in context....
, Developmental Neuroscience
Neuroscience
Neuroscience is the scientific study of the nervous system. Traditionally, neuroscience has been seen as a branch of biology. However, it is currently an interdisciplinary science that collaborates with other fields such as chemistry, computer science, engineering, linguistics, mathematics,...
and research in Physical Therapy
Physical therapy
Physical therapy , often abbreviated PT, is a health care profession. Physical therapy is concerned with identifying and maximizing quality of life and movement potential within the spheres of promotion, prevention, diagnosis, treatment/intervention,and rehabilitation...
and Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapy
Occupational therapy is a discipline that aims to promote health by enabling people to perform meaningful and purposeful activities. Occupational therapists work with individuals who suffer from a mentally, physically, developmentally, and/or emotionally disabling condition by utilizing treatments...
. The participants have produced numerous patents and developments as well as translational research in fundamental biomedical technologies including applications of high temperature superconductivity, imaging science
Imaging science
Imaging science is a multidisciplinary field concerned with the generation, collection, duplication, analysis, modification, and visualization of images . As an evolving field it includes research and researchers from physics, mathematics, electrical engineering, computer vision, computer science,...
, brain pacemaker
Brain pacemaker
"Brain pacemakers" are used to treat people who suffer from epilepsy, Parkinson's disease, major depression and other diseases. The pacemaker is a medical device that is implanted into the brain to send electrical signals into the tissue. Depending on the area of the brain that is targeted, the...
s, apnea
Apnea
Apnea, apnoea, or apnœa is a term for suspension of external breathing. During apnea there is no movement of the muscles of respiration and the volume of the lungs initially remains unchanged...
monitoring, laparoscopy
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy is an operation performed in the abdomen or pelvis through small incisions with the aid of a camera...
, pain management
Pain management
Pain management is a branch of medicine employing an interdisciplinary approach for easing the suffering and improving the quality of life of those living with pain. The typical pain management team includes medical practitioners, clinical psychologists, physiotherapists, occupational therapists,...
systems, neural nets, treatments for decubitus ulcer, drug delivery systems, non-invasive anesthesia
Anesthesia
Anesthesia, or anaesthesia , traditionally meant the condition of having sensation blocked or temporarily taken away...
, acoustic body parts identification, acoustic correlation transform, miniaturized MRI, and neurochemical modulation by weak magnetic fields.
The Institute is affiliated with Winthrop-University Hospital
Winthrop-University Hospital
Winthrop-University Hospital was founded in 1896 under the name Nassau Hospital as Long Island, New York's first voluntary hospital. The location was originally constructed in 1900. It was renamed Winthrop-University Hospital in the 1980s to avoid confusion with Nassau County Medical Center, now...
in Mineola, N.Y., USA.
A doctoral program in Rehabilitation Sciences and in Clinical Rehabilitation Neuropsychology is offered by C.E.R.A.N. through the Faculty of Health of Leeds Metropolitan University
Leeds Metropolitan University
Leeds Metropolitan University is a British University with three campuses. Two are situated in Leeds, West Yorkshire, England while the third is situated in Bhopal, India...
http://drgersh.googlepages.com/ph.dprogrammeinrehabilitationneuropsychohttp://www.leedsmet.ac.uk/health/psychology/features/crossboundaries.htmhttp://drgersh.googlepages.com/home
Research Groups
Biomedical Engineering Group- This group has addressed applications areas such as: Positron Emission TomographyPositron emission tomographyPositron emission tomography is nuclear medicine imaging technique that produces a three-dimensional image or picture of functional processes in the body. The system detects pairs of gamma rays emitted indirectly by a positron-emitting radionuclide , which is introduced into the body on a...
(PET) and Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging fMRI as well as developments in the treatment of decubitus ulcer by sitting, orthoticsOrthoticsOrthotics is a specialty within the medical field concerned with the design, manufacture and application of orthoses. An orthosis is an orthopedic device that supports or corrects the function of a limb or the torso...
and prosthetics, wheelchairs, and assistive aids all towards providing less restrictive environments for those in need of rehabilitation. Also developments in systemicsSystemicsIn the context of systems science and systems philosophy, the term systemics refers to an initiative to study systems from a holistic point of view...
