Benzenediol
Encyclopedia
Benzenediols or dihydroxybenzenes are organic
chemical compound
s in which two hydroxyl groups are substituted onto a benzene ring. These aromatic compounds are classed as phenols
, and more specifically as polyphenol
s. There are three isomer
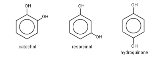
s of benzenediol: 1,2-benzenediol (the ortho isomer
) is commonly known as catechol, 1,3-benzenediol (the meta isomer
) is commonly known as resorcinol
, and 1,4-benzenediol (the para isomer
) is commonly known as hydroquinone.
All three of these compounds are colorless to white granular solid
s at room temperature
and pressure
, but upon exposure to oxygen they may darken. All three isomers have the chemical formula
C6H6O2.
Similar to other phenols, the hydroxyl groups on the aromatic ring of a benzenediol are weakly acidic. Each benzenediol can lose an H+ from one of the hydroxyls to form a type of phenolate ion.
The Dakin oxidation is an organic redox reaction in which an ortho- or para-hydroxylated phenyl aldehyde or ketone reacts with hydrogen peroxide in base to form a benzenediol and a carboxylate. Overall, the carbonyl group is oxidized, and the hydrogen peroxide is reduced.
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
chemical compound
Chemical compound
A chemical compound is a pure chemical substance consisting of two or more different chemical elements that can be separated into simpler substances by chemical reactions. Chemical compounds have a unique and defined chemical structure; they consist of a fixed ratio of atoms that are held together...
s in which two hydroxyl groups are substituted onto a benzene ring. These aromatic compounds are classed as phenols
Phenols
In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of a hydroxyl group bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group...
, and more specifically as polyphenol
Polyphenol
Polyphenols are a structural class of natural, synthetic, and semisynthetic organic chemicals characterized by the presence of large multiples of phenol structural units...
s. There are three isomer
Isomer
In chemistry, isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. Isomers do not necessarily share similar properties, unless they also have the same functional groups. There are many different classes of isomers, like stereoisomers, enantiomers, geometrical...
s of benzenediol: 1,2-benzenediol (the ortho isomer
Arene substitution patterns
Arene substitution patterns are part of organic chemistry IUPAC nomenclature and pinpoint the position of substituents other than hydrogen in relation to each other on an aromatic hydrocarbon.- Ortho, meta, and para substitution :...
) is commonly known as catechol, 1,3-benzenediol (the meta isomer
Arene substitution patterns
Arene substitution patterns are part of organic chemistry IUPAC nomenclature and pinpoint the position of substituents other than hydrogen in relation to each other on an aromatic hydrocarbon.- Ortho, meta, and para substitution :...
) is commonly known as resorcinol
Resorcinol
Resorcinol is a dihydroxy benzene. It is the 1,3-isomer of benzenediol with the formula C6H42.-Nomenclature:Benzene-1,3-diol is the name recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry in its 1993 Recommendations for the Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry.-Production:It is...
, and 1,4-benzenediol (the para isomer
Arene substitution patterns
Arene substitution patterns are part of organic chemistry IUPAC nomenclature and pinpoint the position of substituents other than hydrogen in relation to each other on an aromatic hydrocarbon.- Ortho, meta, and para substitution :...
) is commonly known as hydroquinone.
| ortho isomer |
meta isomer |
para isomer |
|---|---|---|
| Catechol pyrocatechol 1,2-benzenediol o-benzenediol 1,2-dihydroxybenzene o-dihydroxybenzene |
Resorcinol Resorcinol Resorcinol is a dihydroxy benzene. It is the 1,3-isomer of benzenediol with the formula C6H42.-Nomenclature:Benzene-1,3-diol is the name recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry in its 1993 Recommendations for the Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry.-Production:It is... 1,3-benzenediol m-benzenediol 1,3-dihydroxybenzene m-dihydroxybenzene resorcin |
Hydroquinone Hydroquinone Hydroquinone, also benzene-1,4-diol or quinol, is an aromatic organic compound that is a type of phenol, having the chemical formula C6H42. Its chemical structure, shown in the table at right, has two hydroxyl groups bonded to a benzene ring in a para position. It is a white granular solid... 1,4-benzenediol p-benzenediol 1,4-dihydroxybenzene p-dihydroxybenzene |
All three of these compounds are colorless to white granular solid
Solid
Solid is one of the three classical states of matter . It is characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to changes of shape or volume. Unlike a liquid, a solid object does not flow to take on the shape of its container, nor does it expand to fill the entire volume available to it like a...
s at room temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
and pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
, but upon exposure to oxygen they may darken. All three isomers have the chemical formula
Chemical formula
A chemical formula or molecular formula is a way of expressing information about the atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound....
C6H6O2.
Similar to other phenols, the hydroxyl groups on the aromatic ring of a benzenediol are weakly acidic. Each benzenediol can lose an H+ from one of the hydroxyls to form a type of phenolate ion.
The Dakin oxidation is an organic redox reaction in which an ortho- or para-hydroxylated phenyl aldehyde or ketone reacts with hydrogen peroxide in base to form a benzenediol and a carboxylate. Overall, the carbonyl group is oxidized, and the hydrogen peroxide is reduced.

