Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase
Encyclopedia
Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase also known as 5-lipoxygenase or 5-LO is an enzyme
that in humans is encoded by the ALOX5 gene
. Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase is a member of the lipoxygenase
family of enzymes. It transforms EFAs
into leukotrienes and is a current target for pharmaceutical intervention in a number of diseases.
.
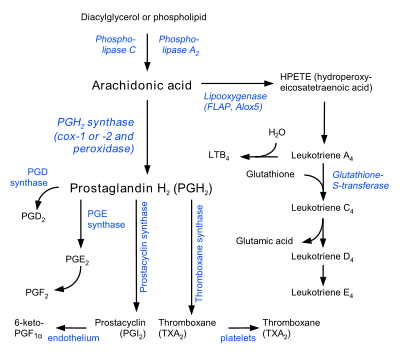 Two other lipoxygenases, 12-LO and 15-LO, act at the 12- and 15-positions, yielding 12- and 15-HPETE. These pathways lead to the leukotriene 12-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid
Two other lipoxygenases, 12-LO and 15-LO, act at the 12- and 15-positions, yielding 12- and 15-HPETE. These pathways lead to the leukotriene 12-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid
(12-HETE) and to the lipoxin
s, respectively.
. Some people with variant allele
s for 5-LO are at elevated risk for CAD. 5-LO is expressed in brain cells and may participate in neuropathologic processes.
Mutations in the promoter region of this gene lead to a diminished response to antileukotriene drugs used in the treatment of asthma and may also be associated with atherosclerosis
and several cancers. Alternatively spliced
transcript variants have been observed, but their full-length nature has not been determined.
, 5-LO inhibitors were developed as asthma treatments. The only 5-LO inhibitor currently licensed for human use in asthma is Zileuton
.
Minocycline
, although primarily a tetracycline antibiotic, is also a 5-LO inhibitor. It may therefore be used as a DMARD-medication in mild rheumatoid arthritis
and other rheumatic conditions.
with Grb2
and COTL1
.
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that in humans is encoded by the ALOX5 gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
. Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase is a member of the lipoxygenase
Lipoxygenase
Lipoxygenases are a family of iron-containing enzymes that catalyse the dioxygenation of polyunsaturated fatty acids in lipids containing a cis,cis-1,4- pentadiene structure. It catalyses the following reaction:...
family of enzymes. It transforms EFAs
Essential fatty acid
Essential fatty acids, or EFAs, are fatty acids that humans and other animals must ingest because the body requires them for good health but cannot synthesize them...
into leukotrienes and is a current target for pharmaceutical intervention in a number of diseases.
Substrates and products
EFA substrates and leukotriene products of 5-LO include:- Arachidonic acidArachidonic acidArachidonic acid is a polyunsaturated omega-6 fatty acid 20:4.It is the counterpart to the saturated arachidic acid found in peanut oil, Arachidonic acid (AA, sometimes ARA) is a polyunsaturated omega-6 fatty acid 20:4(ω-6).It is the counterpart to the saturated arachidic acid found in peanut oil,...
(AA) yields the 4-series leukotrienes (LTB4, LTC4, LTD4, LTE4 — generally proinflammatory) - Eicosapentaenoic acidEicosapentaenoic acidEicosapentaenoic acid is an omega-3 fatty acid. In physiological literature, it is given the name 20:5. It also has the trivial name timnodonic acid...
(EPA) yields the 5-series (LTB5, LTC5, LTD5, LTE5 — antiinflammatory) - Gamma-linolenic acidGamma-Linolenic acidγ-Linolenic acid is a fatty acid found primarily in vegetable oils...
(GLA via the DGLADihomo-gamma-linolenic acidDihomo-γ-linolenic acid is a 20-carbon ω−6 fatty acid. In physiological literature, it is given the name 20:3 . DGLA is a carboxylic acid with a 20-carbon chain and three cis double bonds; the first double bond is located at the sixth carbon from the omega end. DGLA is the elongation product...
intermediary) yields no leukotrienes, but inhibits the conversion of AA.