, optimisationOptimization (mathematics)In mathematics, computational science, or management science, mathematical optimization refers to the selection of a best element from some set of available alternatives....
, and computational models have been pursued as well as in Human Factors and ErgonomicsErgonomicsErgonomics is the study of designing equipment and devices that fit the human body, its movements, and its cognitive abilities.The International Ergonomics Association defines ergonomics as follows:...
, digital image processingDigital image processingDigital image processing is the use of computer algorithms to perform image processing on digital images. As a subcategory or field of digital signal processing, digital image processing has many advantages over analog image processing...
, and in electrophysiologyElectrophysiologyElectrophysiology is the study of the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage change or electric current on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart...
and signal analysis, examining the KinesiologyKinesiologyKinesiology, also known as human kinetics is the scientific study of human movement. Kinesiology addresses physiological, mechanical, and psychological mechanisms. Applications of kinesiology to human health include: biomechanics and orthopedics, rehabilitation, such as physical and occupational...
of movement and gaitGaitGait is the pattern of movement of the limbs of animals, including humans, during locomotion over a solid substrate. Most animals use a variety of gaits, selecting gait based on speed, terrain, the need to maneuver, and energetic efficiency...
, speech synthesis, recognition, and acousticsAcousticsAcoustics is the interdisciplinary science that deals with the study of all mechanical waves in gases, liquids, and solids including vibration, sound, ultrasound and infrasound. A scientist who works in the field of acoustics is an acoustician while someone working in the field of acoustics...
as well as computational systems in rehabilitation.
Neurocybernetics Group
- Developments have included computer models of nervous system function and dysfunction employing applications of theoretical physicsPhysicsPhysics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, artificial neural networksNeural NetworksNeural Networks is the official journal of the three oldest societies dedicated to research in neural networks: International Neural Network Society, European Neural Network Society and Japanese Neural Network Society, published by Elsevier...
, linear and non-linear models, bifurcation theoryBifurcation theoryBifurcation theory is the mathematical study of changes in the qualitative or topological structure of a given family, such as the integral curves of a family of vector fields, and the solutions of a family of differential equations...
, and chaos theoryChaos theoryChaos theory is a field of study in mathematics, with applications in several disciplines including physics, economics, biology, and philosophy. Chaos theory studies the behavior of dynamical systems that are highly sensitive to initial conditions, an effect which is popularly referred to as the...
as vehicles for simulating nervous system function and dysfunction. Additionally, analyses of applications of combinatoricsCombinatoricsCombinatorics is a branch of mathematics concerning the study of finite or countable discrete structures. Aspects of combinatorics include counting the structures of a given kind and size , deciding when certain criteria can be met, and constructing and analyzing objects meeting the criteria ,...
, recurrence relations, and the establishment of asymptotic distributionAsymptotic distributionIn mathematics and statistics, an asymptotic distribution is a hypothetical distribution that is in a sense the "limiting" distribution of a sequence of distributions...
s are studied in relation to biomedical and rehabilitation systems. Research has also examined the effects of trauma and therapeutic interventions on search methods, formal proofFormal proofA formal proof or derivation is a finite sequence of sentences each of which is an axiom or follows from the preceding sentences in the sequence by a rule of inference. The last sentence in the sequence is a theorem of a formal system...
, and knowledgeKnowledgeKnowledge is a familiarity with someone or something unknown, which can include information, facts, descriptions, or skills acquired through experience or education. It can refer to the theoretical or practical understanding of a subject...
representation as well as natural languageNatural languageIn the philosophy of language, a natural language is any language which arises in an unpremeditated fashion as the result of the innate facility for language possessed by the human intellect. A natural language is typically used for communication, and may be spoken, signed, or written...
understanding, scene understanding, learningLearningLearning is acquiring new or modifying existing knowledge, behaviors, skills, values, or preferences and may involve synthesizing different types of information. The ability to learn is possessed by humans, animals and some machines. Progress over time tends to follow learning curves.Human learning...
