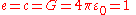Stoney scale units
Encyclopedia
In physics
the Stoney units form a system of units named after the Irish physicist George Johnstone Stoney
, who first proposed them in 1881. They are the first historical example of natural units
, i.e. units of measurement designed so that certain fundamental physical constant
s serve as base unit
s. The set of constants that Stoney used as base units is the following
This means the numerical values, in terms of Stoney units, of all these constants equal one:
Stoney's set of base units is similar to the one used in Planck units
, proposed independently by Planck thirty years later, but Planck replaced the elementary charge with the Planck constant
.
In Stoney units, the numerical value of Planck's constant is not 1, but is
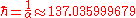
where α is the fine-structure constant
. Planck units are more commonly used than Stoney units in modern physics, especially quantum gravity
(including string theory
). Rarely, Planck units are referred to as Planck-Stoney units.
was one of the first scientists to understand that electric charge was quantized; from this quantization he deduced the units that are now named after him.
James G. O’Hara
pointed out in 1974 that Stoney’s derived estimate of the unit of charge, 10−20 ampere-second, was of the modern value of the charge of the electron. The reason is that Stoney used the approximated value of 1018 for the number of molecules presented in one cubic millimetre of gas at standard temperature and pressure
. Using the modern values for Avogadro’s number and for the volume of a gram-molecule
(at s.t.p.
) of , the modern value is , instead of Stoney's 1018.
are the length and energy scales at which quantum processes and gravity occur together. At these scales, a unified theory of physics is thus required. The only notable attempt to construct such a theory from the Stoney scale was that of H. Weyl, who associated a gravitational unit of charge with the Stoney length
and who appears to have inspired Dirac’s fascination with the large number hypothesis
.
Since then, the Stoney scale has been largely neglected in the development of modern physics, although it is occasionally discussed to this day.
The Planck scale is valid for all known interactions, and does not give prominence to the electromagnetic interaction, as the Stoney scale does.
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
the Stoney units form a system of units named after the Irish physicist George Johnstone Stoney
George Johnstone Stoney
George Johnstone Stoney was an Irish physicist most famous for introducing the term electron as the "fundamental unit quantity of electricity"....
, who first proposed them in 1881. They are the first historical example of natural units
Natural units
In physics, natural units are physical units of measurement based only on universal physical constants. For example the elementary charge e is a natural unit of electric charge, or the speed of light c is a natural unit of speed...
, i.e. units of measurement designed so that certain fundamental physical constant
Physical constant
A physical constant is a physical quantity that is generally believed to be both universal in nature and constant in time. It can be contrasted with a mathematical constant, which is a fixed numerical value but does not directly involve any physical measurement.There are many physical constants in...
s serve as base unit
Base unit
Base unit may refer to:* Fundamental unit, in physics, used to form other compound units for other quantities* Computer case, the main body of a computer* An administrative unit of the United States Army Air Forces ms:Unit asas...
s. The set of constants that Stoney used as base units is the following
- Elementary chargeElementary chargeThe elementary charge, usually denoted as e, is the electric charge carried by a single proton, or equivalently, the absolute value of the electric charge carried by a single electron. This elementary charge is a fundamental physical constant. To avoid confusion over its sign, e is sometimes called...
, e; - Speed of lightSpeed of lightThe speed of light in vacuum, usually denoted by c, is a physical constant important in many areas of physics. Its value is 299,792,458 metres per second, a figure that is exact since the length of the metre is defined from this constant and the international standard for time...
in a vacuum, c; - Gravitational constantGravitational constantThe gravitational constant, denoted G, is an empirical physical constant involved in the calculation of the gravitational attraction between objects with mass. It appears in Newton's law of universal gravitation and in Einstein's theory of general relativity. It is also known as the universal...
, G; - Coulomb constant, 1/(4πε0).
This means the numerical values, in terms of Stoney units, of all these constants equal one:
Stoney's set of base units is similar to the one used in Planck units
Planck units
In physics, Planck units are physical units of measurement defined exclusively in terms of five universal physical constants listed below, in such a manner that these five physical constants take on the numerical value of 1 when expressed in terms of these units. Planck units elegantly simplify...
