
Thermal fluctuations
Encyclopedia
Statistical mechanics
Statistical mechanics or statistical thermodynamicsThe terms statistical mechanics and statistical thermodynamics are used interchangeably...
, thermal fluctuations are random deviations of a system from its equilibrium. All thermal fluctuations become larger and more frequent as the temperature increases, and likewise they disappear altogether as temperature approaches absolute zero
Absolute zero
Absolute zero is the theoretical temperature at which entropy reaches its minimum value. The laws of thermodynamics state that absolute zero cannot be reached using only thermodynamic means....
.
Thermal fluctuations are a basic consequence of the definition of temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
: A system at nonzero temperature does not stay in its equilibrium microscopic state, but instead randomly samples all possible states, with probabilities given by the Boltzmann distribution
Boltzmann distribution
In chemistry, physics, and mathematics, the Boltzmann distribution is a certain distribution function or probability measure for the distribution of the states of a system. It underpins the concept of the canonical ensemble, providing its underlying distribution...
.
Thermal fluctuations generally affect all the degrees of freedom
Degrees of freedom (physics and chemistry)
A degree of freedom is an independent physical parameter, often called a dimension, in the formal description of the state of a physical system...
of a system: There can be random vibrations, random rotations, random electronic excitations, and so forth.
Thermodynamic variables, such as pressure, temperature, or entropy
Entropy
Entropy is a thermodynamic property that can be used to determine the energy available for useful work in a thermodynamic process, such as in energy conversion devices, engines, or machines. Such devices can only be driven by convertible energy, and have a theoretical maximum efficiency when...
, likewise undergo thermal fluctuations. For example, a system has an equilibrium pressure, but its true pressure fluctuates to some extent about the equilibrium.
Thermal fluctuations are a source of noise
Noise
In common use, the word noise means any unwanted sound. In both analog and digital electronics, noise is random unwanted perturbation to a wanted signal; it is called noise as a generalisation of the acoustic noise heard when listening to a weak radio transmission with significant electrical noise...
in many systems. The random forces that give rise to thermal fluctuations are a source of both diffusion
Diffusion
Molecular diffusion, often called simply diffusion, is the thermal motion of all particles at temperatures above absolute zero. The rate of this movement is a function of temperature, viscosity of the fluid and the size of the particles...
and dissipation
Dissipation
In physics, dissipation embodies the concept of a dynamical system where important mechanical models, such as waves or oscillations, lose energy over time, typically from friction or turbulence. The lost energy converts into heat, which raises the temperature of the system. Such systems are called...
(including damping
Damping
In physics, damping is any effect that tends to reduce the amplitude of oscillations in an oscillatory system, particularly the harmonic oscillator.In mechanics, friction is one such damping effect...
and viscosity
Viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of the resistance of a fluid which is being deformed by either shear or tensile stress. In everyday terms , viscosity is "thickness" or "internal friction". Thus, water is "thin", having a lower viscosity, while honey is "thick", having a higher viscosity...
). The competing effects of random drift and resistance to drift are related by the fluctuation-dissipation theorem. Thermal fluctuations play a major role in phase transitions and chemical kinetics
Chemical kinetics
Chemical kinetics, also known as reaction kinetics, is the study of rates of chemical processes. Chemical kinetics includes investigations of how different experimental conditions can influence the speed of a chemical reaction and yield information about the reaction's mechanism and transition...
.
Distribution of fluctuations about equilibrium
The expressions given before are for systems that are close to equilibrium and have negligible quantum effects.Single variable
Suppose is a thermodynamic variable. The probability distribution
is a thermodynamic variable. The probability distribution  for
for  is determined by the entropy
is determined by the entropy 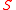 :
:
If the entropy is expanded about its maximum (corresponding to the equilibrium
Equilibrium
Equilibrium is the condition of a system in which competing influences are balanced. The word may refer to:-Biology:* Equilibrioception, the sense of a balance present in human beings and other animals...
state), the lowest order term is a Gaussian distribution:
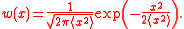
The quantity
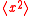 is the mean square fluctuation.
is the mean square fluctuation.Multiple variables
The above expression has a straightforward generalization to the probability distribution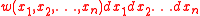 :
: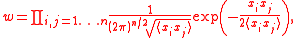
where
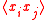 is the mean value of
is the mean value of  .
.Fluctuations of the fundamental thermodynamic quantities
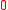
In the table below are given the mean square fluctuations of the thermodynamic variables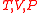 and
and 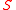 in any small part of a body. The small part must still be large enough, however, to have negligible quantum effects.
in any small part of a body. The small part must still be large enough, however, to have negligible quantum effects.
 |
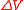 |
 |
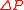 |
|
 |
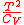 |
0 |  |
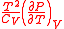 |
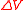 |
0 | 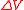 |
 |
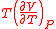 |
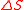 |
 |
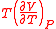 |
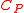 |
 |
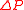 |
 |
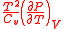 |
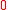 |
 |


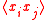 of thermodyamic fluctuations. Temperature is in energy units (divide by Boltzmann's constant
of thermodyamic fluctuations. Temperature is in energy units (divide by Boltzmann's constant 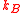 to get degrees).
to get degrees). 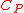 is the
is the 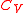 is the
is the