, and expert systems.
Neuroscience Group
- Areas of investigation include Muscle, Nerve, and Work, Clinical Systems Neuroscience using electrophysiological methods including EMGElectromyographyElectromyography is a technique for evaluating and recording the electrical activity produced by skeletal muscles. EMG is performed using an instrument called an electromyograph, to produce a record called an electromyogram. An electromyograph detects the electrical potential generated by muscle...
, EEGEEGEEG commonly refers to electroencephalography, a measurement of the electrical activity of the brain.EEG may also refer to:* Emperor Entertainment Group, a Hong Kong-based entertainment company...
, EOG, evoked potentials and event-related potentialEvent-related potentialAn event-related potential is any measured brain response that is directly the result of a thought or perception. More formally, it is any stereotyped electrophysiological response to an internal or external stimulus....
s, imagingMedical imagingMedical imaging is the technique and process used to create images of the human body for clinical purposes or medical science...
, computational modeling, NeuropharmacologyNeuropharmacologyNeuropharmacology is the study of how drugs affect cellular function in the nervous system. There are two main branches of neuropharmacology: behavioral and molecular. Behavioral neuropharmacology focuses on the study of how drugs affect human behavior , including the study of how drug dependence...
, psychophysicsPsychophysicsPsychophysics quantitatively investigates the relationship between physical stimuli and the sensations and perceptions they effect. Psychophysics has been described as "the scientific study of the relation between stimulus and sensation" or, more completely, as "the analysis of perceptual...
and signal detection theory, NeuroradiologyNeuroradiologyNeuroradiology is a subspecialty of radiology focusing on the diagnosis and characterization of abnormalities of the central and peripheral nervous system, spine, and head and neck. Primary imaging modalities include computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging...
(including CTComputed tomographyX-ray computed tomography or Computer tomography , is a medical imaging method employing tomography created by computer processing...
, MRI PETPositron emission tomographyPositron emission tomography is nuclear medicine imaging technique that produces a three-dimensional image or picture of functional processes in the body. The system detects pairs of gamma rays emitted indirectly by a positron-emitting radionuclide , which is introduced into the body on a...
, and spectral imagingSpectral imagingSpectral imaging is a branch of spectroscopy and of photography in which a complete spectrum or some spectral information is collected at every location in an image plane...
) applied to clinical applications in rehabilitation.
Rehabilitation and Applied Biosciences Group
- Ongoing research in rehabilitation application of Evolutionary PsychologyEvolutionary psychologyEvolutionary psychology is an approach in the social and natural sciences that examines psychological traits such as memory, perception, and language from a modern evolutionary perspective. It seeks to identify which human psychological traits are evolved adaptations, that is, the functional...
, Developmental DisabilityDevelopmental disabilityDevelopmental disability is a term used in the United States and Canada to describe lifelong disabilities attributable to mental or physical impairments, manifested prior to age 18. It is not synonymous with "developmental delay" which is often a consequence of a temporary illness or trauma during...
, CognitionCognitionIn science, cognition refers to mental processes. These processes include attention, remembering, producing and understanding language, solving problems, and making decisions. Cognition is studied in various disciplines such as psychology, philosophy, linguistics, and computer science...
, KinesiologyKinesiologyKinesiology, also known as human kinetics is the scientific study of human movement. Kinesiology addresses physiological, mechanical, and psychological mechanisms. Applications of kinesiology to human health include: biomechanics and orthopedics, rehabilitation, such as physical and occupational...
, and Rehabilitation (neuropsychology)Rehabilitation (neuropsychology)Rehabilitation of sensory and cognitive function typically involves methods for retraining neural pathways or training new neural pathways to regain or improve neurocognitive functioning that has been diminished by disease or traumatic injury....
.