Function
5-LO catalyzes oxidation of AA at the 5-position to yield 5-hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid (5-HPETE). 5-LO then converts 5-HPETE to leukotriene A4Leukotriene A4
Leukotriene A4 is a leukotriene.Leukotriene A4 hydrolase converts it to Leukotriene B4....
.

12-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid
12-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid is an eicosanoid. It is a metabolite of arachidonic acid produced by the action of the enzyme arachidonate 12-lipoxygenase. 12-HETE is a highly selective ligand used to label mu opioid receptors....
(12-HETE) and to the lipoxin
Lipoxin
Lipoxins are a series of anti-inflammatory mediators. Lipoxins are short lived endogenously produced nonclassic eicosanoids whose appearance in inflammation signals the resolution of inflammation....
s, respectively.
Clinical significance
5-LO is a target for pharmaceutical intervention in CADCoronary heart disease
Coronary artery disease is the end result of the accumulation of atheromatous plaques within the walls of the coronary arteries that supply the myocardium with oxygen and nutrients. It is sometimes also called coronary heart disease...
. Some people with variant allele
Allele
An allele is one of two or more forms of a gene or a genetic locus . "Allel" is an abbreviation of allelomorph. Sometimes, different alleles can result in different observable phenotypic traits, such as different pigmentation...
s for 5-LO are at elevated risk for CAD. 5-LO is expressed in brain cells and may participate in neuropathologic processes.
Mutations in the promoter region of this gene lead to a diminished response to antileukotriene drugs used in the treatment of asthma and may also be associated with atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a condition in which an artery wall thickens as a result of the accumulation of fatty materials such as cholesterol...
and several cancers. Alternatively spliced
Alternative splicing
Alternative splicing is a process by which the exons of the RNA produced by transcription of a gene are reconnected in multiple ways during RNA splicing...
transcript variants have been observed, but their full-length nature has not been determined.
5-LO inhibitors
As leukotrienes are important causes of pathological symptoms in asthmaAsthma
Asthma is the common chronic inflammatory disease of the airways characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and bronchospasm. Symptoms include wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath...
, 5-LO inhibitors were developed as asthma treatments. The only 5-LO inhibitor currently licensed for human use in asthma is Zileuton
Zileuton
Zileuton is an orally active inhibitor of 5-lipoxygenase, and thus inhibits leukotrienes formation. Zileuton is used for the maintenance treatment of asthma. Zileuton was introduced in 1996 by Abbott Laboratories and is now marketed in two formulations by Cornerstone Therapeutics Inc. under the...
.
Minocycline
Minocycline
Minocycline is a broad-spectrum tetracycline antibiotic, and has a broader spectrum than the other members of the group. It is a bacteriostatic antibiotic, classified as a long-acting type...
, although primarily a tetracycline antibiotic, is also a 5-LO inhibitor. It may therefore be used as a DMARD-medication in mild rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic, systemic inflammatory disorder that may affect many tissues and organs, but principally attacks synovial joints. The process produces an inflammatory response of the synovium secondary to hyperplasia of synovial cells, excess synovial fluid, and the development...
and other rheumatic conditions.
Interactions
Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase has been shown to interactProtein-protein interaction
Protein–protein interactions occur when two or more proteins bind together, often to carry out their biological function. Many of the most important molecular processes in the cell such as DNA replication are carried out by large molecular machines that are built from a large number of protein...
with Grb2
Grb2
Growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 also known as Grb2 is an adaptor protein involved in signal transduction/cell communication. In humans, the GRB2 protein is encoded by the GRB2 gene....
and COTL1
COTL1
Coactosin-like protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the COTL1 gene.-Interactions:COTL1 has been shown to interact with Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase.-Further reading:...
.

