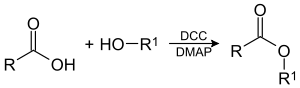
Steglich esterification
Encyclopedia
The Steglich esterification is a variation of an esterfication with dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
as a coupling reagent and 4-dimethylaminopyridine
as a catalyst. The reaction was first described by Wolfgang Steglich
in 1978. It is an adaptation of an older method for the formation of amide
s by means of DCC (dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
) and 1-hydroxybenzotriazole (HOBT).
This reaction generally takes place at room temperature
. A suitable solvent
is dichloromethane
. Because the reaction is mild, esters can be obtained that are inaccessible through other methods for instance esters of the sensitive 1,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid. A characteristic is the formal uptake of water generated in the reaction by DCC, forming the urea
compound dicyclohexylurea
(DCU).
is described as follows:
With amine
s, the reaction proceeds without problems to the corresponding amide
s because amines are more nucleophilic. If the esterification is slow, a side-reaction occurs, diminishing the final yield or complicating purification of the product. This side-reaction is a 1,3-rearrangement of the O-acyl intermediate to a N-acyl urea which is unable to further react with the alcohol
To suppress this reaction, DMAP is added, acting as an acyl transfer-reagent in the following manner:
Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide is an organic compound with chemical formula C13H22N2 whose primary use is to couple amino acids during artificial peptide synthesis. Under standard conditions, it exists in the form of white crystals with a heavy, sweet odor. The low melting point of this material...
as a coupling reagent and 4-dimethylaminopyridine
4-Dimethylaminopyridine
4-Dimethylaminopyridine is a derivative of pyridine with the chemical formula 2NC5H4N. This colourless solid is a useful nucleophilic catalyst for a variety of reactions such as esterifications with anhydrides, the Baylis-Hillman reaction, hydrosilylations, tritylation, the Steglich...
as a catalyst. The reaction was first described by Wolfgang Steglich
Wolfgang Steglich
-Life:Wolfgang Steglich was born in Kamenz and studied chemistry at the Technical University of Berlin and later at the Technical University of Munich where he received his PhD in 1959 for work with Friedrich Weygand...
in 1978. It is an adaptation of an older method for the formation of amide
Amide
In chemistry, an amide is an organic compound that contains the functional group consisting of a carbonyl group linked to a nitrogen atom . The term refers both to a class of compounds and a functional group within those compounds. The term amide also refers to deprotonated form of ammonia or an...
s by means of DCC (dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide is an organic compound with chemical formula C13H22N2 whose primary use is to couple amino acids during artificial peptide synthesis. Under standard conditions, it exists in the form of white crystals with a heavy, sweet odor. The low melting point of this material...
) and 1-hydroxybenzotriazole (HOBT).
This reaction generally takes place at room temperature
Room temperature
-Comfort levels:The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers has listings for suggested temperatures and air flow rates in different types of buildings and different environmental circumstances. For example, a single office in a building has an occupancy ratio per...
. A suitable solvent
Solvent
A solvent is a liquid, solid, or gas that dissolves another solid, liquid, or gaseous solute, resulting in a solution that is soluble in a certain volume of solvent at a specified temperature...
is dichloromethane
Dichloromethane
Dichloromethane is an organic compound with the formula CH2Cl2. This colorless, volatile liquid with a moderately sweet aroma is widely used as a solvent. Although it is not miscible with water, it is miscible with many organic solvents...
. Because the reaction is mild, esters can be obtained that are inaccessible through other methods for instance esters of the sensitive 1,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid. A characteristic is the formal uptake of water generated in the reaction by DCC, forming the urea
Urea
Urea or carbamide is an organic compound with the chemical formula CO2. The molecule has two —NH2 groups joined by a carbonyl functional group....
compound dicyclohexylurea
Dicyclohexylurea
Dicyclohexylurea is an organic compound, specifically, a urea. It is the byproduct of the reaction of dicyclohexylcarbodiimide with amines or alcohols. It may be prepared by the reaction of cyclohexylamine and S,S-dimethyl dithiocarbonate....
(DCU).
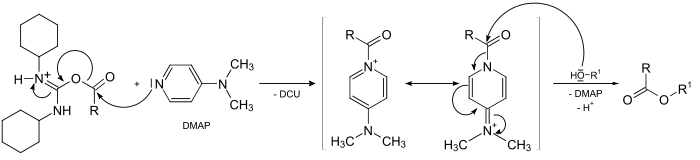
Reaction mechanism
The reaction mechanismReaction mechanism
In chemistry, a reaction mechanism is the step by step sequence of elementary reactions by which overall chemical change occurs.Although only the net chemical change is directly observable for most chemical reactions, experiments can often be designed that suggest the possible sequence of steps in...
is described as follows:
- The carboxylic acidCarboxylic acidCarboxylic acids are organic acids characterized by the presence of at least one carboxyl group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is R-COOH, where R is some monovalent functional group...
reacts with DCC to a O-acylAcylAn acyl group is a functional group derived by the removal of one or more hydroxyl groups from an oxoacid, including inorganic acids.In organic chemistry, the acyl group is usually derived from a carboxylic acid . Therefore, it has the formula RCO-, where R represents an alkyl group that is...
isourea, which is more reactive than the free acid
- The alcoholAlcoholIn chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
attacks this intermediate, forming DCU and the corresponding ester
With amine
Amine
Amines are organic compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines,...
s, the reaction proceeds without problems to the corresponding amide
Amide
In chemistry, an amide is an organic compound that contains the functional group consisting of a carbonyl group linked to a nitrogen atom . The term refers both to a class of compounds and a functional group within those compounds. The term amide also refers to deprotonated form of ammonia or an...
s because amines are more nucleophilic. If the esterification is slow, a side-reaction occurs, diminishing the final yield or complicating purification of the product. This side-reaction is a 1,3-rearrangement of the O-acyl intermediate to a N-acyl urea which is unable to further react with the alcohol
To suppress this reaction, DMAP is added, acting as an acyl transfer-reagent in the following manner:

Further reading
- J. Otera: Esterification. 1. Auflage, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2003, ISBN 3-527-30490-8