Humanities in Biomedicine Group
- Researchers explore ethical issues generated by the application of scientific and technological advances to the preservation, destruction, and programming of human life including orphan drugOrphan drugAn orphan drug is a pharmaceutical agent that has been developed specifically to treat a rare medical condition, the condition itself being referred to as an orphan disease...
development, abortionAbortionAbortion is defined as the termination of pregnancy by the removal or expulsion from the uterus of a fetus or embryo prior to viability. An abortion can occur spontaneously, in which case it is usually called a miscarriage, or it can be purposely induced...
, euthanasiaEuthanasiaEuthanasia refers to the practice of intentionally ending a life in order to relieve pain and suffering....
, behavior control, allocation of medical resources in technology development, ethics of the patient-physician interaction, and the ethicsEthicsEthics, also known as moral philosophy, is a branch of philosophy that addresses questions about morality—that is, concepts such as good and evil, right and wrong, virtue and vice, justice and crime, etc.Major branches of ethics include:...
of technology application.
Cognitive Neuroscience, Neuropsychology, Curriculum, and Human Factors Groups
- Methods of Psychological Science have been employed to develop theoretical and applied strategies in rehabilitation applications. Research bridges the gap between Cognitive ScienceCognitive scienceCognitive science is the interdisciplinary scientific study of mind and its processes. It examines what cognition is, what it does and how it works. It includes research on how information is processed , represented, and transformed in behaviour, nervous system or machine...
, Communication Sciences, SystemicsSystemicsIn the context of systems science and systems philosophy, the term systemics refers to an initiative to study systems from a holistic point of view...
and cellular NeuroscienceNeuroscienceNeuroscience is the scientific study of the nervous system. Traditionally, neuroscience has been seen as a branch of biology. However, it is currently an interdisciplinary science that collaborates with other fields such as chemistry, computer science, engineering, linguistics, mathematics,...
, brain imaging, and Computational NeuroscienceComputational neuroscienceComputational neuroscience is the study of brain function in terms of the information processing properties of the structures that make up the nervous system...
on the one hand and curriculumCurriculumSee also Syllabus.In formal education, a curriculum is the set of courses, and their content, offered at a school or university. As an idea, curriculum stems from the Latin word for race course, referring to the course of deeds and experiences through which children grow to become mature adults...
and instructionEducationEducation in its broadest, general sense is the means through which the aims and habits of a group of people lives on from one generation to the next. Generally, it occurs through any experience that has a formative effect on the way one thinks, feels, or acts...
on the other. Changes in the electrical activity of the brain during cognition have been examined and changes in blood flow and metabolic activity of the brain during cognitionCognitionIn science, cognition refers to mental processes. These processes include attention, remembering, producing and understanding language, solving problems, and making decisions. Cognition is studied in various disciplines such as psychology, philosophy, linguistics, and computer science...
are being examined. Mechanisms by which neural networks generate voluntary actions, memoryMemoryIn psychology, memory is an organism's ability to store, retain, and recall information and experiences. Traditional studies of memory began in the fields of philosophy, including techniques of artificially enhancing memory....
, thinking, problem solvingProblem solvingProblem solving is a mental process and is part of the larger problem process that includes problem finding and problem shaping. Consideredthe most complex of all intellectual functions, problem solving has been defined as higher-order cognitive process that requires the modulation and control of...
, languageLanguageLanguage may refer either to the specifically human capacity for acquiring and using complex systems of communication, or to a specific instance of such a system of complex communication...
and emotionEmotionEmotion is a complex psychophysiological experience of an individual's state of mind as interacting with biochemical and environmental influences. In humans, emotion fundamentally involves "physiological arousal, expressive behaviors, and conscious experience." Emotion is associated with mood,...
are being examined to learn how these capabilities malfunction in persons with brain damage, developmental disabilities, mental illnessMental illnessA mental disorder or mental illness is a psychological or behavioral pattern generally associated with subjective distress or disability that occurs in an individual, and which is not a part of normal development or culture. Such a disorder may consist of a combination of affective, behavioural,...
and dementiaDementiaDementia is a serious loss of cognitive ability in a previously unimpaired person, beyond what might be expected from normal aging...
.
