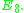A-equivalence
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
,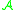 -equivalence, sometimes called right-left equivalence, is an equivalence relation
-equivalence, sometimes called right-left equivalence, is an equivalence relation
between map germs
.
Let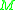 and
and 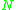 be two manifold
be two manifold
s, and let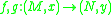 be two smooth map germs
be two smooth map germs
. We say that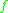 and
and 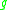 are
are 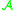 -equivalent if there exist diffeomorphism
-equivalent if there exist diffeomorphism
germs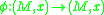 and
and 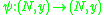 such that
such that 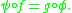
In other words, two map germs
are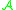 -equivalent if one can be taken onto the other by a diffeomorphic
-equivalent if one can be taken onto the other by a diffeomorphic
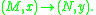
change of co-ordinates in the source (i.e.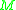 ) and the target (i.e.
) and the target (i.e. 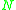 ).
).
Let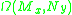 denote the space of smooth map germs
denote the space of smooth map germs
 Let
Let 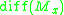 be the group
be the group
of diffeomorphism
germs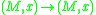 and
and
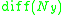 be the group of diffeomorphism
be the group of diffeomorphism
germs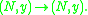 The group
The group 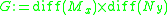 acts on
acts on 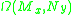 in the natural way:
in the natural way: 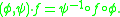 Under this action we see that the map germs
Under this action we see that the map germs
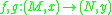 are
are 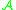 -equivalent if, and only if,
-equivalent if, and only if, 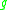 lies in the orbit of
lies in the orbit of 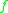 , i.e.
, i.e. 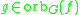 (or vice versa).
(or vice versa).
A map germ is called stable if its orbit under the action
of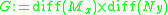 is open
is open
relative to the Whitney topology. Since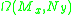 is an infinite dimensional space metric topology is no longer trivial. Whitney topology compares the differences in successive derivatives and gives a notion of proximity within the infinite dimensional space. A base for the open set
is an infinite dimensional space metric topology is no longer trivial. Whitney topology compares the differences in successive derivatives and gives a notion of proximity within the infinite dimensional space. A base for the open set
s of the topology
in question is given by taking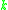 -jets for every
-jets for every 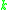 and taking open
and taking open
neighbourhood
s in the ordinary Euclidean sense. Open set
s in the topology
are then union
s of
these base sets.
Consider the orbit of some map germ
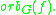 The map germ
The map germ
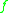 is called simple if there are only finitely many other orbits in a neighbourhood
is called simple if there are only finitely many other orbits in a neighbourhood
of each of its points. Vladimir Arnold
has shown that the only simple singular
map germs
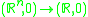 for
for 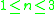 are the infinite sequence
are the infinite sequence 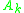 (
(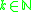 ), the infinite sequence
), the infinite sequence 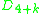 (
(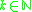 ),
), 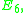
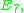 and
and 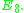
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
,
 -equivalence, sometimes called right-left equivalence, is an equivalence relation
-equivalence, sometimes called right-left equivalence, is an equivalence relationEquivalence relation
In mathematics, an equivalence relation is a relation that, loosely speaking, partitions a set so that every element of the set is a member of one and only one cell of the partition. Two elements of the set are considered equivalent if and only if they are elements of the same cell...
between map germs
Germ (mathematics)
In mathematics, the notion of a germ of an object in/on a topological space captures the local properties of the object. In particular, the objects in question are mostly functions and subsets...
.
Let
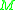 and
and 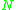 be two manifold
be two manifoldManifold
In mathematics , a manifold is a topological space that on a small enough scale resembles the Euclidean space of a specific dimension, called the dimension of the manifold....
s, and let
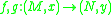 be two smooth map germs
be two smooth map germsGerm (mathematics)
In mathematics, the notion of a germ of an object in/on a topological space captures the local properties of the object. In particular, the objects in question are mostly functions and subsets...
. We say that
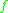 and
and 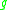 are
are 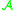 -equivalent if there exist diffeomorphism
-equivalent if there exist diffeomorphismDiffeomorphism
In mathematics, a diffeomorphism is an isomorphism in the category of smooth manifolds. It is an invertible function that maps one differentiable manifold to another, such that both the function and its inverse are smooth.- Definition :...
germs
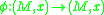 and
and 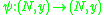 such that
such that 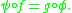
In other words, two map germs
Germ (mathematics)
In mathematics, the notion of a germ of an object in/on a topological space captures the local properties of the object. In particular, the objects in question are mostly functions and subsets...
are
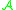 -equivalent if one can be taken onto the other by a diffeomorphic
-equivalent if one can be taken onto the other by a diffeomorphicDiffeomorphism
In mathematics, a diffeomorphism is an isomorphism in the category of smooth manifolds. It is an invertible function that maps one differentiable manifold to another, such that both the function and its inverse are smooth.- Definition :...
change of co-ordinates in the source (i.e.
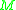 ) and the target (i.e.
) and the target (i.e. 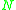 ).
).Let
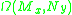 denote the space of smooth map germs
denote the space of smooth map germsGerm (mathematics)
In mathematics, the notion of a germ of an object in/on a topological space captures the local properties of the object. In particular, the objects in question are mostly functions and subsets...
