
Woods Saxon potential
Encyclopedia
The Woods–Saxon potential is a mean field potential
for the nucleon
s (proton
s and neutron
s) inside the atomic nucleus
, which is used to approximately describe the forces applied on each nucleon
, in the shell model for the structure of the nucleus.
The form of the potential, as a function of the distance r from the center of nucleus, is:
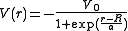
where V0 (having dimension of energy) represents the potential well depth,
a is a length representing the "surface thickness" of the nucleus, and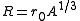 is the nuclear radius where and A is the mass number
is the nuclear radius where and A is the mass number
.
Typical values for the parameters are: , .
For large atomic number A this potential is similar to a potential well
. It has the following desired properties
When using the Schrödinger equation
to find the energy levels of nucleons subjected to the Woods Saxon potential, it cannot be solved analytically, and must be treated numerically.
Potential
*In linguistics, the potential mood*The mathematical study of potentials is known as potential theory; it is the study of harmonic functions on manifolds...
for the nucleon
Nucleon
In physics, a nucleon is a collective name for two particles: the neutron and the proton. These are the two constituents of the atomic nucleus. Until the 1960s, the nucleons were thought to be elementary particles...
s (proton
Proton
The proton is a subatomic particle with the symbol or and a positive electric charge of 1 elementary charge. One or more protons are present in the nucleus of each atom, along with neutrons. The number of protons in each atom is its atomic number....
s and neutron
Neutron
The neutron is a subatomic hadron particle which has the symbol or , no net electric charge and a mass slightly larger than that of a proton. With the exception of hydrogen, nuclei of atoms consist of protons and neutrons, which are therefore collectively referred to as nucleons. The number of...
s) inside the atomic nucleus
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the very dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. It was discovered in 1911, as a result of Ernest Rutherford's interpretation of the famous 1909 Rutherford experiment performed by Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden, under the direction of Rutherford. The...
, which is used to approximately describe the forces applied on each nucleon
Nucleon
In physics, a nucleon is a collective name for two particles: the neutron and the proton. These are the two constituents of the atomic nucleus. Until the 1960s, the nucleons were thought to be elementary particles...
, in the shell model for the structure of the nucleus.
The form of the potential, as a function of the distance r from the center of nucleus, is:
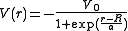
where V0 (having dimension of energy) represents the potential well depth,
a is a length representing the "surface thickness" of the nucleus, and
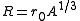 is the nuclear radius where and A is the mass number
is the nuclear radius where and A is the mass numberMass number
The mass number , also called atomic mass number or nucleon number, is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atomic nucleus. Because protons and neutrons both are baryons, the mass number A is identical with the baryon number B as of the nucleus as of the whole atom or ion...
.
Typical values for the parameters are: , .
For large atomic number A this potential is similar to a potential well
Potential well
A potential well is the region surrounding a local minimum of potential energy. Energy captured in a potential well is unable to convert to another type of energy because it is captured in the local minimum of a potential well...
. It has the following desired properties
- It is monotonically increasing with distance, i.e. attracting.
- For large A, it is approximately flat in the center.
- Nucleons near the surface of the nucleus (i.e. having within a distance of order a) experience a large force towards the center.
- It rapidly approaches zero as r goes to infinity , reflecting the short-distance nature of the strong nuclear force.
When using the Schrödinger equation
Schrödinger equation
The Schrödinger equation was formulated in 1926 by Austrian physicist Erwin Schrödinger. Used in physics , it is an equation that describes how the quantum state of a physical system changes in time....
to find the energy levels of nucleons subjected to the Woods Saxon potential, it cannot be solved analytically, and must be treated numerically.