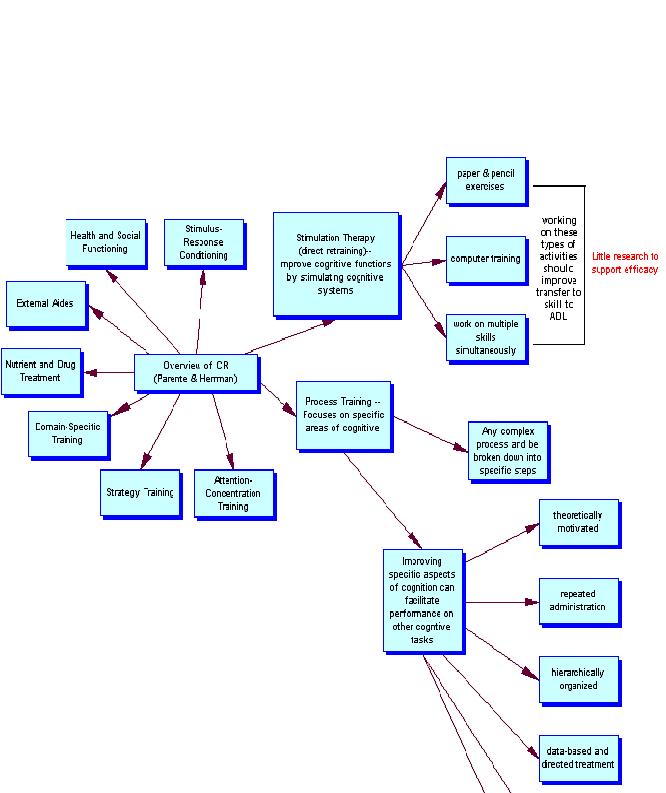
- Rehabilitation applications include: direct retraining, process training, attentionAttentionAttention is the cognitive process of paying attention to one aspect of the environment while ignoring others. Attention is one of the most intensely studied topics within psychology and cognitive neuroscience....
-concentration training, strategy training, nutrient and drug treatment effects of cognitive performance, orthoticsOrthoticsOrthotics is a specialty within the medical field concerned with the design, manufacture and application of orthoses. An orthosis is an orthopedic device that supports or corrects the function of a limb or the torso...
methods, and domain specific training to facilitate return to work, ability to function independently, the facilitation of specialized school placement, and forensic issues.
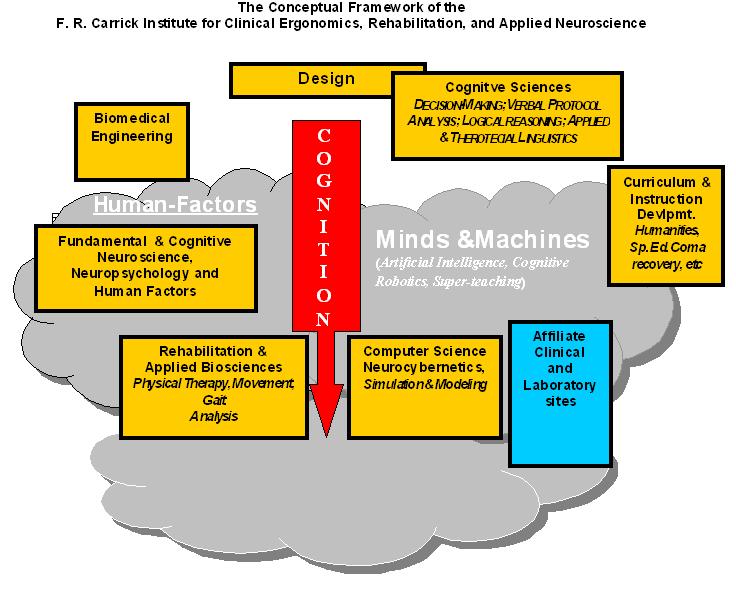
The Central Model for Cognitive Neuroscience and Education in Rehabilitation

- As language and communication are central and fundamental to traumatic brain dysfunction, developmental disabilities and training, intensive independent work in Applied and Theoretical Linguistics includes:
- Linguistic Theory
- SociolinguisticsSociolinguisticsSociolinguistics is the descriptive study of the effect of any and all aspects of society, including cultural norms, expectations, and context, on the way language is used, and the effects of language use on society...
