
Bacterial cellular morphologies
Encyclopedia
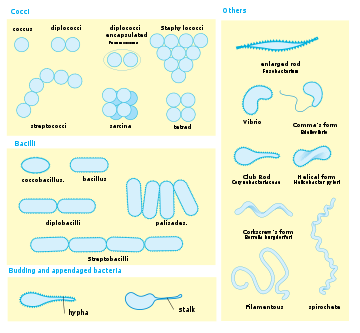
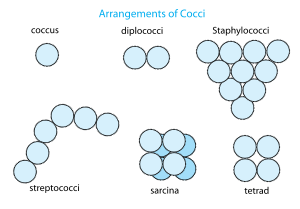
The basic forms are spheres (coccus) and round-ended cylinders (bacillus). But there may be others such as helically-twisted cylinders (spirochetes), cylinders curved in one plane (Selenomonads) and unusual morphologies (square bacteria). They also conform diplos, tetrads, staphylos, streptos, palizadas etc.
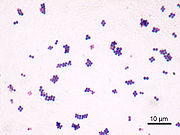
Coccus
Microorganism
A microorganism or microbe is a microscopic organism that comprises either a single cell , cell clusters, or no cell at all...
(usually bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
) whose overall shape is spherical
Sphere
A sphere is a perfectly round geometrical object in three-dimensional space, such as the shape of a round ball. Like a circle in two dimensions, a perfect sphere is completely symmetrical around its center, with all points on the surface lying the same distance r from the center point...
or nearly spherical. Describing a bacterium as a coccus, or sphere, distinguishes it from bacillus
Bacillus (shape)
The word bacillus may be used to describe any rod-shaped bacterium, and such bacilli are found in many different taxonomic groups of bacteria. However, the name Bacillus, capitalized and italicized, refers to a specific genus of bacteria...
, or rod. This is the first of many taxonomic traits for identifying and classifying a bacterium according to binomial nomenclature.
Aggregations
Aggregations of coccoid bacteria often occur and these forms have specific names as well; listed here are the basic forms as well as representative bacterial generaGenus
In biology, a genus is a low-level taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms, which is an example of definition by genus and differentia...
:
- pairs, or diplococciDiplococcusA diplococcus is a round bacterium that typically occurs in the form of two joined cells. Examples are Streptococcus pneumoniae, Moraxella catarrhalis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis...
(NeisseriaNeisseriaThe Neisseria is a large genus of commensal bacteria that colonize the mucosal surfaces of many animals. Of the 11 species that colonize humans, only two are pathogens. N. meningitidis and N. gonorrhoeae often cause asymptomatic infections, a commensal-like behavior...
) - groups of four or eight known as tetrads or sarcinaSarcina (genus)Sarcina is a genus of Gram-positive cocci bacteria in the family Clostridiaceae. A synthesizer of microbial cellulose, they have a cuboidal cell arrangement...
(Micrococci) - bead-like chains, or streptococci (StreptococcusStreptococcusStreptococcus is a genus of spherical Gram-positive bacteria belonging to the phylum Firmicutes and the lactic acid bacteria group. Cellular division occurs along a single axis in these bacteria, and thus they grow in chains or pairs, hence the name — from Greek στρεπτος streptos, meaning...
) - grapelike clusters, or staphylococci (StaphylococcusStaphylococcusStaphylococcus is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria. Under the microscope they appear round , and form in grape-like clusters....
)
Diplococcus
A diplococcus (plural diplococci) is a round bacteriumBacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
(a coccus
Coccus
Coccus can be used to describe any bacterium that has a spherical shape. It is one of the three distinct types of bacteria shapes, the other two being bacillus and spirillum cells...
) that typically occurs in pairs of two joined cells. Examples are Streptococcus pneumoniae
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Streptococcus pneumoniae, or pneumococcus, is Gram-positive, alpha-hemolytic, aerotolerant anaerobic member of the genus Streptococcus. A significant human pathogenic bacterium, S...
, Moraxella catarrhalis
Moraxella catarrhalis
Moraxella catarrhalis is a fastidious, nonmotile, Gram-negative, aerobic, oxidase-positive diplococcus that can cause infections of the respiratory system, middle ear, eye, central nervous system and joints of humans.-History:...
, Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Neisseria gonorrhoeae, also known as gonococci , or gonococcus , is a species of Gram-negative coffee bean-shaped diplococci bacteria responsible for the sexually transmitted infection gonorrhea.N...
and Neisseria meningitidis
Neisseria meningitidis
Neisseria meningitidis, often referred to as meningococcus, is a bacterium that can cause meningitis and other forms of meningococcal disease such as meningococcemia, a life threatening sepsis. N. meningitidis is a major cause of morbidity and mortality during childhood in industrialized countries...
