Sulfanilamides
Encyclopedia
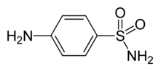
Sulfanilamide is a sulfonamide
antibacterial. Chemically, it is a molecule containing the sulfonamide
functional group attached to an aniline
.
As a sulfonamide antibiotic, it functions by competitively inhibiting (i.e., by acting as a substrate analogue) enzymatic reactions involving para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA). PABA is needed in enzymatic reactions that produce folic acid which acts as a coenzyme in the synthesis of purine, pyrimidine and other amino acids.
The term "sulfanilamides" is also used to describe a family of molecules containing these functional groups. Examples include:
Gerhard Domagk
, who directed the testing of the prodrug
Prontosil
in 1935, and Jacques and Thérèse Tréfouël, who along with Federico Nitti and Daniel Bovet
in the laboratory of Ernest Fourneau
at the Pasteur Institute
, discovered the active component, 4-aminobenzenesulfonamide, are generally credited with the discovery of sulfanilamide as a chemotherapeutic agent. Domagk was awarded the Nobel Prize for his work.
Sulfonamide (medicine)
Sulfonamide or sulphonamide is the basis of several groups of drugs. The original antibacterial sulfonamides are synthetic antimicrobial agents that contain the sulfonamide group. Some sulfonamides are also devoid of antibacterial activity, e.g., the anticonvulsant sultiame...
antibacterial. Chemically, it is a molecule containing the sulfonamide
Sulfonamide (chemistry)
In chemistry, the sulfonamide functional group is -S2-NH2, a sulfonyl group connected to an amine group.A sulfonamide is a compound that contains this group. The general formula is RSO2NH2, where R is some organic group. For example, "methanesulfonamide" is CH3SO2NH2...
functional group attached to an aniline
Aniline
Aniline, phenylamine or aminobenzene is an organic compound with the formula C6H5NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the prototypical aromatic amine. Being a precursor to many industrial chemicals, its main use is in the manufacture of precursors to polyurethane...
.
As a sulfonamide antibiotic, it functions by competitively inhibiting (i.e., by acting as a substrate analogue) enzymatic reactions involving para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA). PABA is needed in enzymatic reactions that produce folic acid which acts as a coenzyme in the synthesis of purine, pyrimidine and other amino acids.
The term "sulfanilamides" is also used to describe a family of molecules containing these functional groups. Examples include:
- FurosemideFurosemideFurosemide or frusemide is a loop diuretic used in the treatment of congestive heart failure and edema. It is most commonly marketed by Sanofi-Aventis under the brand name Lasix...
, a loop diureticLoop diureticLoop diuretics are diuretics that act on the ascending loop of Henle in the kidney. They are primarily used in medicine to treat hypertension and edema often due to congestive heart failure or renal insufficiency... - SulfadiazineSulfadiazineSulfadiazine is a sulfonamide antibiotic.-Uses:It eliminates bacteria that cause infections by stopping the production of folic acid inside the bacterial cell, and is commonly used to treat urinary tract infections ....
, an antibioticAntibioticAn antibacterial is a compound or substance that kills or slows down the growth of bacteria.The term is often used synonymously with the term antibiotic; today, however, with increased knowledge of the causative agents of various infectious diseases, antibiotic has come to denote a broader range of... - SulfamethoxazoleSulfamethoxazoleSulfamethoxazole is a sulfonamide bacteriostatic antibiotic.It is most often used as part of a synergistic combination with trimethoprim in a 5:1 ratio in co-trimoxazole , also known under trade names such as Bactrim, Septrin, or Septra; in Eastern Europe it is marketed as Biseptol...
, an antibioticAntibioticAn antibacterial is a compound or substance that kills or slows down the growth of bacteria.The term is often used synonymously with the term antibiotic; today, however, with increased knowledge of the causative agents of various infectious diseases, antibiotic has come to denote a broader range of...
Gerhard Domagk
Gerhard Domagk
Gerhard Johannes Paul Domagk was a German pathologist and bacteriologist credited with the discovery of Sulfonamidochrysoidine – the first commercially available antibiotic – for which he received the 1939 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.Domagk was born in Lagow, Brandenburg, the...
, who directed the testing of the prodrug
Prodrug
A prodrug is a pharmacological substance administered in an inactive form. Once administered, the prodrug is metabolised in vivo into an active metabolite, a process termed bioactivation. The rationale behind the use of a prodrug is generally for absorption, distribution, metabolism, and...
Prontosil
Prontosil
Prontosil, the first commercially available antibacterial antibiotic , was developed by a research team at the Bayer Laboratories of the IG Farben conglomerate in Germany...
in 1935, and Jacques and Thérèse Tréfouël, who along with Federico Nitti and Daniel Bovet
Daniel Bovet
Daniel Bovet was a Swiss-born Italian pharmacologist who won the 1957 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for his discovery of drugs that block the actions of specific neurotransmitters. He is best known for his discovery in 1937 of antihistamines, which block the neurotransmitter histamine and...
in the laboratory of Ernest Fourneau
Ernest Fourneau
Ernest Fourneau was a French medicinal chemist, who played a major role in the discovery of synthetic local anesthetics, as well as in the synthesis of suramin...
at the Pasteur Institute
Pasteur Institute
The Pasteur Institute is a French non-profit private foundation dedicated to the study of biology, micro-organisms, diseases, and vaccines. It is named after Louis Pasteur, who made some of the greatest breakthroughs in modern medicine at the time, including pasteurization and vaccines for anthrax...
, discovered the active component, 4-aminobenzenesulfonamide, are generally credited with the discovery of sulfanilamide as a chemotherapeutic agent. Domagk was awarded the Nobel Prize for his work.
See also
- Sulfonamide (medicine)Sulfonamide (medicine)Sulfonamide or sulphonamide is the basis of several groups of drugs. The original antibacterial sulfonamides are synthetic antimicrobial agents that contain the sulfonamide group. Some sulfonamides are also devoid of antibacterial activity, e.g., the anticonvulsant sultiame...
- Nazi human experimentation -- Sulfonamide experiments
- Elixir sulfanilamide

