
Alpha-7 nicotinic receptor
Encyclopedia
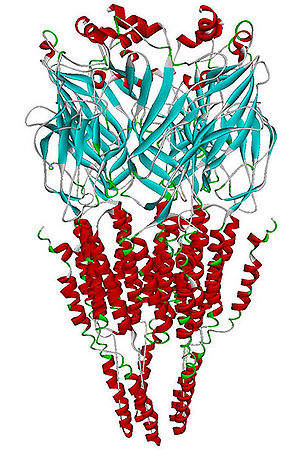
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, or nAChRs, are cholinergic receptors that form ligand-gated ion channels in the plasma membranes of certain neurons and on the postsynaptic side of the neuromuscular junction...
, consisting entirely of α7
CHRNA7
Neuronal acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha-7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CHRNA7 gene.-See also:* Alpha-7 nicotinic receptor* Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor* Acetylcholine receptor...
subunits.. As with other nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, functional α7 receptors are pentameric [i.e., (α7)5 stoichiometry
Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry is a branch of chemistry that deals with the relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions. In a balanced chemical reaction, the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of whole numbers...
].
It is located in the brain
Brain
The brain is the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few primitive invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, sea squirts and starfishes do not have one. It is located in the head, usually close to primary sensory apparatus such as vision, hearing,...
, and spleen
Spleen
The spleen is an organ found in virtually all vertebrate animals with important roles in regard to red blood cells and the immune system. In humans, it is located in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen. It removes old red blood cells and holds a reserve of blood in case of hemorrhagic shock...
where activation yields post-
Excitatory postsynaptic potential
In neuroscience, an excitatory postsynaptic potential is a temporary depolarization of postsynaptic membrane potential caused by the flow of positively charged ions into the postsynaptic cell as a result of opening of ligand-sensitive channels...
and presynaptic excitation, mainly by increased Ca2+
Calcium
Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
permeability.
Agonists
- (+)-N-(1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl)benzo[b]furan- 2-carboxamide: potent and highly subtype-selective
- A-582941: partial agonist; activates ERK1/2 and CREBCREBCREB is a cellular transcription factor. It binds to certain DNA sequences called cAMP response elements , thereby increasing or decreasing the transcription of the downstream genes....
phosphorylationPhosphorylationPhosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate group to a protein or other organic molecule. Phosphorylation activates or deactivates many protein enzymes....
; enhances cognitive performance - AR-R17779AR-R17779AR-R17779 is a drug that acts as a potent and selective full agonist for the α7 subtype of neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. It has nootropic effects in animal studies, but its effects do not substitute for those of nicotine. It has also recently been studied as a potential novel treatment...
: full agonist, nootropic - TC-1698: subtype-selective; neuroprotective effects via activation of the JAK2Janus kinase 2Janus kinase 2 is a human protein that has been implicated in signaling by members of the type II cytokine receptor family , the GM-CSF receptor family , the gp130 receptor family , and the single chain receptors...
/PI-3K cascade, neutralized by angiotensin II AT(2) receptor activation - TC-5619TC-5619TC-5619 is a drug developed by Targacept that acts as a partial agonist at the α7 subtype of the neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. It showed cognitive enhancing effects in animal studies, and is currently being developed through a collaboration between Targacept and AstraZeneca as a...
- partial agonist, in development for treatment of schizophreniaSchizophreniaSchizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by a disintegration of thought processes and of emotional responsiveness. It most commonly manifests itself as auditory hallucinations, paranoid or bizarre delusions, or disorganized speech and thinking, and it is accompanied by significant social... - GTS-21GTS-21GTS-21 is a drug that acts as a partial agonist at neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. It binds to both the α4β2 and α7 subtypes, but activates only the α7 to any significant extent....
- partial agonist, in development for treatment of schizophrenia and/or Alzheimer's diseaseAlzheimer's diseaseAlzheimer's disease also known in medical literature as Alzheimer disease is the most common form of dementia. There is no cure for the disease, which worsens as it progresses, and eventually leads to death... - PHA-543,613PHA-543,613PHA-543,613 is a drug that acts as a potent and selective agonist for the α7 subtype of neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, with a high level of brain penetration and good oral bioavailability. It is under development as a possible treatment for cognitive deficits in schizophrenia....