.
Its name comes from diplo, meaning double, and coccus, meaning berry. This is because berries are round, like a diplococcus, and diplococci come in pairs of two.
In former times, a bacterial genus
Genus
In biology, a genus is a low-level taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms, which is an example of definition by genus and differentia...
Diplococcus was recognized, but it is not used anymore.
Coccobacillus
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
. The word coccobacillus reflects an intermediate shape between coccus (spherical) and bacillus (elongated). Coccobacilli rods are so short and wide that they resemble cocci. Haemophilus influenzae
Haemophilus influenzae
Haemophilus influenzae, formerly called Pfeiffer's bacillus or Bacillus influenzae, Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium first described in 1892 by Richard Pfeiffer during an influenza pandemic. A member of the Pasteurellaceae family, it is generally aerobic, but can grow as a facultative anaerobe. H...
and Chlamydia trachomatis
Chlamydia trachomatis
Chlamydia trachomatis, an obligate intracellular human pathogen, is one of three bacterial species in the genus Chlamydia. C. trachomatis is a Gram-negative bacteria, therefore its cell wall components retain the counter-stain safranin and appear pink under a light microscope.The inclusion bodies...
are coccobacilli. Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans is an oral commensal found also in severe infections in the oral cavity, mainly the periodontium. A. actinomycetemcomitans, previously Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, is a gram negative facultative non-motile rod. It is also associated with non-oral...
is a gram negative coccobacillus which is prevalent in subgingival plaques. Acinetobacter
Acinetobacter
Acinetobacter [asz−in−ée−toe–back−ter] is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria belonging to the Gammaproteobacteria. Acinetobacter species are non-motile and oxidase-negative, and occur in pairs under magnification....
strains may grow on solid media as coccobacilli.
Coxiella burnetti is also a coccobacillus.
Clinical significance
Important human pathogenPathogen
A pathogen gignomai "I give birth to") or infectious agent — colloquially, a germ — is a microbe or microorganism such as a virus, bacterium, prion, or fungus that causes disease in its animal or plant host...
s caused by coccoid bacteria include staphylococci infections, some types of food poisoning,
some urinary tract infection
Urinary tract infection
A urinary tract infection is a bacterial infection that affects any part of the urinary tract. Symptoms include frequent feeling and/or need to urinate, pain during urination, and cloudy urine. The main causal agent is Escherichia coli...
s, toxic shock syndrome
Toxic shock syndrome
Toxic shock syndrome is a potentially fatal illness caused by a bacterial toxin. Different bacterial toxins may cause toxic shock syndrome, depending on the situation. The causative bacteria include Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes...
, gonorrhea
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is a common sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. The usual symptoms in men are burning with urination and penile discharge. Women, on the other hand, are asymptomatic half the time or have vaginal discharge and pelvic pain...
, as well as some forms of meningitis
Meningitis
Meningitis is inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, known collectively as the meninges. The inflammation may be caused by infection with viruses, bacteria, or other microorganisms, and less commonly by certain drugs...
, throat infections, pneumonia
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung—especially affecting the microscopic air sacs —associated with fever, chest symptoms, and a lack of air space on a chest X-ray. Pneumonia is typically caused by an infection but there are a number of other causes...
s, and sinusitis
Sinusitis
Sinusitis is inflammation of the paranasal sinuses, which may be due to infection, allergy, or autoimmune issues. Most cases are due to a viral infection and resolve over the course of 10 days...
.
Bacillus
Although BacillusBacillus
Bacillus is a genus of Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria and a member of the division Firmicutes. Bacillus species can be obligate aerobes or facultative anaerobes, and test positive for the enzyme catalase. Ubiquitous in nature, Bacillus includes both free-living and pathogenic species...
, capitalized and italicized, specifically refers to the genus, the word bacillus may also be used to describe any rod-shaped bacterium, and in this sense, bacilli are found in many different taxonomic groups of bacteria. There is no connection between the shape of a bacterium and its colors in the Gram staining.
Bacilli are usually solitary, but can combine to form diplobacilli, streptobacilli, and palisades.
MacConkey agar
MacConkey agar
MacConkey agar is a culture medium designed to grow Gram-negative bacteria and stain them for lactose fermentation.-Contents:It contains bile salts MacConkey agar is a culture medium designed to grow Gram-negative bacteria and stain them for lactose fermentation.-Contents:It contains bile salts...
can be used to distinguish among Gram negative bacilli.

