
Conductivity of transparency
Encyclopedia
The conductivity of transparency describes the combination of the sheet resistance
and the transparency
and utilizes the properties of graphene
as the reference.
and the transparency
(at 550 nm). The conductivity of transparency was introduced on the basis of graphene
to compare different materials without the use of two independent parameters.
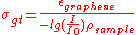
 : conductivity of transparency based on graphene;
: conductivity of transparency based on graphene;
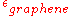 : absorption coefficient of graphene;
: absorption coefficient of graphene;
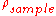 : sheet resistance of the sample;
: sheet resistance of the sample;
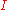 : intensity of light after absorption;
: intensity of light after absorption;
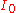 : intensity of light before absorption.
: intensity of light before absorption.
layer was published in 2008. So graphene
absorbs 2.3 % of white light. Hence, assuming that the ideal inter-layer distance of two graphene sheets is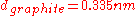 , as in graphite
, as in graphite
, one can calculate the absorption coefficient of graphene according to the Bouguer-Lambert law to .
.
Applied Bouguer-Lambert law:

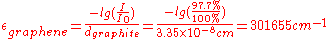
The outcome of this is the general formula to determine the conductivity of transparency of arbitrary electroconductive and transparent materials, utilizing graphene as the reference:
So, to determine the conductivity of transparency it is necessary to measure the transmission (at 550 nm) and the sheet resistance
of the sample. The sheet resistance
can be obtained by four-point probe measurement (Sheet resistance
, Van der Pauw method
). Contrary to the electrical conductivity it is not necessary to determine the thickness of the sample, because graphene
is utilized as the reference by using the transparency.
Sheet resistance
Sheet resistance is a measure of resistance of thin films that are namely uniform in thickness. It is commonly used to characterize materials made by semiconductor doping, metal deposition, resistive paste printing, and glass coating. Examples of these processes are: doped semiconductor regions...
and the transparency
Transparency and translucency
In the field of optics, transparency is the physical property of allowing light to pass through a material; translucency only allows light to pass through diffusely. The opposite property is opacity...
and utilizes the properties of graphene
Graphene
Graphene is an allotrope of carbon, whose structure is one-atom-thick planar sheets of sp2-bonded carbon atoms that are densely packed in a honeycomb crystal lattice. The term graphene was coined as a combination of graphite and the suffix -ene by Hanns-Peter Boehm, who described single-layer...
as the reference.
Description
The properties of electroconductive and transparent materials can be described by the sheet resistanceSheet resistance
Sheet resistance is a measure of resistance of thin films that are namely uniform in thickness. It is commonly used to characterize materials made by semiconductor doping, metal deposition, resistive paste printing, and glass coating. Examples of these processes are: doped semiconductor regions...
and the transparency
Transparency and translucency
In the field of optics, transparency is the physical property of allowing light to pass through a material; translucency only allows light to pass through diffusely. The opposite property is opacity...
(at 550 nm). The conductivity of transparency was introduced on the basis of graphene
Graphene
Graphene is an allotrope of carbon, whose structure is one-atom-thick planar sheets of sp2-bonded carbon atoms that are densely packed in a honeycomb crystal lattice. The term graphene was coined as a combination of graphite and the suffix -ene by Hanns-Peter Boehm, who described single-layer...
to compare different materials without the use of two independent parameters.
Conductivity of Transparency
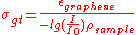
 : conductivity of transparency based on graphene;
: conductivity of transparency based on graphene;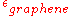 : absorption coefficient of graphene;
: absorption coefficient of graphene;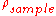 : sheet resistance of the sample;
: sheet resistance of the sample;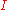 : intensity of light after absorption;
: intensity of light after absorption;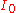 : intensity of light before absorption.
: intensity of light before absorption.Derivation
The absorption of a single grapheneGraphene
Graphene is an allotrope of carbon, whose structure is one-atom-thick planar sheets of sp2-bonded carbon atoms that are densely packed in a honeycomb crystal lattice. The term graphene was coined as a combination of graphite and the suffix -ene by Hanns-Peter Boehm, who described single-layer...
layer was published in 2008. So graphene
Graphene
Graphene is an allotrope of carbon, whose structure is one-atom-thick planar sheets of sp2-bonded carbon atoms that are densely packed in a honeycomb crystal lattice. The term graphene was coined as a combination of graphite and the suffix -ene by Hanns-Peter Boehm, who described single-layer...
absorbs 2.3 % of white light. Hence, assuming that the ideal inter-layer distance of two graphene sheets is
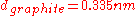 , as in graphite
, as in graphiteGraphite
The mineral graphite is one of the allotropes of carbon. It was named by Abraham Gottlob Werner in 1789 from the Ancient Greek γράφω , "to draw/write", for its use in pencils, where it is commonly called lead . Unlike diamond , graphite is an electrical conductor, a semimetal...
