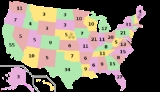
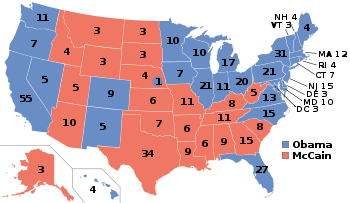
United States Electoral College
Encyclopedia
President of the United States
The President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
and Vice President of the United States
Vice President of the United States
The Vice President of the United States is the holder of a public office created by the United States Constitution. The Vice President, together with the President of the United States, is indirectly elected by the people, through the Electoral College, to a four-year term...
. Since 1964, there have been 538 electors in each presidential election. Article II, Section 1, Clause 2 of the Constitution specifies how many electors each state is entitled to have and that each state's legislature decides how its electors are to be chosen. U.S. territories are not represented in the Electoral College. The Electoral College is an example of an indirect election
Indirect election
Indirect election is a process in which voters in an election don't actually choose between candidates for an office but rather elect persons who will then make the choice. It is one of the oldest form of elections and is still used today for many upper houses and presidents...
, as opposed to a direct election
Direct election
Direct election is a term describing a system of choosing political officeholders in which the voters directly cast ballots for the person, persons or political party that they desire to see elected. The method by which the winner or winners of a direct election are chosen depends upon the...
by United States citizens
Citizenship in the United States
Citizenship in the United States is a status given to individuals that entails specific rights, duties, privileges, and benefits between the United States and the individual...
.
The voters of each state, and the District of Columbia
Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly referred to as Washington, "the District", or simply D.C., is the capital of the United States. On July 16, 1790, the United States Congress approved the creation of a permanent national capital as permitted by the U.S. Constitution....
, vote for electors to be the authorized constitutional participants in a presidential election. In early U.S. history, some state laws delegated the choice of electors to the state legislature. Electors are free to vote for anyone eligible to be President, but in practice pledge to vote for specific candidates and voters cast ballots for favored presidential and vice presidential candidates by voting for correspondingly pledged electors.
The Twelfth Amendment
Twelfth Amendment to the United States Constitution
The Twelfth Amendment to the United States Constitution provides the procedure for electing the President and Vice President. It replaced Article II, Section 1, Clause 3, which provided the original procedure by which the Electoral College functioned. Problems with the original procedure arose in...
provides for each elector to cast one vote for President and one vote for Vice President. It also specifies how a President and Vice President are elected. The Twenty-third Amendment
Twenty-third Amendment to the United States Constitution
The Twenty-third Amendment to the United States Constitution permits citizens in the District of Columbia to vote for Electors for President and Vice President. The amendment was proposed by Congress on June 17, 1960, and ratified by the states on March 29, 1961...
specifies how many electors the District of Columbia is entitled to have.
The Electoral College's existence is controversial. A 2001 Gallup
The Gallup Organization
The Gallup Organization, is primarily a research-based performance-management consulting company. Some of Gallup's key practice areas are - Employee Engagement, Customer Engagement and Well-Being. Gallup has over 40 offices in 27 countries. World headquarters are in Washington, D.C. Operational...
article noted that "a majority of Americans have continually expressed support for the notion of an official amendment of the U.S. Constitution that would allow for direct election of the president" since one of the first-ever public polls on the matter in 1944, and Gallup found no significant change in 2004. Critics argue that the Electoral College is archaic, inherently undemocratic and gives certain swing state
Swing state
In United States presidential politics, a swing state is a state in which no single candidate or party has overwhelming support in securing that state's electoral college votes...
s disproportionate influence in selecting the President and Vice President. Proponents argue that the Electoral College is an important, distinguishing feature of federalism in the United States and that it protects the rights of smaller states. Numerous constitutional amendments
Article Five of the United States Constitution
Article Five of the United States Constitution describes the process whereby the Constitution may be altered. Altering the Constitution consists of proposing an amendment and subsequent ratification....
have been introduced in the Congress
United States Congress
The United States Congress is the bicameral legislature of the federal government of the United States, consisting of the Senate and the House of Representatives. The Congress meets in the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C....
seeking to alter the Electoral College or replace it with a direct popular vote; however, no proposal has ever passed the Congress.
Background
At the Constitutional ConventionPhiladelphia Convention
The Constitutional Convention took place from May 14 to September 17, 1787, in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, to address problems in governing the United States of America, which had been operating under the Articles of Confederation following independence from...
, the delegates used the Virginia Plan
Virginia Plan
The Virginia Plan was a proposal by Virginia delegates, for a bicameral legislative branch. The plan was drafted by James Madison while he waited for a quorum to assemble at the Constitutional Convention of 1787...
as the basis for discussions, as the Virginia delegation had proposed it first. The Virginia Plan called for the Executive to be elected by the Legislature. Delegates from a majority of states agreed to this mode of election. However, the Committee of Eleven, formed to work out various details including the mode of election of the President, recommended instead that the election be by a group of people apportioned among the states in the same numbers as their representatives in Congress (the formula for which had been resolved in lengthy debates resulting in the Connecticut Compromise
Connecticut Compromise
The Connecticut Compromise was an agreement that large and small states reached during the Constitutional Convention of 1787 that in part defined the legislative structure and representation that each state would have under the United States Constitution...
and Three-fifths compromise
Three-fifths compromise
The Three-Fifths Compromise was a compromise between Southern and Northern states reached during the Philadelphia Convention of 1787 in which three-fifths of the enumerated population of slaves would be counted for representation purposes regarding both the distribution of taxes and the...
), but chosen by each state "in such manner as its Legislature may direct." Committee member Gouverneur Morris
Gouverneur Morris
Gouverneur Morris , was an American statesman, a Founding Father of the United States, and a native of New York City who represented Pennsylvania in the Constitutional Convention of 1787. He was a signatory to the Articles of Confederation. Morris was also an author of large sections of the...
explained the reasons for the change; among others, there were fears of "intrigue" if the President was chosen by a small group of men who met together regularly, as well as concerns for the independence of the President if he was elected by the Congress. Some delegates, including James Wilson and James Madison, preferred popular election of the executive. Madison acknowledged that while a popular vote would be ideal, it would be difficult to get consensus on the proposal given the prevalence of slavery
Slavery
Slavery is a system under which people are treated as property to be bought and sold, and are forced to work. Slaves can be held against their will from the time of their capture, purchase or birth, and deprived of the right to leave, to refuse to work, or to demand compensation...
in the South:
The Convention approved the Committee's Electoral College proposal, with minor modifications, on September 6, 1787. Delegates from the small states generally favored the Electoral College out of concern that the large states would otherwise control presidential elections.
Origin of name
Although the United States Constitution refers to "Electors" and "electors", the name "Electoral College" — or any other name — is never used to describe the electors collectively. It was not until the early 19th century that the name "Electoral College" came into general usage as the collective designation for the electors selected to cast votes for President and Vice President. It was first written into federal law in 1845 and today the term appears in , in the section heading and in the text as "college of electors."

