
Sheet resistance
Encyclopedia

Sheet resistance is a measure of resistance
Electrical resistance
The electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical...
of thin films that are namely uniform in thickness. It is commonly used to characterize materials made by semiconductor doping, metal deposition, resistive paste printing, and glass coating
Insulated glazing
Insulated glazing also known as double glazing are double or triple glass window panes separated by an air or other gas filled space to reduce heat transfer across a part of the building envelope....
. Examples of these processes are: doped semiconductor
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity due to electron flow intermediate in magnitude between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means a conductivity roughly in the range of 103 to 10−8 siemens per centimeter...
regions (e.g. silicon
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. A tetravalent metalloid, it is less reactive than its chemical analog carbon, the nonmetal directly above it in the periodic table, but more reactive than germanium, the metalloid directly below it in the table...
or polysilicon), and the resistors that are screen printed onto the substrates of thick-film hybrid microcircuits.
The utility of sheet resistance as opposed to resistance
Electrical resistance
The electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical...
or resistivity
Resistivity
Electrical resistivity is a measure of how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allows the movement of electric charge. The SI unit of electrical resistivity is the ohm metre...
is that it is directly measured using a four-terminal sensing
Four-terminal sensing
Four-terminal sensing , 4-wire sensing, or 4-point probes method is an electrical impedance measuring technique that uses separate pairs of current-carrying and voltage-sensing electrodes to make more accurate measurements than traditional two-terminal sensing...
measurement (also known as a four-point probe measurement).
Calculations
Resistivity
Electrical resistivity is a measure of how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allows the movement of electric charge. The SI unit of electrical resistivity is the ohm metre...
as used in three-dimensional systems. When the term sheet resistance is used, it is implied that the current flow is along the plane of the sheet, not perpendicular to it.
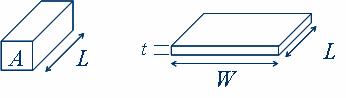
In a regular three-dimensional conductor, the resistance
Electrical resistance
The electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical...
can be written as
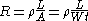
where
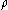 is the resistivity,
is the resistivity, 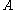 is the cross-sectional area and
is the cross-sectional area and 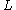 is the length. The cross-sectional area can be split into the width
is the length. The cross-sectional area can be split into the width 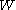 and the sheet thickness
and the sheet thickness  .
.Upon clubbing the resistivity with the thickness, the resistance can then be written as:
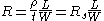
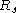 is then the sheet resistance.
is then the sheet resistance.Units
Because the bulk resistance is multiplied with a dimensionless quantity to obtain sheet resistance, the units of sheet resistance are ohmOhm
The ohm is the SI unit of electrical resistance, named after German physicist Georg Simon Ohm.- Definition :The ohm is defined as a resistance between two points of a conductor when a constant potential difference of 1 volt, applied to these points, produces in the conductor a current of 1 ampere,...
s. An alternate, common unit is "ohms per square" (denoted "Ω/sq" or "
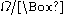 "), which is dimensionally equal to an ohm, but is exclusively used for sheet resistance. This is an advantage, because sheet resistance of 1Ω could be taken out of context and misinterpreted as bulk resistance of 1 ohm, whereas sheet resistance of 1Ω/sq cannot thusly be misinterpreted.
"), which is dimensionally equal to an ohm, but is exclusively used for sheet resistance. This is an advantage, because sheet resistance of 1Ω could be taken out of context and misinterpreted as bulk resistance of 1 ohm, whereas sheet resistance of 1Ω/sq cannot thusly be misinterpreted.The reason for the name "ohms per square" is that a square sheet with sheet resistance 10 ohm/square has an actual resistance of 10 ohm, regardless of the size of the square. (For a square,
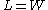 , so
, so 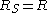 .) The unit can be thought of as, loosely, "ohms per aspect ratio
.) The unit can be thought of as, loosely, "ohms per aspect ratioAspect ratio
The aspect ratio of a shape is the ratio of its longer dimension to its shorter dimension. It may be applied to two characteristic dimensions of a three-dimensional shape, such as the ratio of the longest and shortest axis, or for symmetrical objects that are described by just two measurements,...
".
For semiconductors
For semiconductors doped through diffusion or surface peaked ion implantation we define the sheet resistance using the average resistivity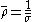 of the material:
of the material: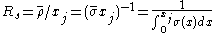
which in materials with majority-carrier properties can be approximated by (neglecting intrinsic charge carriers):
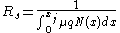
where
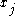 is the junction depth,
is the junction depth, 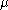 is the majority-carrier mobility,
is the majority-carrier mobility, 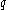 is the carrier charge and
is the carrier charge and 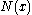 is the net impurity concentration in terms of depth. Knowing the background carrier concentration
is the net impurity concentration in terms of depth. Knowing the background carrier concentration 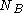 and the surface impurity concentration the sheet resistance-junction depth product
and the surface impurity concentration the sheet resistance-junction depth product 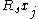 can be found using Irvin's curves, which are numerical solutions to the above equation.
can be found using Irvin's curves, which are numerical solutions to the above equation.Measurement
A four point probeFour-terminal sensing
Four-terminal sensing , 4-wire sensing, or 4-point probes method is an electrical impedance measuring technique that uses separate pairs of current-carrying and voltage-sensing electrodes to make more accurate measurements than traditional two-terminal sensing...
is used to avoid contact resistance, which can often be the same magnitude as the sheet resistance. Typically a constant current
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
is applied to two probes and the potential on the other two probes is measured with a high impedance voltmeter
Voltmeter
A voltmeter is an instrument used for measuring electrical potential difference between two points in an electric circuit. Analog voltmeters move a pointer across a scale in proportion to the voltage of the circuit; digital voltmeters give a numerical display of voltage by use of an analog to...
. A geometry factor needs to be applied according to the shape of the four point array. Two common arrays are square and in-line. For more details see Van der Pauw method
Van der Pauw method
The van der Pauw Method is a technique commonly used to measure the Resistivity and the Hall Coefficient of a sample. Its power lies in its ability to accurately measure the properties of a sample of any arbitrary shape, so long as the sample is approximately two-dimensional The van der Pauw...
.
A very crude two point probe method is to measure resistance with the probes close together and the resistance with the probes far apart.
The difference between these two resistances will be the order of magnitude of the sheet resistance.
External links
- Sheet resistivity measurement Measuring sheet resistivity of thin conductive coatings e.g. metallization, wafers, ITO, TCO, CVD, PVD,etc.