 Let
Let 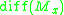 be the group
be the groupGroup (mathematics)
In mathematics, a group is an algebraic structure consisting of a set together with an operation that combines any two of its elements to form a third element. To qualify as a group, the set and the operation must satisfy a few conditions called group axioms, namely closure, associativity, identity...
of diffeomorphism
Diffeomorphism
In mathematics, a diffeomorphism is an isomorphism in the category of smooth manifolds. It is an invertible function that maps one differentiable manifold to another, such that both the function and its inverse are smooth.- Definition :...
germs
 and
and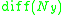 be the group of diffeomorphism
be the group of diffeomorphismDiffeomorphism
In mathematics, a diffeomorphism is an isomorphism in the category of smooth manifolds. It is an invertible function that maps one differentiable manifold to another, such that both the function and its inverse are smooth.- Definition :...
germs
 The group
The group 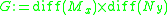 acts on
acts on 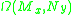 in the natural way:
in the natural way: 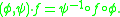 Under this action we see that the map germs
Under this action we see that the map germsGerm (mathematics)
In mathematics, the notion of a germ of an object in/on a topological space captures the local properties of the object. In particular, the objects in question are mostly functions and subsets...
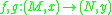 are
are  -equivalent if, and only if,
-equivalent if, and only if, 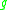 lies in the orbit of
lies in the orbit of 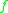 , i.e.
, i.e. 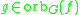 (or vice versa).
(or vice versa).A map germ is called stable if its orbit under the action
Group action
In algebra and geometry, a group action is a way of describing symmetries of objects using groups. The essential elements of the object are described by a set, and the symmetries of the object are described by the symmetry group of this set, which consists of bijective transformations of the set...
of
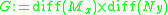 is open
is openOpen set
The concept of an open set is fundamental to many areas of mathematics, especially point-set topology and metric topology. Intuitively speaking, a set U is open if any point x in U can be "moved" a small amount in any direction and still be in the set U...
relative to the Whitney topology. Since
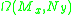 is an infinite dimensional space metric topology is no longer trivial. Whitney topology compares the differences in successive derivatives and gives a notion of proximity within the infinite dimensional space. A base for the open set
is an infinite dimensional space metric topology is no longer trivial. Whitney topology compares the differences in successive derivatives and gives a notion of proximity within the infinite dimensional space. A base for the open setOpen set
The concept of an open set is fundamental to many areas of mathematics, especially point-set topology and metric topology. Intuitively speaking, a set U is open if any point x in U can be "moved" a small amount in any direction and still be in the set U...
s of the topology
Topology
Topology is a major area of mathematics concerned with properties that are preserved under continuous deformations of objects, such as deformations that involve stretching, but no tearing or gluing...
in question is given by taking
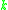 -jets for every
-jets for every 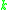 and taking open
and taking openOpen set
The concept of an open set is fundamental to many areas of mathematics, especially point-set topology and metric topology. Intuitively speaking, a set U is open if any point x in U can be "moved" a small amount in any direction and still be in the set U...
neighbourhood
Neighbourhood (mathematics)
In topology and related areas of mathematics, a neighbourhood is one of the basic concepts in a topological space. Intuitively speaking, a neighbourhood of a point is a set containing the point where you can move that point some amount without leaving the set.This concept is closely related to the...
s in the ordinary Euclidean sense. Open set
Open set
The concept of an open set is fundamental to many areas of mathematics, especially point-set topology and metric topology. Intuitively speaking, a set U is open if any point x in U can be "moved" a small amount in any direction and still be in the set U...
s in the topology
Topology
Topology is a major area of mathematics concerned with properties that are preserved under continuous deformations of objects, such as deformations that involve stretching, but no tearing or gluing...
are then union
Union (set theory)
In set theory, the union of a collection of sets is the set of all distinct elements in the collection. The union of a collection of sets S_1, S_2, S_3, \dots , S_n\,\! gives a set S_1 \cup S_2 \cup S_3 \cup \dots \cup S_n.- Definition :...
s of
these base sets.
Consider the orbit of some map germ
Germ (mathematics)
In mathematics, the notion of a germ of an object in/on a topological space captures the local properties of the object. In particular, the objects in question are mostly functions and subsets...
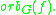 The map germ
The map germGerm (mathematics)
In mathematics, the notion of a germ of an object in/on a topological space captures the local properties of the object. In particular, the objects in question are mostly functions and subsets...
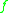 is called simple if there are only finitely many other orbits in a neighbourhood
is called simple if there are only finitely many other orbits in a neighbourhoodNeighbourhood
A neighbourhood or neighborhood is a geographically localised community within a larger city, town or suburb. Neighbourhoods are often social communities with considerable face-to-face interaction among members. "Researchers have not agreed on an exact definition...
of each of its points. Vladimir Arnold
Vladimir Arnold
Vladimir Igorevich Arnold was a Soviet and Russian mathematician. While he is best known for the Kolmogorov–Arnold–Moser theorem regarding the stability of integrable Hamiltonian systems, he made important contributions in several areas including dynamical systems theory, catastrophe theory,...
has shown that the only simple singular
Mathematical singularity
In mathematics, a singularity is in general a point at which a given mathematical object is not defined, or a point of an exceptional set where it fails to be well-behaved in some particular way, such as differentiability...
map germs
Germ (mathematics)
In mathematics, the notion of a germ of an object in/on a topological space captures the local properties of the object. In particular, the objects in question are mostly functions and subsets...
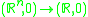 for
for 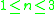 are the infinite sequence
are the infinite sequence 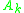 (
(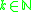 ), the infinite sequence
), the infinite sequence 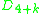 (
(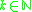 ),
), 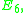
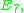 and
and