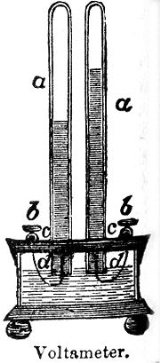
Voltameter
Encyclopedia
A Voltameter is a scientific instrument
used for measuring quantity of electricity
. It should not be confused with a voltmeter
which measures electric potential
. An alternative name is coulometer.
The SI unit for quantity of electricity is the coulomb, while the SI unit for electric potential is the volt
.
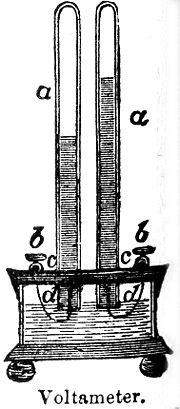 The voltameter is an electrolytic cell
The voltameter is an electrolytic cell
and the measurement is made by weighing the element
deposited or released at the cathode
in a specified time.
plates in a solution of silver nitrate
. When current is flowing, silver dissolves at the anode
and is deposited at the cathode
. The cathode is weighed, current is passed for a measured time, then the cathode is weighed again and again.
and the solution is copper sulfate, acidified with sulfuric acid
. It is cheaper than the silver voltameter, but slightly less accurate.
and the solution is dilute sulfuric acid. Hydrogen
is released at the cathode and collected in a graduated tube so that its volume can be measured. The volume is adjusted to standard temperature and pressure
and the mass
of hydrogen is calculated from the volume. This kind of voltameter is sometimes called Hofmann voltameter
.
of that element (in gram
s) transported by 1 coulomb of electricity.
Measuring instrument
In the physical sciences, quality assurance, and engineering, measurement is the activity of obtaining and comparing physical quantities of real-world objects and events. Established standard objects and events are used as units, and the process of measurement gives a number relating the item...
used for measuring quantity of electricity
Quantity of electricity
In physics the term quantity of electricity refers to the quantity of electric charge. It is designated by the letter Q and in the SI system is measured in derived units called Coulombs.- Pre-English origins :...
. It should not be confused with a voltmeter
Voltmeter
A voltmeter is an instrument used for measuring electrical potential difference between two points in an electric circuit. Analog voltmeters move a pointer across a scale in proportion to the voltage of the circuit; digital voltmeters give a numerical display of voltage by use of an analog to...
which measures electric potential
Electric potential
In classical electromagnetism, the electric potential at a point within a defined space is equal to the electric potential energy at that location divided by the charge there...
. An alternative name is coulometer.
The SI unit for quantity of electricity is the coulomb, while the SI unit for electric potential is the volt
Volt
The volt is the SI derived unit for electric potential, electric potential difference, and electromotive force. The volt is named in honor of the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta , who invented the voltaic pile, possibly the first chemical battery.- Definition :A single volt is defined as the...
.
Types of voltameter

Electrolytic cell
An electrolytic cell decomposes chemical compounds by means of electrical energy, in a process called electrolysis; the Greek word lysis means to break up. The result is that the chemical energy is increased...
and the measurement is made by weighing the element
Chemical element
A chemical element is a pure chemical substance consisting of one type of atom distinguished by its atomic number, which is the number of protons in its nucleus. Familiar examples of elements include carbon, oxygen, aluminum, iron, copper, gold, mercury, and lead.As of November 2011, 118 elements...
deposited or released at the cathode
Cathode
A cathode is an electrode through which electric current flows out of a polarized electrical device. Mnemonic: CCD .Cathode polarity is not always negative...
in a specified time.
Silver voltameter
This is the most accurate type. It consists of two silverSilver
Silver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it has the highest electrical conductivity of any element and the highest thermal conductivity of any metal...
plates in a solution of silver nitrate
Silver nitrate
Silver nitrate is an inorganic compound with chemical formula . This compound is a versatile precursor to many other silver compounds, such as those used in photography. It is far less sensitive to light than the halides...
. When current is flowing, silver dissolves at the anode
Anode
An anode is an electrode through which electric current flows into a polarized electrical device. Mnemonic: ACID ....
and is deposited at the cathode
Cathode
A cathode is an electrode through which electric current flows out of a polarized electrical device. Mnemonic: CCD .Cathode polarity is not always negative...
. The cathode is weighed, current is passed for a measured time, then the cathode is weighed again and again.
Copper voltameter
This is similar to the silver voltameter but the anode and cathode are copperCopper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
and the solution is copper sulfate, acidified with sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid is a strong mineral acid with the molecular formula . Its historical name is oil of vitriol. Pure sulfuric acid is a highly corrosive, colorless, viscous liquid. The salts of sulfuric acid are called sulfates...
. It is cheaper than the silver voltameter, but slightly less accurate.
Sulfuric acid voltameter
The anode and cathode are platinumPlatinum
Platinum is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Pt and an atomic number of 78. Its name is derived from the Spanish term platina del Pinto, which is literally translated into "little silver of the Pinto River." It is a dense, malleable, ductile, precious, gray-white transition metal...
and the solution is dilute sulfuric acid. Hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
is released at the cathode and collected in a graduated tube so that its volume can be measured. The volume is adjusted to standard temperature and pressure
Standard conditions for temperature and pressure
Standard condition for temperature and pressure are standard sets of conditions for experimental measurements established to allow comparisons to be made between different sets of data...
and the mass
Mass
Mass can be defined as a quantitive measure of the resistance an object has to change in its velocity.In physics, mass commonly refers to any of the following three properties of matter, which have been shown experimentally to be equivalent:...
of hydrogen is calculated from the volume. This kind of voltameter is sometimes called Hofmann voltameter
Hofmann voltameter
A Hofmann voltameter is an apparatus for electrolyzing water, invented by August Wilhelm von Hofmann in 1866. It consists of three joined upright cylinders, usually glass. The inner cylinder is open at the top to allow addition of water and an ionic compound to improve conductivity, such as a...
.
Electrochemical equivalents
The electrochemical equivalent of an element is the massMass
Mass can be defined as a quantitive measure of the resistance an object has to change in its velocity.In physics, mass commonly refers to any of the following three properties of matter, which have been shown experimentally to be equivalent:...
of that element (in gram
Gram
The gram is a metric system unit of mass....
s) transported by 1 coulomb of electricity.
| Element | Electrochemical equivalent |
|---|---|
| Silver | 0.0011181 |
| Copper | 0.0003281 |
| Hydrogen | 0.0000104 |
Historical derivation of the name
Faraday used an apparatus that he termed a "volta-electrometer", subsequently Daniell called this a "voltameter".Sources
- Practical Electricity by W. E. Ayrton and T. Mather, published by Cassell and Company, London, 1911, pp 12–26