- PNU-282,987PNU-282,987PNU-282,987 is a drug that acts as a potent and selective agonist for the α7 subtype of neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. In animal studies, it shows nootropic effects, and derivatives may be useful in the treatment of schizophrenia, although PNU-282,987 is not suitable for use in humans...
- PHA-709829: potent and subtype-selective; robust in vivo efficacy in a rat auditory sensory gatingSensory gatingSensory gating describes neurological processes of filtering out redundant or unnecessary stimuli in the brain from all possible environmental stimuli. Also referred to as filtering, or sensorimotor gating, sensory gating prevents an overload of irrelevant information in the higher cortical...
model- Analogues: improved hERGHERGhERG is a gene that codes for a protein known as Kv11.1 potassium ion channel...
safety profile over PNU-282,987
- Analogues: improved hERG
- SSR-180,711SSR-180,711SSR-180,711 is a drug that acts as a potent and selective partial agonist for the α7 subtype of neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. In animal studies, it shows nootropic effects and may be useful in the treatment of schizophrenia....
: partial agonist - TropisetronTropisetronTropisetron is a serotonin 5-HT3 receptor antagonist used mainly as an antiemetic to treat nausea and vomiting following chemotherapy, although it has been used experimentally as an analgesic in cases of fibromyalgia. The drug is available in a 5 mg oral preparation or in 2 mg...
: subtype-selective partial agonist; 5-HT3 receptor antagonist - WAY-317,538WAY-317,538WAY-317,538 is a drug that acts as a potent and selective full agonist for the α7 subtype of neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptors...
- Anabaseine
- CholineCholineCholine is a water-soluble essential nutrient. It is usually grouped within the B-complex vitamins. Choline generally refers to the various quaternary ammonium salts containing the N,N,N-trimethylethanolammonium cation....
- NicotineNicotineNicotine is an alkaloid found in the nightshade family of plants that constitutes approximately 0.6–3.0% of the dry weight of tobacco, with biosynthesis taking place in the roots and accumulation occurring in the leaves...
PAMs
At least two types of positive allosteric modulators (PAMs) can be distinguished.- PNU-120,596PNU-120,596PNU-120,596 is a drug that acts as a potent and selective positive allosteric modulator for the α7 subtype of neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. It is used in scientific research into cholinergic regulation of dopamine and glutamate release in the brain....
- NS-1738: marginal effects on α7 desensitization kinetics; modestly brain-penetrant
- AVL-3288: unlike the above PAMs, AVL-3288 does not affect α7 desensitization kinetics, and is readily brain penetrant. Improves cognitive behavior in animal models In clinical development for cognitive deficits in schizophrenia.
- A-867744
- Ivermectin
- GalantamineGalantamineGalantamine is used for the treatment of mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease and various other memory impairments, in particular those of vascular origin...
Antagonists
- α-conotoxinConotoxinA conotoxin is one of a group of neurotoxic peptides isolated from the venom of the marine cone snail, genus Conus.Conotoxins, which are peptides consisting of 10 to 30 amino acid residues, typically have one or more disulfide bonds. Conotoxins have a variety of mechanisms of actions, most of...
ArIB[V11L,V16D]: potent and highly subtype-selective; slowly reversible - Memantine
- Quinolizidine (–)-1-epi-207I: α7 subtype preferring blocker
- α-Bungarotoxin
See also
- α3β4-Nicotinic receptorAlpha-3 beta-4 nicotinic receptorThe alpha-3 beta-4 nicotinic receptor, also known as the α3β4 receptor, is a type of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, consisting of α3 and β4 subunits. It is located in the brain, where activation yields post- and presynaptic excitation....
- α4β2-Nicotinic receptorAlpha-4 beta-2 nicotinic receptorThe alpha-4 beta-2 nicotinic receptor, also known as the α4β2 receptor, is a type of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, consisting of α4 and β2 subunits...