, proposed independently by Planck thirty years later, but Planck replaced the elementary charge with the Planck constant
Planck constant
The Planck constant , also called Planck's constant, is a physical constant reflecting the sizes of energy quanta in quantum mechanics. It is named after Max Planck, one of the founders of quantum theory, who discovered it in 1899...
.
In Stoney units, the numerical value of Planck's constant is not 1, but is
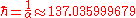
where α is the fine-structure constant
Fine-structure constant
In physics, the fine-structure constant is a fundamental physical constant, namely the coupling constant characterizing the strength of the electromagnetic interaction. Being a dimensionless quantity, it has constant numerical value in all systems of units...
. Planck units are more commonly used than Stoney units in modern physics, especially quantum gravity
Quantum gravity
Quantum gravity is the field of theoretical physics which attempts to develop scientific models that unify quantum mechanics with general relativity...
(including string theory
String theory
String theory is an active research framework in particle physics that attempts to reconcile quantum mechanics and general relativity. It is a contender for a theory of everything , a manner of describing the known fundamental forces and matter in a mathematically complete system...
). Rarely, Planck units are referred to as Planck-Stoney units.
History
George StoneyGeorge Johnstone Stoney
George Johnstone Stoney was an Irish physicist most famous for introducing the term electron as the "fundamental unit quantity of electricity"....
was one of the first scientists to understand that electric charge was quantized; from this quantization he deduced the units that are now named after him.
James G. O’Hara
pointed out in 1974 that Stoney’s derived estimate of the unit of charge, 10−20 ampere-second, was of the modern value of the charge of the electron. The reason is that Stoney used the approximated value of 1018 for the number of molecules presented in one cubic millimetre of gas at standard temperature and pressure
Standard conditions for temperature and pressure
Standard condition for temperature and pressure are standard sets of conditions for experimental measurements established to allow comparisons to be made between different sets of data...
. Using the modern values for Avogadro’s number and for the volume of a gram-molecule
Mole (unit)
The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value...
(at s.t.p.
Standard conditions for temperature and pressure
Standard condition for temperature and pressure are standard sets of conditions for experimental measurements established to allow comparisons to be made between different sets of data...
) of , the modern value is , instead of Stoney's 1018.
Stoney units and Planck units
The Stoney length and the Stoney energy, collectively called the Stoney scale, are not far from the Planck length and the Planck energy, the Planck scale. The Stoney scale and the Planck scalePlanck scale
In particle physics and physical cosmology, the Planck scale is an energy scale around 1.22 × 1019 GeV at which quantum effects of gravity become strong...
are the length and energy scales at which quantum processes and gravity occur together. At these scales, a unified theory of physics is thus required. The only notable attempt to construct such a theory from the Stoney scale was that of H. Weyl, who associated a gravitational unit of charge with the Stoney length
and who appears to have inspired Dirac’s fascination with the large number hypothesis
Dirac large numbers hypothesis
The Dirac large numbers hypothesis is an observation made by Paul Dirac in 1937 relating ratios of size scales in the Universe to that of force scales. The ratios constitute very large, dimensionless numbers: some 40 orders of magnitude in the present cosmological epoch...
.
Since then, the Stoney scale has been largely neglected in the development of modern physics, although it is occasionally discussed to this day.
The Planck scale is valid for all known interactions, and does not give prominence to the electromagnetic interaction, as the Stoney scale does.
See also
- Dimensional analysisDimensional analysisIn physics and all science, dimensional analysis is a tool to find or check relations among physical quantities by using their dimensions. The dimension of a physical quantity is the combination of the basic physical dimensions which describe it; for example, speed has the dimension length per...
- Natural unitsNatural unitsIn physics, natural units are physical units of measurement based only on universal physical constants. For example the elementary charge e is a natural unit of electric charge, or the speed of light c is a natural unit of speed...
- Physical constantPhysical constantA physical constant is a physical quantity that is generally believed to be both universal in nature and constant in time. It can be contrasted with a mathematical constant, which is a fixed numerical value but does not directly involve any physical measurement.There are many physical constants in...
s - Planck scalePlanck scaleIn particle physics and physical cosmology, the Planck scale is an energy scale around 1.22 × 1019 GeV at which quantum effects of gravity become strong...