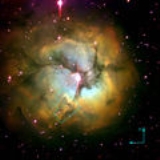
Trifid Nebula
Encyclopedia
The Trifid Nebula is an H II region
located in Sagittarius. Its name means 'divided into three lobes'. The object is an unusual combination of an open cluster
of star
s, an emission nebula
(the lower, red portion), a reflection nebula
(the upper, blue portion) and a dark nebula
(the apparent 'gaps' within the emission nebula that cause the trifid appearance; these are also designated Barnard 85). Viewed through a small telescope
, the Trifid Nebula is a bright and colorful object, and is thus a perennial favorite of amateur astronomers.
in 1997, using filters that isolate emission from hydrogen
atom
s, ion
ized sulfur
atoms, and doubly ionized oxygen
atom. The images were combined into a false-color composite picture to suggest how the nebula might look to the eye.
The close-up images show a dense cloud of dust and gas, which is a stellar nursery full of embryonic stars. This cloud is about
8 light years away from the nebula's central star. A stellar jet protrudes from the head of the cloud and is about 0.75 light-year
s long. The jet's source is a young stellar object deep within the cloud. Jets are the exhaust gasses of star formation. Radiation from the nebula's central star makes the jet glow.
The images also showed a finger-like stalk to the right of the jet. It points from the head of the dense cloud directly toward the star that powers the Trifid nebula. This stalk is a prominent example of evaporating gaseous globule
s, or 'EGGs'. The stalk has survived because its tip is a knot of gas that is dense enough to resist being eaten away by the powerful radiation from the star.
In January, 2005, NASA
's Spitzer Space Telescope
discovered 30 embryonic stars and 120 newborn stars not seen in visible light images.
It is approximately 5,200 light years away. It is in a magnitude of 6.3.
H II region
An H II region is a large, low-density cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place. The short-lived, blue stars forged in these regions emit copious amounts of ultraviolet light, ionizing the surrounding gas...
located in Sagittarius. Its name means 'divided into three lobes'. The object is an unusual combination of an open cluster
Open cluster
An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist...
of star
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
s, an emission nebula
Emission nebula
An emission nebula is a cloud of ionized gas emitting light of various colors. The most common source of ionization is high-energy photons emitted from a nearby hot star...
(the lower, red portion), a reflection nebula
Reflection nebula
In Astronomy, reflection nebulae are clouds of dust which are simply reflecting the light of a nearby star or stars. The energy from the nearby star, or stars, is insufficient to ionize the gas of the nebula to create an emission nebula, but is enough to give sufficient scattering to make the dust...
(the upper, blue portion) and a dark nebula
Dark nebula
A dark nebula is a type of interstellar cloud that is so dense that it obscures the light from the background emission or reflection nebula or that it blocks out background stars . The extinction of the light is caused by interstellar dust grains located in the coldest, densest parts of larger...
(the apparent 'gaps' within the emission nebula that cause the trifid appearance; these are also designated Barnard 85). Viewed through a small telescope
Telescope
A telescope is an instrument that aids in the observation of remote objects by collecting electromagnetic radiation . The first known practical telescopes were invented in the Netherlands at the beginning of the 1600s , using glass lenses...
, the Trifid Nebula is a bright and colorful object, and is thus a perennial favorite of amateur astronomers.
Characteristics
The Trifid Nebula was the subject of an investigation by astronomers using the Hubble Space TelescopeHubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope is a space telescope that was carried into orbit by a Space Shuttle in 1990 and remains in operation. A 2.4 meter aperture telescope in low Earth orbit, Hubble's four main instruments observe in the near ultraviolet, visible, and near infrared...
in 1997, using filters that isolate emission from hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
s, ion
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
ized sulfur
Sulfur
Sulfur or sulphur is the chemical element with atomic number 16. In the periodic table it is represented by the symbol S. It is an abundant, multivalent non-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow...
atoms, and doubly ionized oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
atom. The images were combined into a false-color composite picture to suggest how the nebula might look to the eye.
The close-up images show a dense cloud of dust and gas, which is a stellar nursery full of embryonic stars. This cloud is about
8 light years away from the nebula's central star. A stellar jet protrudes from the head of the cloud and is about 0.75 light-year
Light-year
A light-year, also light year or lightyear is a unit of length, equal to just under 10 trillion kilometres...
s long. The jet's source is a young stellar object deep within the cloud. Jets are the exhaust gasses of star formation. Radiation from the nebula's central star makes the jet glow.
The images also showed a finger-like stalk to the right of the jet. It points from the head of the dense cloud directly toward the star that powers the Trifid nebula. This stalk is a prominent example of evaporating gaseous globule
Evaporating gaseous globule
Evaporating Gaseous Globules, or EGGs, are dense centers of hydrogen gas and dust that act as incubators for new stars.- External links :* — ESA/NASA Image...
s, or 'EGGs'. The stalk has survived because its tip is a knot of gas that is dense enough to resist being eaten away by the powerful radiation from the star.
In January, 2005, NASA
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research...
's Spitzer Space Telescope
Spitzer Space Telescope
The Spitzer Space Telescope , formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility is an infrared space observatory launched in 2003...
discovered 30 embryonic stars and 120 newborn stars not seen in visible light images.
It is approximately 5,200 light years away. It is in a magnitude of 6.3.
External links
- Spitzer IR Trifid discoveries
- Messier 20, SEDS Messier pages
- Trifid Nebula at ESA/Hubble
See also
- Messier objectMessier objectThe Messier objects are a set of astronomical objects first listed by French astronomer Charles Messier in 1771. The original motivation of the catalogue was that Messier was a comet hunter, and was frustrated by objects which resembled but were not comets...
- List of Messier objects
- New General CatalogueNew General CatalogueThe New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars is a well-known catalogue of deep sky objects in astronomy. It contains 7,840 objects, known as the NGC objects...
- List of nebulas
- Wikipedia Project: Astronomical Objects