, one can calculate the absorption coefficient of graphene according to the Bouguer-Lambert law to
 .
.Applied Bouguer-Lambert law:

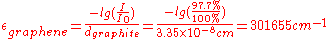
The outcome of this is the general formula to determine the conductivity of transparency of arbitrary electroconductive and transparent materials, utilizing graphene as the reference:
Formula to determine the Conductivity of Transparency
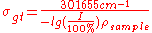 |
|---|
So, to determine the conductivity of transparency it is necessary to measure the transmission (at 550 nm) and the sheet resistance
Sheet resistance
Sheet resistance is a measure of resistance of thin films that are namely uniform in thickness. It is commonly used to characterize materials made by semiconductor doping, metal deposition, resistive paste printing, and glass coating. Examples of these processes are: doped semiconductor regions...
of the sample. The sheet resistance
Sheet resistance
Sheet resistance is a measure of resistance of thin films that are namely uniform in thickness. It is commonly used to characterize materials made by semiconductor doping, metal deposition, resistive paste printing, and glass coating. Examples of these processes are: doped semiconductor regions...
can be obtained by four-point probe measurement (Sheet resistance
Sheet resistance
Sheet resistance is a measure of resistance of thin films that are namely uniform in thickness. It is commonly used to characterize materials made by semiconductor doping, metal deposition, resistive paste printing, and glass coating. Examples of these processes are: doped semiconductor regions...
, Van der Pauw method
Van der Pauw method
The van der Pauw Method is a technique commonly used to measure the Resistivity and the Hall Coefficient of a sample. Its power lies in its ability to accurately measure the properties of a sample of any arbitrary shape, so long as the sample is approximately two-dimensional The van der Pauw...
). Contrary to the electrical conductivity it is not necessary to determine the thickness of the sample, because graphene
Graphene
Graphene is an allotrope of carbon, whose structure is one-atom-thick planar sheets of sp2-bonded carbon atoms that are densely packed in a honeycomb crystal lattice. The term graphene was coined as a combination of graphite and the suffix -ene by Hanns-Peter Boehm, who described single-layer...
is utilized as the reference by using the transparency.
Examples
| Materials | I (%) | 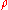 (Ω) (Ω) |
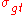 (S/cm) (S/cm) |
references |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| graphene Graphene Graphene is an allotrope of carbon, whose structure is one-atom-thick planar sheets of sp2-bonded carbon atoms that are densely packed in a honeycomb crystal lattice. The term graphene was coined as a combination of graphite and the suffix -ene by Hanns-Peter Boehm, who described single-layer... |
97.7 | 6000 | 4975 | Blake et al. |
| graphene oxide Graphene oxide Graphite oxide, formerly called graphitic oxide or graphitic acid, is a compound of carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen in variable ratios, obtained by treating graphite with strong oxidizers... |
96 | 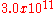 |
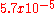 |
Becerril et al. |
| reduced graphene oxide Graphene oxide Graphite oxide, formerly called graphitic oxide or graphitic acid, is a compound of carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen in variable ratios, obtained by treating graphite with strong oxidizers... |
87 |  |
50 | Eda et al. |
| nanographene (1100°C) | 56 | 1600 | 749 | Wang et al. |
| graphene (CVD) | 90 | 350 | 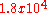 |
Li et al. |
| SWCNTs Carbon nanotube Carbon nanotubes are allotropes of carbon with a cylindrical nanostructure. Nanotubes have been constructed with length-to-diameter ratio of up to 132,000,000:1, significantly larger than for any other material... |
70 | 30 | 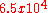 |
Wu et al. |
| ITO Indium tin oxide Indium tin oxide is a solid solution of indium oxide and tin oxide , typically 90% In2O3, 10% SnO2 by weight. It is transparent and colorless in thin layers while in bulk form it is yellowish to grey... |
77 | 100 |  |
Sigma–Aldrich catalog no. 639281 |