- SemanticsSemanticsSemantics is the study of meaning. It focuses on the relation between signifiers, such as words, phrases, signs and symbols, and what they stand for, their denotata....
- PhoneticsPhoneticsPhonetics is a branch of linguistics that comprises the study of the sounds of human speech, or—in the case of sign languages—the equivalent aspects of sign. It is concerned with the physical properties of speech sounds or signs : their physiological production, acoustic properties, auditory...
and PhonologyPhonologyPhonology is, broadly speaking, the subdiscipline of linguistics concerned with the sounds of language. That is, it is the systematic use of sound to encode meaning in any spoken human language, or the field of linguistics studying this use... - SyntaxSyntaxIn linguistics, syntax is the study of the principles and rules for constructing phrases and sentences in natural languages....
- Language Universals
- Language Acquisition and Linguistic Theory
- Discourse AnalysisDiscourse analysisDiscourse analysis , or discourse studies, is a general term for a number of approaches to analyzing written, spoken, signed language use or any significant semiotic event....
- Neural and Computational Methods of Speech Perception and Production
- Artificial IntelligenceArtificial intelligenceArtificial intelligence is the intelligence of machines and the branch of computer science that aims to create it. AI textbooks define the field as "the study and design of intelligent agents" where an intelligent agent is a system that perceives its environment and takes actions that maximize its...
- Natural Language Processing
- Computational LinguisticsComputational linguisticsComputational linguistics is an interdisciplinary field dealing with the statistical or rule-based modeling of natural language from a computational perspective....
- Language Acquisition
- Cognitive Development and Language
- Language Acquisition and Linguistic Theory
- Developmental PsycholinguisticsPsycholinguisticsPsycholinguistics or psychology of language is the study of the psychological and neurobiological factors that enable humans to acquire, use, comprehend and produce language. Initial forays into psycholinguistics were largely philosophical ventures, due mainly to a lack of cohesive data on how the...
- Individual Patterns of Language Development
- Second Language Acquisition, Bilingualism, and Language Teaching
- Neurolinguistics and Language Disorders
- Phonological Disorders
- Child Language Disorders
- Adult AphasiaAphasiaAphasia is an impairment of language ability. This class of language disorder ranges from having difficulty remembering words to being completely unable to speak, read, or write....
- Communicative Disorders and Exceptionality

- At its core, CERAN has a sharp focus on basic issues in Experimental Psychology, and extensions into two primary areas: (1) Human Factors Engineering and Design (HFED); and (2) Applied Cognitive Science, applied to Rehabilitation Sciences.
- CERAN has developed an integrated research focus formalized through graduate training that addresses central issues of modern cognitive science applied to rehabilitation outlined in the figure below. Because of the significant opportunities (and potential problems) created by the rapid proliferation of information technologies, the core also includes focus specific to this domain, including the following: Psychology of Information TechnologyInformation technologyInformation technology is the acquisition, processing, storage and dissemination of vocal, pictorial, textual and numerical information by a microelectronics-based combination of computing and telecommunications...
; and LogicLogicIn philosophy, Logic is the formal systematic study of the principles of valid inference and correct reasoning. Logic is used in most intellectual activities, but is studied primarily in the disciplines of philosophy, mathematics, semantics, and computer science...
and Computer ScienceComputer scienceComputer science or computing science is the study of the theoretical foundations of information and computation and of practical techniques for their implementation and application in computer systems...
. Rehabilitation Sciences cannot possibly be studied from a uni-disciplinary perspective.
- CERAN'S mission stresses standard and novel strategies employing traditional Psychological as well as Engineering approaches to Rehabilitation Science clinically and experimentally focusing on the design of user-interface, instrumentation, technology, and principles to do what ever is necessary for the vocational rehabilitation of impaired individuals and children to get them in or returned to the work force or becoming more effective learners.

